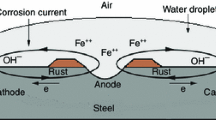
Abstract
In principle, bare particles used in magnetorheological suspensions exhibit apparent corrosion instability. To suppress substantially this adverse phenomenon, the carbonyl iron particles modified with cholesteryl group (CI-chol) were suspended in silicone oil. There was found a deterioration of magnetorheological efficiency in comparison when only bare carbonyl iron (CI) particles are used; nevertheless, from the viewpoint of applicability, this change is fully acceptable. However, an anti-corrosion stability was significantly improved. Furthermore, dynamic oscillatory measurements and other characterizations were carried out and analyzed when both CI and CI-chol particles are applied.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bombard AJF, Knobel M, Alcantara MR (2007) Phosphate coating on the surface of carbonyl iron powder and its effect in magnetorheological suspensions. Int J Mod Phys B 21:4858–4867
Bossis G, Lacis S, Meunier A, Volkova O (2002) Magnetorheological fluids. J Magn Magn Mater 252:224–228
Klingenberg DJ, Ulicny JC, Golden MA (2007) Mason numbers for magnetorheology. J Rheol 51:883–893
Park BJ, Fang FF, Choi HJ (2010) Magnetorheology: materials and application. Soft Matter 6:5246–5253
Fang FF, Choi HJ (2010) Fabrication of multiwalled carbon nanotube-wrapped magnetic carbonyl iron microspheres and their magnetorheology. Colloid Polym Sci 288:79–84
Fang FF, Choi HJ, Choi WS (2010) Two-layer coating with polymer and carbon nanotube on magnetic carbonyl iron particle and its magnetorheology. Colloid Polym Sci 288:359–363
Kim IG, Song KH, Park BO, Choi BI, Choi HJ (2011) Nano-sized Fe soft-magnetic particle and its magnetorheology. Colloid Polym Sci 289:79–83
Mrlik M, Sedlacik M, Pavlinek V, Bazant P, Saha P, Peer P, Filip P (2013) Synthesis and magnetorheological characteristics of ribbon-like, polypyrrole-coated carbonyl iron suspensions under oscillatory shear. J Appl Polym Sci 128:2977–2982
Sedlacik M, Moucka R, Kozakova Z, Kazantseva NE, Pavlinek V, Kuritka I, Kaman O, Peer P (2013) Correlation of structural and magnetic properties of Fe3O4 nanoparticles with their calorimetric and magnetorheological performance. J Magn Magn Mater 326:7–13
Sedlacik M, Pavlinek V, Saha P, Svrcinova P, Filip P (2012) The role of particles annealing temperature on magnetorheological effect. Mod Phys Lett B 26:1150013
Fang FF, Kim JH, Choi HJ (2009) Synthesis of core-shell structured PS/Fe3O4 microbeads and their magnetorheology. Polymer 50:2290–2293
Fang FF, Liu YD, Choi HJ (2013) Electrorheological and magnetorheological response of polypyrrole/magnetite nanocomposite particles. Colloid Polym Sci 291:1781–1786
Kuzhir P, Gomez-Ramirez A, Lopez-Lopez MT, Bossis G, Zubarev AY (2011) Non-linear viscoelastic response of magnetic fiber suspensions in oscillatory shear. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 166:373–385
Bombard AJF, Alcantara MR, Knobel M, Volpe PLO (2005) Experimental study of MR suspensions of carbonyl iron powders with different particle sizes. Int J Mod Phys B 19:1332–1338
Bombard AJF, Teodoro JVR (2011) Magnetorheological fluids with carbonyl and water atomized iron powders. Int J Mod Phys B 25:943–946
Liu YD, Lee J, Choi SB, Choi HJ (2013) Silica-coated carbonyl iron microsphere based magnetorheological fluid and its damping force characteristics. Smart Mater Struct 22:065022
Sim HH, Kwon SH, Choi HJ (2013) Xanthan gum-coated soft magnetic carbonyl iron composite particles and their magnetorheology. Colloid Polym Sci 291:963–969
