Abstract
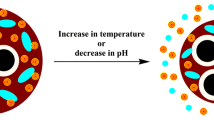
Nanostructures are gaining interest in drug release applications. Amphiphilic molecules can give, in water solution, a variety of nanostructures as well as thermodynamically stable mesophases three-dimensional inverse cubic structures. These mesophases are attractive candidates for biomedical applications containing extensive water channel networks and could act as very efficient delivery systems of drugs or contrast agents. In order to discover, optimize, and develop these systems, we have performed a deep physicochemical characterization by dynamic light scattering and small-angle neutron scattering of nanoparticles of monoolein (MO) and Pluronic PF127, containing different amounts (1, 5, 10, and 20 %) of the synthetic amphiphilic gadolinium complex (C18)2DTPA(Gd). Nanoparticle size is found in the 70–400 nm range for all investigated systems; the morphology of the aggregates is driven by the main constituents MO/PF127 and is a mixture of multilayer vesicles and bicontinuous aggregates. Nanostructures are also able to encapsulate doxorubicin (drug-loading content between 70 and 90 % for the different systems) acting as a potential theranostic for simultaneous cancer therapy and MRI visualization.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Accardo A, Tesauro D, Morelli G (2013) Peptide-based targeting strategies for simultaneous imaging and therapy with nanovectors. Polym J 45:481–494
Park K, Lee S, Kang E, Kim K, Choi K, Kwon IC (2009) New generation of multifunctional nanoparticles for cancer imaging and therapy. Adv Funct Mater 19:1553–1566
Simeone L, Mangiapia G, Vitiello G, Irace C, Colonna A, Ortona O, Montesarchio D, Paduano L (2012) Cholesterol-based nucleolipid-ruthenium complex stabilized by lipid aggregates for antineoplastic therapy. Bioconjugate Chem 23:758–770
Mangiapia G, D’Errico G, Simeone L, Irace C, Radulescu A, Di Pascale A, Colonna A, Montesarchio D, Paduano L (2012) Ruthenium-based complex nanocarriers for cancer therapy. Biomaterials 33:3770–3782
Thakare VS, Das M, Jain AK, Patil S, Jain S (2010) Carbon nanotubes in cancer theragnosis. Nanomedicine 5:1277–1301
Delli Castelli D, Gianolio E, Geninatti Crich S, Terreno E, Aime S (2008) Metal containing nanosized systems for MR-molecular imaging applications. Coord Chem Rev 252:2424–2443
Mulder WJM, Strijkers GJ, Van Tilborg GAF, Cormode DP, Fayad ZA, Nicolay K (2009) Nanoparticulate assemblies of amphiphiles and diagnostically active materials for multimodality imaging. Acc Chem Res 42:904–914
Accardo A, Tesauro D, Aloj L, Pedone C, Morelli G (2009) Supramolecular aggregates containing lipophilic Gd(III) complexes as contrast agents in MRI. Coord Chem Rev 253(17–18):2193–2213
Mulder WJM, Strijkers GJ, van Tilborg GAF, Griffioen AW, Nicolay K (2006) Lipid-based nanoparticles for contrast-enhanced MRI and molecular imaging. NMR Biomed 19(1):142–164
Tesauro D, Accardo A, Gianolio E, Paduano L, Texeira J, Schillen K, Aime S, Morelli G (2007) Peptide derivatized lamellar aggregates as target specific MRI contrast agents. ChemBioChem 8:950–955
van Tilborg GAF, Mulder WJM, Deckers N, Storm G, Reutelingsperger CPM, Strijkers GJ, Nicolay K (2006) Annexin A5-functionalized bimodal lipid-based contrast agents for the detection of apoptosis. Bioconjugate Chem 17:741–749
Mulder WJM, van der Schaft DWJ, Hautvast PAI, Strijkers GJ, Koning GA, Storm G, Mayo KH, Griffioen AW, Nicolay K (2007) Early in vivo assessment of angiostatic therapy efficacy by molecular MRI. FASEB J 21(2):378–383
Brandwijk RJMGE, Mulder WJM, Nicolay K, Mayo KH, Thijssen VLJL, Griffioen AW (2007) Anginex-conjugated liposomes for targeting of angiogenic endothelial cells. Bioconjugate Chem 18:785–790
Vaccaro M, Mangiapia G, Paduano L, Gianolio E, Accardo A, Tesauro D, Morelli G (2007) Structural and relaxometric characterization of peptide aggregates containing gadolinium complexes as potential selective contrast agents in MRI. ChemPhysChem 8:2526–2538
Morisco A, Accardo A, Gianolio E, Tesauro D, Benedetti E, Morelli G (2009) Micelles derivatized with octreotide as potential target-selective contrast agents in MRI. J Pept Sci 15:242–250
Mulder WJM, Strijkers GJ, Griffioen AW, van Bloois L, Molema G, Storm G, Koning G, Nicolay K (2004) A liposomal system for contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of molecular targets. Bioconjugate Chem 15:799–806
Mulder WJM, Strijkers GJ, Briley-Saebo KC, Frias JC, Aguinado JGS, Vudic E, Amirbekian V, Tang C, Chin PTK, Nicolay K, Fayad ZA (2007) Molecular imaging of macrophages in atherosclerotic plaques using bimodal PEG-micelles. Magn Reson Med 58(6):1164–1170
Lipinski MJ, Amirbekian V, Frias JC, Aguinado JGS, Mani V, Briley-Saebo KC, Fuster V, Fallon JT, Fisher EA, Fayad ZA (2006) MRI to detect atherosclerosis with gadolinium-containing immunomicelles targeting the macrophage scavenger receptor. Magn Reson Med 56(3):601–610
