Abstract
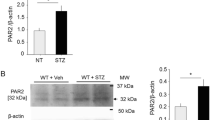
Protease-activated receptor-2 (PAR2) is expressed in endothelial cells and mediates endothelium-dependent vasodilation. We hypothesized that PAR2 regulates tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α)-induced coronary arteriolar dysfunction in type 2 diabetic (db/db) mice. To test this, coronary arterioles from WT control, db/db, db/db mice treated with PAR2 antagonist FSLLRY–NH2 (db/db+FSLLRY–NH2) and db/db mice null for TNF (dbTNF−/dbTNF−) were isolated and pressurized (60 cmH2O) without flow. Although vasodilation to the endothelium-independent vasodilator sodium nitroprusside (SNP) was not different among WT, db/db, db/db+FSLLRY–NH2 and dbTNF−/dbTNF−, endothelium-dependent acetylcholine (ACh)- and flow-mediated vasodilation were impaired in db/db mice but were enhanced in dbTNF−/dbTNF− mice and db/db mice treated with PAR2 antagonist. NOS inhibitor N G-nitro-l-arginine-methyl ester (l-NAME) significantly reduced ACh-induced dilation in WT, dbTNF−/dbTNF− and db/db+FSLLRY–NH2, but did not alter the vasodilation in db/db mice. In contrast, cyclooxygenase (COX) inhibitor indomethacin (Indo) did not alter ACh-induced vasodilation in these four groups of mice. PAR2-activating peptide (PAR2-AP, 2-Furoyl-LIGRLO-am)-induced dilation was higher in db/db mice than that in WT, dbTNF−/dbTNF− and db/db mice treated with PAR2 antagonist. These effects were abolished by denudation, or in the presence of l-NAME or Indo. Protein expressions of TNF-α, PAR2, gp91phox and p47phox in the heart and isolated coronary arterioles were higher in db/db mice compared to WT mice. Administration of PAR2 antagonist to db/db mice reduced protein expression of TNF-α, gp91phox and PAR2. Protein expression of gp91phox and p47phox was lower in dbTNF−/dbTNF− compared to db/db mice. These results indicate that PAR2 plays a pivotal role in endothelial dysfunction in type 2 diabetes by up-regulating the expression/production of TNF-α and activating NAD(P)H oxidase subunit p47phox.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atsufumi K, Ryotaro K, Takeshi M, Kazuo K, Mamoru T (1998) Increased vascular permeability by a specific agonist of protease-activated receptor-2 in rat hindpaw. Br J Pharmacol 125:419–422
Banfi C, Brioschi M, Barbieri SS, Eligini S, Barcella S, Tremoli E, Colli S, Mussoni L (2009) Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species: a common pathway for PAR1- and PAR2-mediated tissue factor induction in human endothelial cells. J Thromb Haemost 7:206–216
Bramos D, Ikonomidis I, Tsirikos N, Kottis G, Kostopoulou V, Pamboucas C, Papadopoulou E, Venetsanou K, Giatrakos N, Yang GZ, Nihoyannopoulos P, Toumanidis S (2008) The association of coronary flow changes and inflammatory indices to ischaemia–reperfusion microvascular damage and left ventricular remodeling. Basic Res Cardiol 103:345–355
Chappell D, Hofmann-Kiefer K, Jacob K, Rehm M, Briegel J, Welsch U, Conzen P, Becker BF (2009) TNF-α induced shedding of the endothelial glycocalyx is prevented by hydrocortisone and antithrombin. Basic Res Cardiol 104:78–89
Cicala C (2002) Protease activated receptor 2 and the cardiovascular system. Br J Pharmacol 135:14–20
Cicala C, Pinto A, Bucci M, Sorrentino R, Walker B, Harriot P, Cruchley A, Kapas S, Howells GL, Cirino G (1999) Protease-activated receptor-2 involvement in hypotension in normal and endotoxemic rats in vivo. Circulation 99:2590–2597
Cocks TM, Moffatt JD (2000) Protease-activated receptors: sentries for inflammation? Trends Pharmacol Sci 21:103–108
D’Andrea MR, Derian CK, Leturcq D, Baker SM, Brunmark A, Ling P, Darrow AL, Santulli RJ, Brass LF, Andrade-Gordon P (1998) Characterization of protease-activated receptor-2 immunoreactivity in normal human tissues. J Histochem Cytochem 46:157–164
Duncan BB, Schmidt MI, Pankow JS, Ballantyne CM, Couper D, Vigo A, Hoogeveen R, Folsom AR, Heiss G (2003) Low-grade systemic inflammation and the development of type 2 diabetes: the atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Diabetes 52:1799–1805
Ebrahimian TG, Heymes C, You D, Blanc-Brude O, Mees B, Waeckel L, Duriez M, Vilar J, Brandes RP, Levy BI, Shah AM, Silvestre J-S (2006) NADPH oxidase-derived overproduction of reactive oxygen species impairs postischemic neovascularization in mice with type 1 diabetes. Am J Pathol 169:719–728
