Abstract
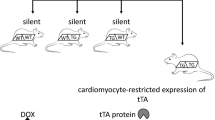
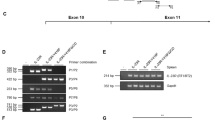
We previously found that myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) initiates expression of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF) leading to coronary endothelial dysfunction. However, it is not clear whether there is a direct relationship between levels of TNF expression and endothelial dysfunction in reperfusion injury. We studied levels of TNF expression by using different transgenic animals expressing varying amounts of TNF in I/R. We crossed TNF overexpression (TNF++/++) with TNF knockout (TNF−/−) mice; thus we have a heterozygote population of mice with the expression of TNF “in between” the TNF−/− and TNF++/++ mice. Mouse hearts were subjected to 30 min of global ischemia followed by 90 min of reperfusion and their vasoactivity before and after I/R was examined in wild type (WT), TNF−/−, TNF++/++ and TNF heterozygote (TNF−/++, cross between TNF−/− and TNF++/++) mice. In heterozygote TNF−/++ mice with intermediate cardiac-specific expression of TNF, acetylcholine-induced or flow-induced endothelial-dependent vasodilation following I/R was between TNF++/++ and TNF−/− following I/R. Neutralizing antibodies to TNF administered immediately before the onset of reperfusion-preserved endothelial-dependent dilation following I/R in WT, TNF−/++ and TNF++/++ mice. In WT, TNF−/++ and TNF++/++ mice, I/R-induced endothelial dysfunction was progressively lessened by administration of free-radical scavenger TEMPOL immediately before initiating reperfusion. During I/R, production of superoxide (O2 ·−) was greatest in TNF++/++ mice as compared to WT, TNF−/++ and TNF−/− mice. Following I/R, arginase mRNA expression was elevated in the WT, substantially elevated in the TNF−/++ and TNF++/++ mice and not affected in the TNF−/− mice. These results suggest that the level of TNF expression determines arginase expression in endothelial cells during myocardial I/R, which is one of the mechanisms by which TNF compromises coronary endothelial function in reperfusion injury.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ammar RF Jr, Gutterman DD, Brooks LA, Dellsperger KC (2000) Free radicals mediate endothelial dysfunction of coronary arterioles in diabetes. Cardiovasc Res 47:595–601
Aoki N, Siegfried M, Lefer AM (1989) Anti-EDRF effect of tumor necrosis factor in isolated, perfused cat carotid arteries. Am J Physiol 256:H1509–H1512
Bagi Z, Koller A, Kaley G (2004) PPAR-g activation, by reducing oxidative stress, increases NO bioavailability in coronary arterioles of mice with type 2 diabetes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 286:H742–H748
Bose D, von Birgelen C, Zhou XY, Schmermund A, Philipp S, Sack S, Konorza T, Mohlenkamp S, Leineweber K, Kleinbongard P, Wijns W, Heusch G, Erbel R (2008) Impact of atherosclerotic plaque composition on coronary microembolization during percutaneous coronary interventions. Basic Res Cardiol 103:587–597
Bramos D, Ikonomidis I, Tsirikos N, Kottis G, Kostopoulou V, Pamboucas C, Papadopoulou E, Venetsanou K, Giatrakos N, Yang GZ, Nihoyannopoulos P, Toumanidis S (2008) The association of coronary flow changes and inflammatory indices to ischaemia–reperfusion microvascular damage and left ventricular remodelling. Basic Res Cardiol 103:345–355
Chandrasekar B, Colston JT, Freeman GL (1997) Induction of proinflammatory cytokine and antioxidant enzyme gene expression following brief myocardial ischemia. Clin Exp Immunol 108:346–351
Dorge H, Schulz R, Belosjorow S, Post H, van de Sand A, Konietzka I, Frede S, Hartung T, Vinten-Johansen J, Youker KA, Entman ML, Erbel R, Heusch G (2002) Coronary microembolization: the role of TNF-alpha in contractile dysfunction. J Mol Cell Cardiol 34:51–62
Fischer P, Hilfiker-Kleiner D (2007) Survival pathways in hypertrophy and heart failure: the gp130-STAT axis. Basic Res Cardiol 102:393–411
Gao X, Xu X, Belmadani S, Park Y, Tang Z, Feldman AM, Chilian WM, Zhang C (2007) TNF-alpha contributes to endothelial dysfunction by upregulating arginase in ischemia/reperfusion injury. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27:1269–1275
