Abstract
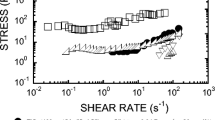
The linear viscoelastic properties of a suspension composed of titanium dioxide nanoparticles were measured under the direct current (dc) electric field with narrow gap distances between the electrodes. The yielding behavior under no external electric fields was also discussed. The wall slip at the interface between the parallel plates and the nano-suspension was briefly discussed. Under the dc electric field, a fine chain-like microstructure was optically found within a narrow gap of 50 μm between the electrodes in the quiescent state. The nano-suspension confined to a narrow gap of 65 μm between the parallel plates was rather viscoelastic even at the highest strength of the electric field of 16 kV·mm−1. Furthermore, fast and slow relaxations of the dynamic moduli were found after removal of the electric field. It was pointed out that the linear viscoelasticity was an appropriate measure of the microstructure before yielding.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Winslow WM (1949) J Appl Phys 20:1137
Block H, Kelly JP, Qin A, Watson T (1990) Langmuir 6:6
Filisko FE, Radzilowski LH (1990) J Rheol 34:539
Conrad H, Sprecher AF, Choi Y, Chen Y (1991) J Rheol 35:1393
Otsubo Y, Edamura K (1995) J Colloid Interface Sci 172:530
Tanaka K, Wakayasu T, Kubono A, Akiyama R (2004) Sens Actuators A 112:376
Kraynic AM (1990) In: Carlson JD, Sprecher AF, Conrad H (eds) Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on ER Fluids. Technomic Publishing, Lancaster, pp. 445
Barnes HA, Walters K (1985) Rheol Acta 24:323
Hartnett JP, Hu RYZ (1989) J Rheol 33:671
Yoshimura A, Prud’homme RK (1987) J Rheol 31:699
Tanaka K, Ichizawa K, Akiyama R, Kubono A (2001) Nihon Reoroji Gakkaishi (J Soc Rheol, Jpn) 29:105
Onogi S, Masuda T, Matsumoto T (1970) Trans Soc Rheol 14:275
Tanaka K, Akiyama R, Takano M, Kutsumizu S, Yamaguchi T (2004) Trans Mater Res Soc Jpn 29:815
Tanaka K, Fujioka Y, Kubono A, Akiyama R (2006) Colloid Polym Sci 284:562
Parthasarathy M, Ahn KH, Belongia BM, Klingenberg DJ (1994) Int J Mod Phys B 8:2789
Otsubo Y, Sekine M, Katayama S (1992) J Rheol 36:479
Tao R, Sun JM (1991) Phys Rev Lett 67:398
Tao R, Xu X (2006) Energy Fuels 20:2046
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanaka, K., Nakahori, H., Katayama, K. et al. Linear viscoelastic properties of electro-rheological nano-suspension confined to narrow gap between electrodes. Colloid Polym Sci 285, 1201–1211 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-007-1673-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-007-1673-1