Abstract
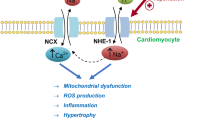
Sodium-hydrogen exchange is involved in ischemia-reperfusion injury. Despite the strong research support for the use of sodium-hydrogen exchange blockers to protect the myocardium during ischemia-reperfusion, there is still controversy regarding the most effective time for drug delivery. Studies that initiate drug treatment immediately before or at reperfusion have given conflicting results. The conflict in results may be due to differences in the experimental design. Post-ischemic cardioprotection may be less than optimal due to the vascular permeability barrier or a limited collateral circulation. Increasing the drug dose or allowing more time for the drug to cross the vessel wall may overcome this limitation. Determining the correct dose and delivery protocol, therefore, will be critical for the generation of positive results in future clinical trials and will optimize the beneficial effects of sodium-hydrogen exchange inhibition in the treatment of reperfusion injury.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 23 April 2001 / Returned for revision: 16 May 2001 / Revision received: 11 June 2001 / Accepted: 12 June 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hurtado, C., Pierce, G. Sodium-hydrogen exchange inhibition: pre-versus post-ischemic treatment. Basic Res Cardiol 96, 312–317 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003950170038
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003950170038