Gao X, Zhang H, Belmadani S, Wu J, Xu X, Elford H, Potter BJ, Zhang C (2008) Role of TNF-alpha-induced reactive oxygen species in endothelial dysfunction during reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 295:H2242–H2249
Garcia SC, Pomblum V, Gams E, Langenbach MR, Schipke JD (2007) Independency of myocardial stunning of endothelial stunning? Basic Res Cardiol 102:359–367
Gilmont RR, Dardano A, Engle JS, Adamson BS, Welsh MJ, Li T, Remick DG, Smith DJJ, Rees RS (1996) TNF-alpha potentiates oxidant and reperfusion-induced endothelial cell injury. J Surg Res 61:175–182
Gurevitch J, Frolkis I, Yuhas Y, Lifschitz-Mercer B, Berger E, Paz Y, Matsa M, Kramer A, Mohr R (1997) Anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha improves myocardial recovery after ischemia and reperfusion. J Am Coll Cardiol 30:1554–1561
Hein TW, Zhang C, Wang W, Chang CI, Thengchaisri N, Kuo L (2003) Ischemia–reperfusion selectively impairs nitric oxide-mediated dilation in coronary arterioles: counteracting role of arginase. FASEB J 17:2328–2330
Herskowitz A, Choi S, Ansari AA, Wesselingh S (1995) Cytokine mRNA expression in postischemic/reperfused myocardium. Am J Pathol 146:419–428
Huber SA, Feldman AM, Sartini D (2006) Coxsackie virus B3 induces T regulatory cells, which inhibit cardiomyopathy in tumor necrosis factor-alpha transgenic mice. Circ Res 99:1109–1116
Kupatt C, Habazettl H, Goedecke A, Wolf D, Zahler S, Boekstegers P, Kelly R, Becker B (1999) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha contributes to ischemia- and reperfusion-induced endothelial activation in isolated hearts. Circ Res 84:392–400
Lawson DL, Mehta JL, Nichols WW (1990) Coronary reperfusion in dogs inhibits endothelium-dependent relaxation: role of superoxide radicals. Free Radic Biol Med 8:373–380
Lefer AM, Lefer DJ (1993) Pharmacology of the endothelium in ischemia–reperfusion and circulatory shock. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 33:71–90
Lefer AM, Ma X (1993) Cytokines and growth factors in endothelial dysfunction. Crit Care Med 21(Suppl):S9–S14
Lefer AM, Ma XL (1993) Cytokines and growth factors in endothelial dysfunction. Crit Care Med 21:S9–S14
Lefer AM, Tsao PS, Ma X-L (1991) Shock- and ischemia-induced mechanisms of impairment of endothelium-mediated vasodilation. Chest 100:160S–163S
Levine B, Kalman J, Mayer L, Fillit HM, Packer M (1990) Elevated circulating levels of tumor necrosis factor in severe chronic heart failure. N Engl J Med 323:236–241
Murray DR, Freeman GL (1996) Tumor necrosis factor-α induces a biphasic effect on myocardial contractility in conscious dogs. Circ Res 78:154–160
Oral H, Dorn GW 2nd, Mann DL (1997) Sphingosine mediates the immediate negative inotropic effects of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the adult mammalian cardiac myocyte. J Biol Chem 272:4836–4842
Pereda J, Sabater L, Cassinello N, Gomez-Cambronero L, Closa D, Folch-Puy E, Aparisi L, Calvete J, Cerda M, Lledo S, Vina J, Sastre J (2004) Effect of simultaneous inhibition of TNF-alpha production and xanthine oxidase in experimental acute pancreatitis: the role of mitogen activated protein kinases. Ann Surg 240:108–116
Picchi A, Gao X, Belmadani S, Potter BJ, Focardi M, Chilian WM, Zhang C (2006) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces endothelial dysfunction in the prediabetic metabolic syndrome. Circ Res 99:69–77
Schmidt A, Geigenmuller S, Volker W, Buddecke E (2006) The antiatherogenic and antiinflammatory effect of HDL-associated lysosphingolipids operates via Akt >NF-kappaB signalling pathways in human vascular endothelial cells. Basic Res Cardiol 101:109–116
Schulz R, Aker S, Belosjorow S, Heusch G (2004) TNFalpha in ischemia/reperfusion injury and heart failure. Basic Res Cardiol 99:8–11
Schulz R, Heusch G (2009) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and its receptors 1 and 2: Yin and Yang in myocardial infarction? Circulation 119:1355–1357
