Abstract
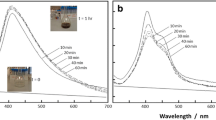
By a simple method, large compound vesicles (LCVs) and LCVs with silver nanoparticles (Ag@LCVs) are created from asymmetric polystyrene-block-polyacrylonitrile (PS-b-PAN) and silver precursor. The asymmetric PS-b-PAN is polymerized by sequential reverse atom transfer radical polymerization and atom transfer radical polymerization. Afterwards, by using N,N′-dimethylformamide as solvent and reductant for the silver precursor, LCVs and Ag@LCVs are produced through simple drop casting and evaporation of solution on the substrate. Transmission electron microscope images together with scanning electron microscopy images show that both LCVs and Ag@LCVs are flowerlike and of rough surfaces. Ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometer confirms the formation of Ag nanoparticles (Ag NPs). Specifically, the distribution of Ag NPs in Ag@LCVs is not uniform and they are principally in the center. Otherwise, adherence of simple vesicles and small hybrid nanoparticles of Ag NPs encapsulated within PS-b-PAN are observed. Finally, formation mechanisms for LCVs and Ag@LCVs are discussed.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choucair A, Eisenberg A (2003) Control of amphiphilic block copolymer morphologies using solution conditions. Eur Phys J E 10:37–44
He F, Gadt T, Jones M, Scholes GD, Manners I, Winnik MA (2009) Synthesis and self-assembly of fluorescent micelles from poly(ferrocenyldimethylsilane-b-2-vinylpyridine-b-2,5-di(2′-ethylhexyloxy)-1,4-phenylvinylene) triblock copolymer. Macromolecules 42:7953–7960
Smith AE, Xu XW, Kirkland-York SE, Savin DA, McCormick CL (2010) “Schizophrenic” self-assembly of block copolymers synthesized via aqueous raft polymerization: from micelles to vesicles. Macromolecules 43:1210–1217
Yoshida E, Tanaka M, Takata T (2005) Self-assembly control of a pyridine-containing diblock copolymer by perfluorinated counter anions during salt-induced micellization. Colloid Polym Sci 283:1100–1107
Mai YY, Eisenberg A (2010) Controlled incorporation of particles into the central portion of vesicle walls. J Am Chem Soc 132:10078–10084
Mendoza C, Gindy N, Gutmann JS, Frömsdorf A, Förster S, Fahmi A (2009) In situ synthesis and alignment of au nanoparticles within hexagonally packed cylindrical domains of diblock copolymers in bulk. Langmuir 25:9571–9578
Gong J, Zu XH, Mu W, Deng YL (2012) In situ self-assembly synthesis of gold nanoparticle arrays on polystyrene microspheres and their surface plasmon resonance. Colloid Polym Sci. doi:10.1007/s00396-012-2601-6
Yu K, Zhang LF, Eisenberg A (1996) Novel morphologies of “crew-cut” aggregates of amphiphilic diblock copolymers in dilute solution. Langmuir 12:5980–5984
Zhang LF, Eisenberg A (1996) Morphogenic effect of added ions on crew-cut aggregates of polystyrene-b-poly(acrylic acid) block copolymers in solutions. Macromolecules 29:8805–8815
Yu K, Eisenberg A (1998) Bilayer morphologies of self-assembled crew-cut aggregates of amphiphilic PS-b-PEO diblock copolymers in solution. Macromolecules 31:3509–3518
Du JZ, Chen YM (2004) Organic-inorganic hybrid nanoparticles with a complex hollow structure. Angew Chem Int Ed 43:5084–5087
Yu HJ, Wang L, Chen T (2009) Novel organic/inorganic hybrid self-assembly aggregates of ferrocene-poly(styrene)-b-poly[3-(trimethyoxysilyl) propyl methacrylate]. Eur Polymer J 45:639–642
Zhang Y, Tan H, Li H, Liu YQ, Kartawidjaja FC, Yang ZC, Wang J (2011) Hybrid titania microspheres of novel superstructures templated by block copolymers. Chem Mater 23:2745–2752
Jang YH, Kochuveedu ST, Jang YJ, Shin HY, Yoon S, Steinhart M, Kim DH (2011) The fabrication of graphitic thin films with highly dispersed noble metal nanoparticles by direct carbonization of block copolymer inverse micelle templates. Carbon 49:2120–2126
Nisola GM, Park JS, Beltran AB, Chung WJ (2012) Silver nanoparticles in a polyether-block-polyamide copolymer towards antimicrobial and antifouling membranes. RSC Adv 2:2439–2448