Gao X, Belmadani S, Picchi A, Xu X, Potter BJ, Tewari-Singh N, Capobianco S, Chilian WM, Zhang C (2007) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces endothelial dysfunction in Lepr(db) mice. Circulation 115:245–254
Gao X, Zhang H, Schmidt AM, Zhang C (2008) AGE/RAGE produces endothelial dysfunction in coronary arterioles in Type 2 diabetic mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 295:H491–H498
Greenberg AS, McDaniel ML (2002) Identifying the links between obesity, insulin resistance and beta-cell function: potential role of adipocyte-derived cytokines in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. Eur J Clin Invest 32:24–34
Hamilton JR, Frauman AG, Cocks TM (2001) Increased expression of protease-activated receptor-2 (PAR2) and PAR4 in human coronary artery by inflammatory stimuli unveils endothelium-dependent relaxations to PAR2 and PAR4 agonists. Circ Res 89:92–98
Hirano K (2007) The roles of proteinase-activated receptors in the vascular physiology and pathophysiology. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27:27–36
Hwa JJ, Ghibaudi L, Williams P, Chintala M, Zhang R, Chatterjee M, Sybertz E (1996) Evidence for the presence of a proteinase-activated receptor distinct from the thrombin receptor in vascular endothelial cells. Circ Res 78:581–588
Ihm SH, Chang K, Kim HY, Baek SH, Youn HJ (2010) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ activation attenuates cardiac fibrosis in type 2 diabetic rats: the effect of rosiglitazone on myocardial expression of receptor for advanced glycation end products and of connective tissue growth factor. Basic Res Cardiol 105:399–407
Jiang R, Zatta A, Kin H, Wang N, Reeves JG, Mykytenko J, Deneve J, Zhao ZQ, Guyton RA, Vinten-Johansen J (2007) PAR-2 activation at the time of reperfusion salvages myocardium via an ERK1/2 pathway in in vivo rat hearts. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 293:H2845–H2852
Kawabata A, Nakaya Y, Kuroda R, Wakisaka M, Masuko T, Nishikawa H, Kawai K (2003) Involvement of EDHF in the hypotension and increased gastric mucosal blood flow caused by PAR-2 activation in rats. Br J Pharmacol 140:247–254
Kim M-S, Jo H, Um J-Y, Yi J-M, Kim D-K, Choi S-C, Kim T-H, Nah Y-H, Kim H-M, Lee Y-M (2002) Agonists of proteinase-activated receptor 2 induce TNF-alpha secretion from astrocytoma cells. Cell Biochem Funct 20:339–345
Kleinbongard P, Heusch G, Schulz R (2010) TNFα in atherosclerosis, myocardial ischemia/reperfusion and heart failure. Pharmacol Ther 127:295–314
Knight DA, Lim S, Scaffidi AK, Roche N, Chung KF, Stewart GA, Thompson PJ (2001) Protease-activated receptors in human airways: upregulation of PAR-2 in respiratory epithelium from patients with asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 108:797–803
Lan RS, Stewart GA, Goldie RG, Henry PJ (2004) Altered expression and in vivo lung function of protease-activated receptors during influenza a virus infection in mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 286:L388–L398
Leger AJ, Covic L, Kuliopulos A (2006) Protease-activated receptors in cardiovascular diseases. Circulation 114:1070–1077
Li S, Zhong S, Zeng K, Luo Y, Fea Zhang (2010) Blockade of NF-κB by pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate attenuates myocardial inflammatory response and ventricular dysfunction following coronary microembolization induced by homologous microthrombi in rats. Basic Res Cardiol 105:139–150
Macfarlane SR, Seatter MJ, Kanke T, Hunter GD, Plevin R (2001) Proteinase-activated receptors. Pharmacol Rev 53:245–282
McGuire JJ (2004) Proteinase-activated receptor 2 (PAR2): a challenging new target for treatment of vascular diseases. Curr Pharm Des 10:2769–2778
McIntosh KA, Plevin R, Ferrell WR, Lockhart JC (2007) The therapeutic potential of proteinase-activated receptors in arthritis. Curr Opin Pharmacol 7:334–338
Nystedt S, Ramakrishnan V, Sundelin J (1996) The proteinase-activated receptor 2 is induced by inflammatory mediators in human endothelial cells. Comparison with the thrombin receptor. J Biol Chem 271:14910–14915