Iglesias GR, Lopez-Lopez MT, Duran JDG, Gonzalez-Caballero F, Delgado AV (2012) Dynamic characterization of extremely bidisperse magnetorheological fluids. J Colloid Interface Sci 377:153–159
Jiang WQ, Zhang YL, Xuan SH, Guo CY, Gong XL (2011) Dimorphic magnetorheological fluid with improved rheological properties. J Magn Magn Mater 323:3246–3250
Ngatu GT, Wereley NM, Karli JO, Bell RC (2008) Dimorphic magnetorheological fluids: exploiting partial substitution of microspheres by nanowires. Smart Mater Struct 17:045022
Sedlacik M, Pavlinek V, Vyroubal R, Peer P, Filip P (2013) A dimorphic magnetorheological fluid with improved oxidation and chemical stability under oscillatory shear. Smart Mater Struct 22:035011
Hu B, Fuchs A, Huseyin S, Gordaninejad F, Evrensel C (2006) Atom transfer radical polymerized MR fluids. Polymer 47:7653–7663
Kim YH, Lee JE, Cho SK, Park SY, Jeong IB, Jeong MG, Kim YD, Choi HJ, Cho SM (2012) Ultrathin polydimethylsiloxane-coated carbonyl iron particles and their magnetorheological characteristics. Colloid Polym Sci 290:1093–1098
Liu YD, Fang FF, Choi HJ (2011) Core–shell-structured silica-coated magnetic carbonyl iron microbead and its magnetorheology with anti-acidic characteristics. Colloid Polym Sci 289:1295–1298
Sedlacik M, Pavlinek V, Lehocky M, Mracek A, Grulich O, Svrcinova P, Filip P, Vesel A (2011) Plasma-treated carbonyl iron particles as a dispersed phase in magnetorheological fluids. Colloid Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 387:99–103
Sedlacik M, Pavlinek V, Saha P, Svrcinova P, Filip P, Stejskal J (2010) Rheological properties of magnetorheological suspensions based on core–shell structured polyaniline-coated carbonyl iron particles. Smart Mater Struct 19:115008
Machovsky M, Mrlik M, Kuritka I, Pavlinek V, Babayan V (2014) Novel synthesis of core-shell urchin-like ZnO coated carbonyl iron microparticles with enhanced magnetorheological activity. RSC Adv 4:996–1003
Mrlik M, Ilcikova M, Pavlinek V, Mosnacek J, Peer P, Filip P (2013) Improved thermooxidation and sedimentation stability of covalently-coated carbonyl iron particles with cholesteryl groups and their influence on magnetorheology. J Colloid Interface Sci 396:146–151
Langevin P (1905) Magnetism and theory of electrons. Ann Chim Phys 5:70–127
Shliomis MI (1974) Magnetic fluids. Phys Usp 17:153–167
Laun HM, Schmidt G, Gabriel C, Kieburg C (2008) Reliable plate-plate MRF magnetorheometry based on validated radial magnetic flux density profile simulations. Rheol Acta 47:1049–1059
Acknowledgments
Author M.S. wish to thank the Grant Agency of the Czech Republic (14-32114P) for financial support. This article was written with support of the Operational Program Research and Development for Innovations co-funded by the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) and the National Budget of Czech Republic, within the framework of the project Centre of Polymer Systems (CZ.1.05/2.1.00/03.0111). M. I. and J. M. thank the Centre of Excellence SAS for Functionalized Multiphase Materials (FUN-MAT).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mrlik, M., Ilcikova, M., Sedlacik, M. et al. Cholesteryl-coated carbonyl iron particles with improved anti-corrosion stability and their viscoelastic behaviour under magnetic field. Colloid Polym Sci 292, 2137–2143 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-014-3245-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-014-3245-5