Niskanen J, Shan J, Tenhu H, Jiang H, Kauppinen E, Barranco V, Picó F, Yliniemi K, Kontturi K (2010) Synthesis of copolymer-stabilized silver nanoparticles for coating materials. Colloid Polym Sci 288:543–553
Bryaskova R, Pencheva D, Kyulavska M, Bozukova D, Debuigne A, Detrembleur C (2010) Antibacterial activity of poly(vinyl alcohol)-b-poly(acrylonitrile) based micelles loaded with silver nanoparticles. J Colloid Interf Sci 344:424–428
Shmakov SN, Pinkhassik E (2010) Simultaneous templating of polymer nanocapsules and entrapped silver Nanoparticles. Chem Commun 46:7346–7348
Pastoriza-Santos I, Liz-Marzán LM (2000) Reduction of silver nanoparticles in DMF. Formation of monolayers and stable colloids. Pure Appl Chem 72:83–90
Pastoriza-Santos I, Serra-Rodriguez C, Liz-Marzan LM (2000) Self-assembly of silver particle monolayers on glass from Ag+ solutions in DMF. J Colloid Interf Sci 221:236–241
Matyjaszewski K, Xia JH (2001) Atom transfer radical polymerization. Chem Rev 101:2921–2990
Degirmenci M, Catalgil-Giz H, Yagci Y (2004) Synthesis of block copolymers by combined ultrasonic irradiation and reverse atom transfer radical polymerization processes. J Polymer Sci, Part A: Polymer Chem 42:534–540
Limer A, Haddleton DM (2006) Reverse atom transfer radical polymerisation (RATRP) of methacrylates using copper(I)/pyridinimine catalysts in conjunction with AIBN. Eur Polymer J 42:61–68
Wang JS, Matyjaszewski K (1995) “Living”/controlled radical polymerization transition-metal-catalyzed atom transfer radical polymerization in the presence of a conventional radical initiator. Macromolecules 28:7572–7573
Yi Z, Pan K, Jiang L, Zhang J, Dan Y (2007) Copper-based reverse ATRP process of styrene in mixed solvents. Eur Polymer J 43:2557–2563
Cheng ZP, Zhu XL, Zhou NC, Zhu J, Zhang ZB (2005) Atom transfer radical polymerization of styrene under pulsed microwave irradiation. Radiat Phys Chem 72:695–701
Aimi J, McCullough LA, Matyjaszewski K (2008) Synthesis of poly(vinylacetylene) block copolymers by atom transfer radical polymerization. Macromolecules 41:9522–9524
Lazzari M, Chiantore O, Mendichi R, López-Quintela MA (2005) Synthesis of polyacrylonitrile-block-polystyrene copolymers by atom transfer radical polymerization. Macromol Chem Phys 206:1382–1388
Zhang LF, Eisenberg A (1995) Multiple morphologies of “crew-cut” aggregates of polystyrene-b-poly (acrylic acid) block copolymers. Science 268:1728–1731
Mai YY, Eisenberg A (2011) Controlled incorporation of particles into the central portion of block copolymer rods and micelles. Macromolecules 44:3179–3183
Kang YJ, Taton TA (2005) Core/shell gold nanoparticles by self-assembly and crosslinking of micellar, block-copolymer shells. Angew Chem 117:413–416
He XH, Liang HJ, Huang L, Pan CY (2004) Complex microstructures of amphiphilic diblock copolymer in dilute solution. J Phys Chem B 108:1731–1735
Liz-Marzán LM (2006) Tailoring surface plasmons through the morphology and assembly of metal nanoparticles. Langmuir 22:32–41
Liu HR, Ge XW, Ni YH, Ye Q, Zhang ZC (2001) Synthesis and characterization of polyacrylonitrile–silver nanocomposites by< i> γ</i>-irradiation. Radiat Phys Chem 61:89–91
Acknowledgments
This work is financially supported by Key Program of Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province (2009JZ004), Basic Research Foundation of Northwestern Polytechnical University (JC201158) and Entrepreneurship Seed Fund of postgraduate in Northwester Polytechnical University (Z2012157).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, L., Ma, X., Song, Y. et al. A simple way of preparing large compound vesicles loaded with and without silver nanoparticles based on polystyrene-block-polyacrylonitrile. Colloid Polym Sci 291, 893–902 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-012-2806-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-012-2806-8