Amirbekian V, Lipinski MJ, Briley-Saebo KC, Amirbekian S, Aguinado JGS, Weinreb DB, Vucic E, Frias JC, Hyafil F, Mani V, Fisher EA, Fayad ZA (2007) Detecting and assessing macrophages in vivo to evalute atherosclerosis noninvasively using molecular MRI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104(3):961–966
Yaghmur A, Glatter O (2009) Characterization and potential applications of nanostructured aqueous dispersions. Adv in Colloid Interface Sci 147–148:333–342
Liu G, Conn CE, Waddington LJ, Mudie ST, Drummond CJ (2010) Colloidal amphiphile self-assembly particles composed of gadolinium oleate and myverol: evaluation as contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging. Langmuir 26(4):2383–2391
Liu G, Conn CE, Drummond CJ (2009) Lanthanide oleates: chelation, self-assembly, and exemplification of ordered nanostructured colloidal contrast agents for medical imaging. J Phys Chem B 113:15949–15959
Conn CE, Panchagnula V, Weerawardena A, Waddington LJ, Kennedy DF, Drummond CJ (2010) Lanthanide phytanates. Liquid-crystalline phase behavior, colloidal particle dispersions, and potential as medical imaging agents. Langmuir 26(9):6240–6249
Moghaddam MJ, de Campo L, Waddington LJ, Weerawardena A, Kirby N, Drummond CJ (2011) Chelating oleyl-EDTA amphiphiles: self-assembly, colloidal particles, complexation with paramagnetic metal ions and promise as magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. Soft Matter 7:10994–11005
Moghaddam MJ, de Campo L, Waddington LJ, Drummond CJ (2010) Chelating phytanyl-EDTA amphiphiles. Self-assembly and promise as contrast agents for medical imaging. Soft Matter 6:5915–5929
Accardo A, Gianolio E, Arena F, Barnert S, Schubert R, Tesauro D, Morelli G (2013) Nanostructures based on monoolein or diolein and amphiphilic gadolinium complexes as MRI contrast agents. J Mater Chem B 1:617–628
Shah JC, Sadhale Y, Chilukuri DM (2001) Cubic phase gels as drug delivery systems. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 25:229–250
Anderson DM, Wennerström H (1990) Self-diffusion in bicontinuous cubic phases, L3 phases, and microemulsions. J Phys Chem 94:8683–8694
Kogan A, Garti N (2006) Microemulsions as transdermal drug delivery vehicles. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 123–126:369–385
Accardo A, Morisco A, Gianolio E, Tesauro D, Mangiapia G, Radulescu A, Brandt S, Morelli G (2011) Nanoparticles containing octreotide peptides and gadolinium complexes for MRI applications. J Pept Sci 17:154–162
Fritze A, Hens F, Kimpfler A, Schubert R, Peschka-Süss R (2006) Remote loading of doxorubicin into liposomes driven by a transmembrane phosphate gradient. BBA Biomembranes 1758:1633–1640
Vergara A, Paduano L, Sartorio R (2001) Multicomponent diffusion in systems containing molecules of different size. 4. Mutual diffusion in the ternary system tetra(ethylene glycol)-di(ethylene glycol)-water. J Phys Chem B 105:328–334
Wignall GD, Bates FS (1987) Absolute calibration of small-angle neutron scattering data. J Appl Crystallogr 20:28–40
Russell TP, Lin JS, Spooner S, Wignall GD (1988) Inter- and absolute calibration of SAXS and SANS data. J Appl Crystallogr 21:629–638
Vaccaro M, Mangiapia G, Radulescu A, Schillén K, D’Errico G, Morelli G, Paduano L (2009) Colloidal particles composed of amphiphilic molecules binding gadolinium complexes and peptides as tumor-specific contrast agents in MRI: physico-chemical characterization. Soft Matter 5:2504–2512
Gustafsson J, Ljusberg-Wahren H, Almgren M, Larsson K (1997) Submicron particles of reversed lipid phases in water stabilized by anonionic amphiphilic polymer. Langmuir 13:6964–6971
Vaccaro M, Del Litto R, Mangiapia G, Carnerup AM, D’Errico G, Ruffo F, Paduano L (2009) Lipid based nanovectors containing ruthenium complexes: a potential route in cancer therapy. Chem Commun 1404–1406
Frielinghaus H (2007) Physical review E. Stat Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys 76:051603/051601–051603/051608
Mangiapia G, Vaccaro M, D’Errico G, Frielinghaus H, Radulescu A, Pipich V, Carnerup AM, Paduano L (2011) Cubosomes for ruthenium complex delivery: formulation and characterization. Soft Matter 7:10577–10580
Morisco A, Accardo A, Tesauro D, Palumbo R, Benedetti E, Morelli G (2011) Peptide labeled supramolecular aggregates as selective doxorubicin carriers for delivery to tumor cells. Biopolymers Pept Sci 86:88–96
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Italian Minister of Research (MIUR): grant FIRB RBRN07BMCT, grant PRIN E61J11000300001, and grant PRIN 2009235JB7. The Italian Consortium CIRCMSB is also gratefully acknowledged. Some of the authors (N.S.,V.P., A.L., and L.P.) thank the Julich Centre for Neutron Science for provision of beam time. SANS experiments were supported by the European Commission, NMI3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Accardo, A., Ringhieri, P., Szekely, N. et al. Structural insights on nanoparticles containing gadolinium complexes as potential theranostic. Colloid Polym Sci 292, 1121–1127 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-013-3159-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-013-3159-7