Ossovskaya VS, Bunnett NW (2004) Protease-activated receptors: contribution to physiology and disease. Physiol Rev 84:579–621
Park Y, Capobianco S, Gao X, Falck JR, Dellsperger KC, Zhang C (2008) Role of EDHF in type 2 diabetes-induced endothelial dysfunction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 295:H1982–H1988
Picchi A, Gao X, Belmadani S, Potter BJ, Focardi M, Chilian WM, Zhang C (2006) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces endothelial dysfunction in the prediabetic metabolic syndrome. Circ Res 99:69–77
Ritchie E, Saka M, MacKenzie C, Drummond R, Wheeler-Jones C, Kanke T, Plevin R (2007) Cytokine upregulation of proteinase-activated-receptors 2 and 4 expression mediated by p38 MAP kinase and inhibitory kappa B kinase β in human endothelial cells. Br J Pharmacol 150:1044–1054
Robin J, Kharbanda R, McLean P, Campbell R, Vallance P (2003) Protease-activated receptor 2-mediated vasodilatation in humans in vivo: role of nitric oxide and prostanoids. Circulation 107:954–959
Roman-Campos D, Duarte HLL, Sales PA, Natali AJ, Cea Ropert (2009) Changes in cellular contractility and cytokines profile during Trypanosoma cruzi infection in mice. Basic Res Cardiol 104:238–246
Roviezzo F, Bucci M, Brancaleone V, Di Lorenzo A, Geppetti P, Farneti S, Parente L, Lungarella G, Fiorucci S, Cirino G (2005) Proteinase-activated receptor-2 mediates arterial vasodilation in diabetes. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25:2349–2354
Sobey CG, Moffatt JD, Cocks TM, Kontos HA (1999) Evidence for selective effects of chronic hypertension on cerebral artery vasodilatation to protease-activated receptor-2 activation. Stroke 30:1933–1941
Trottier G, Hollenberg M, Wang X, Gui Y, Loutzenhiser K, Loutzenhiser R (2002) PAR-2 elicits afferent arteriolar vasodilation by NO-dependent and NO-independent actions. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 282:F891–F897
Wang J, Zheng H, Hollenberg MD, Wijesuriya SJ, Ou X, Hauer-Jensen M (2003) Up-regulation and activation of proteinase-activated receptor 2 in early and delayed radiation injury in the rat intestine: influence of biological activators of proteinase-activated receptor 2. Radiat Res 160:524–535
Yang J, Park Y, Zhang H, Xu X, Laine GA, Dellsperger KC, Zhang C (2009) Feed-forward signaling of TNF-alpha and NF-kappaB via IKK-beta pathway contributes to insulin resistance and coronary arteriolar dysfunction in type 2 diabetic mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 296:H1850–H1858
Zhang C (2008) The role of inflammatory cytokines in endothelial dysfunction. Basic Res Cardiol 103:398–406
Zhang C, Hein TW, Wang W, Kuo L (2003) Divergent roles of angiotensin II AT1 and AT2 receptors in modulating coronary microvascular function. Circ Res 92:322–329
Zhang C, Wu C, Xu X, Potter BJ, Gao X (2010) Direct relationship between levels of TNF-α expression and endothelial dysfunction in reperfusion injury. Basic Res Cardiol 105:453–464
Zhang C, Xu X, Potter BJ, Wang W, Kuo L, Michael L, Bagby GJ, Chilian WM (2006) TNF-alpha contributes to endothelial dysfunction in ischemia/reperfusion injury. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 26:475–480
Zhang H, Zhang J, Ungvari Z, Zhang C (2009) Resveratrol improves endothelial function: role of TNF{alpha} and vascular oxidative stress. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 29:1164–1171
Zhong B, Wang DH (2009) Protease-activated receptor 2-mediated protection of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury: role of transient receptor potential vanilloid receptors. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 297:R1681–R1690
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from American Heart Association Scientist Development Grant (110350047A), Pfizer Atorvastatin Research Award (2004-37) and NIH grants (RO1-HL077566 and RO1-HL085119) to Dr. Cuihua Zhang.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, Y., Yang, J., Zhang, H. et al. Effect of PAR2 in regulating TNF-α and NAD(P)H oxidase in coronary arterioles in type 2 diabetic mice. Basic Res Cardiol 106, 111–123 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-010-0129-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-010-0129-9