Tanner FC, van der Loo B, Shaw S, Greutert H, Bachschmid MM, Berrozpe M, Rozenberg I, Blau N, Siebenmann R, Schmidli J, Meyer P, Luscher TF (2007) Inactivity of nitric oxide synthase gene in the atherosclerotic human carotid artery. Basic Res Cardiol 102:308–317
Thielmann M, Dorge H, Martin C, Belosjorow S, Schwanke U, van De Sand A, Konietzka I, Buchert A, Kruger A, Schulz R, Heusch G (2002) Myocardial dysfunction with coronary microembolization: signal transduction through a sequence of nitric oxide, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and sphingosine. Circ Res 90:807–813
Tiefenbacher CP, Chilian WM, Mitchell M, DeFily DV (1999) Restoration of endothelium-dependent vasodilation after reperfusion injury by tetrahydrobiopterin. Circulation 94:1423–1429
Tracey KJ, Beutler B, Lowry SF, Merryweather J, Wolpe S, Milsark IW, Hariri RJ, Fahey TJ 3rd, Zentella A, Albert JD et al (1986) Shock and tissue injury induced by recombinant human cachectin. Science 234:470–474
Tracey KJ, Vlassara H, Cerami A (1987) Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor. N Engl J Med 316:379–385
Tsao PS, Aoki N, Lefer DJ, Johnson G III, Lefer AM (1990) Time course of endothelial dysfunction and myocardial injury during myocardial ischemia and reperfusion in the cat. Circulation 82:1402–1412
Tsao PS, Ma X, Lefer AM (1992) Activated neutrophils aggravate endothelial dysfunction after reperfusion of the ischemic feline myocardium. Am Heart J 123:1464–1471
Vasquez-Vivar J, Kalyanaraman B, Martasek P, Hogg N, Masters BS, Karoui H, Tordo P, Pritchard KA Jr (1998) Superoxide generation by endothelial nitric oxide synthase: the influence of cofactors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:9220–9225
Weyrich AS, Ma XL, Lefer AM (1992) The role of l-arginine in ameliorating reperfusion injury after myocardial ischemia in the cat. Circulation 86:279–288
Yamamoto S, Matsui K, Itoh N, Ohaashi N (2001) The effect of an Na+/H+ exchange inhibitor, SM-20550, on ischemia/reperfusion-induced endothelial dysfunction in isolated perfused rat hearts. Int J Tissue React 23:1–7
Yang J, Park Y, Zhang H, Xu X, Laine GA, Dellsperger KC, Zhang C (2009) Feed-forward signaling of TNF-alpha and NF-kappaB via IKK-beta pathway contributes to insulin resistance and coronary arteriolar dysfunction in type 2 diabetic mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 296:H1850–H1858
Zhang C (2008) The role of inflammatory cytokines in endothelial dysfunction. Basic Res Cardiol 103:398–406
Zhang C, Hein TW, Wang W, Chang CI, Kuo L (2001) Constitutive expression of arginase in microvascular endothelial cells counteracts nitric oxide-mediated vasodilatory function. FASEB J 15:1264–1266
Zhang C, Hein TW, Wang W, Ren Y, Shipley RD, Kuo L (2006) Activation of JNK and xanthine oxidase by TNF-alpha impairs nitric oxide-mediated dilation of coronary arterioles. J Mol Cell Cardiol 40:247–257
Zhang C, Park Y, Picchi A, Potter BJ (2008) Maturation-induces endothelial dysfunction via vascular inflammation in diabetic mice. Basic Res Cardiol 103:407–416
Zhang C, Xu X, Potter BJ, Wang W, Kuo L, Michael L, Bagby GJ, Chilian WM (2006) TNF-alpha contributes to endothelial dysfunction in ischemia/reperfusion injury. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 26:475–480
Zhang DX, Yi FX, Zou AP, Li PL (2002) Role of ceramide in TNF-alpha-induced impairment of endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation in coronary arteries. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 283:H1785–H1794
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Grants from American Heart Association Grant-in-Aid (0455435B), Atorvastatin Research Award (2004-37), American Heart Association SDG (110350047A) and NIH Grants (RO1-HL077566 and RO1-HL085119) to Dr. C Zhang.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C., Wu, J., Xu, X. et al. Direct relationship between levels of TNF-α expression and endothelial dysfunction in reperfusion injury. Basic Res Cardiol 105, 453–464 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-010-0083-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-010-0083-6