Abstract.
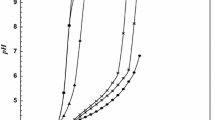
The competitive binding of monovalent and divalent counterions to poly(alkylene phosphate) related to bacterial teichoic acids and poly(styrenesulfonate) was studied experimentally by potentiometry with ion-selective electrodes. The binding of calcium ions and the release of sodium ions accompanying calcium ions binding in aqueous solutions of the polyelectrolytes was analysed and the mean exchange ratio Na+/Ca2+ was estimated. It was found that in the process of addition of calcium ions to sodium poly(alkylene phosphate) and sodium poly(styrenesulfonate) solutions all the Ca2+ ions added are bound to polyions and the initially condensed Na+ ions are released proportionally to the concentration of the added Ca2+ ions up to the critical concentration of the Ca2+ ions added. For a molar concentration ratio of calcium counterions to charged groups on the polyion up to 0.20 the exchange ratio was approximately equal to 1 or 2 for the sodium poly(alkylene phosphate)/CaCl2 and sodium poly(styrenesulfonate)/CaCl2 systems, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ostrowska-Czubenko, J. Competitive binding of Na+ and Ca2+ ions to teichoic acid analogues. Colloid Polym Sci 280, 1015–1020 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-002-0724-x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-002-0724-x