Abstract
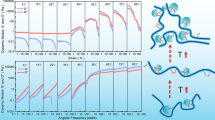
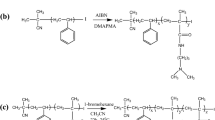
Three series of block copolymers of acrylamide (AM) and styrene (St) as hydrophobic comonomer with varied microstructures were prepared in microemulsion medium by changing feed ratio of monomers, ratio of St to surfactant, and amount of initiator, respectively. The effects of microstructure factors of the amphiphilic block copolymers PAM-b-PSt on their aqueous solution properties were investigated by fluorescence probe technique and surface tension measurement in detail. The experimental results show that the aqueous solution properties of PAM-b-PSt are strongly dependent on their microstructure factors, such as the length and content of PSt hydrophobic blocks in the copolymers and their molecular weight. It was found that the main microstructure factors which effect the hydrophobic association behavior of the copolymer PAM-b-PSt are the length and content of PSt hydrophobic blocks in the copolymer, whereas the hydrophobic association behavior of the copolymer is not affected nearly so much by molecular weight in more dilute regions. At the same time, it was also found that the main microstructure factors which affect the surface activity of the copolymer are the content of PSt hydrophobic blocks in the copolymer and molecular weight, whereas the length of PSt blocks in copolymer does not affect surface activity of the copolymer nearly so much under fixed content of PSt hydrophobic blocks and molecular weight in the copolymer.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dowling KC,Thomas JK (1990) J Macromol 23:1059
Kevin C,Taylor Hisham A,Nasr-EI-DIN (1998) J Petrol Sci Eng 19:265
Schulz DN, MaurerJ, Bock J et al (1987) J Polym 28:2111
KwonGS, Kataoka K (1995) J Adv Drug Delivery Rev 16:295
Tuzar Z, Iranian J (1995) J Polym Sci Tech 41:34
Gao BJ, YangYF, Jiu HF (2001) Acta Polym Sin (China ) 5:608
Gao BJ, YangYF, Ge Z (2002) Chin J Anal Chem (China) 30:69
Ge Z, Gao BJ, Yang YF (2002) Acta Polym Sin (China )6:712
Gao BJ, Xu RX, Yu SK, Xu L, Ge Z Acta (2003) Acta Polym Sin (China) 3:368
Hill A, Candau F, Selb J (1993) J Macromol 26:4521
Volpert E, Selb J, Candau F (1998) J Polym 39:1025
Cao Y, Li HLJ (2001) Chem J Chin Univ 22:312
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Science Foundation of Province Shanxi of China for financial support of this work (contact No: 94012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, B., Xu, R., Yu, S. et al. Studies on microstructure and aqueous solution properties of block copolymer of acrylamide-styrene. Colloid Polym Sci 282, 1008–1015 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-003-1025-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-003-1025-8