Abstract
Background
Patients with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) are at increased risk for cardiovascular disease. Increased sympathetic drive is considered as one of the underlying mechanisms. Both heart rate turbulence (HRT) and heart rate variability (HRV) are parameters to describe autonomic regulation. We investigated the influence of sleep–disordered breathing (SDB) on HRT and HRV in patients with OSA.
Methods
Sixty–five patients underwent overnight polysomnography for clinically suspected SDB and simultaneous Holter monitoring (11 p.m.–6 a.m.). Patients with diabetes mellitus, a history of cardiac disease, left ventricular dysfunction, periodic breathing pattern, and those on beta–blockers or theophylline were excluded. According to the apnea–hypopnea index (AHI), the patients were assigned to group A (AHI <20, n = 31) or group B (AHI ≥20, n = 34). HRV (time domain, frequency domain) and HRT (onset, slope) were then related to the severity of SDB.
Results
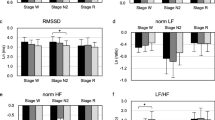
Nighttime turbulence slope (TS) correlated inversely with the AHI (r = –0.45, p = 0.01) and was significantly lower in group B (8.9 ± 1.6 ms/R–R interval) compared with that in group A (19.8 ± 4.0 ms/R–R interval, P = 0.01). This relationship remained stable after adjusting TS for the number of ventricular premature contractions. No significant differences in turbulence onset or parameters of nighttime HRV were observed.
Conclusions
Alterations in nighttime HRT correlate with the severity of SDB, indicating abnormalities in cardiac autonomic activity in moderate–to–severe OSA even in the absence of overt cardiac disease. These changes may be associated with the subsequent development of cardiovascular disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AHI :
-
= apnea–hypopnea index
- HF:
-
= high frequency
- HRT:
-
= heart rate turbulence
- HRV:
-
= heart rate variability
- LF:
-
= low frequency
- OSA:
-
= obstructive sleep apnea
- pNN 50:
-
= number of pairs of adjacent R–R intervals differing by more than 50 ms, divided by the total number of all NN intervals
- rMSSD:
-
= square root of the mean of the sum of squared differences of successive R–R intervals
- SDANN:
-
= standard deviation of the averages of R–R intervals in all 5–minute segments of the entire recording
- SDB:
-
= sleep–disordered breathing
- SDNN:
-
= standard deviation of all R–R intervals
- TO:
-
= turbulence onset
- TP:
-
= total power
- TS s:
-
= turbulence slope
- VLF:
-
= very low frequency
- VPC:
-
= ventricular premature contraction
- vTS:
-
= turbulence slope adjusted for the number of VPC
References
Barthel P, Schneider R, Bauer A, Ulm K, Schmitt C, Schömig A, Schmidt G (2003) Risk stratification after acute myocardial infarction by heart rate turbulence. Circulation 108:1221–1226
Bigger JT Jr, Fleiss JL, Rolnitzky LM, Steinman RC (1993) Frequency domain measures of heart period variability to assess risk late after myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol 21:729–736
Bliwise DL, Bliwise NG, Partinen M, Pursley AM, Dement WC (1988) Sleep apnea and mortality in an aged cohort. Am J Public Health 78:544–547
Brown TE, Beightol LA, Koh J, Eckberg DL (1993) Important influence of respiration on human R–R interval power spectra is largely ignored. J Appl Physiol 75:2310–2317
Can I, Aytemir K, Demir AU, Deniz A, Sahin A, Tokgozoglu L (2003) Heart rate turbulence in obstructive sleep apnea (abstr). Europace 4:B170
Cerutti S, Bianchi AM, Mainardi LT (1995) Spectral analysis of the heart rate variability signal. In: Malik M, Camm AJ (eds) Heart rate variability. Futura Publishing Company, Armonk, NY, pp 63–74
Dingli K, Assimakopoulos T, Wraith PK, Fietze I, Witt C, Douglas NJ (2003) Spectral oscillations of RR intervals in sleep apnoea/hypopnoea syndrome patients. Eur Respir J 22:943–950
Dyken ME, Somers VK, Yamada T, Ren ZY, Zimmerman MB (1996) Investigating the relationship between stroke and obstructive sleep apnea. Stroke 27:401–407
Fei L, Copie X, Malik M, Camm AJ (1996) Short– and long–term assessment of heart rate variability for risk stratification after acute myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol 77:681–684
Fletcher EC, Miller J, Schaaf JW, Fletcher JG (1987) Urinary catecholamines before and after tracheostomy in patients with obstructive sleep apnea and hypertension. Sleep 10:35–44
Guilleminault C, Connolly S, Winkle R, Melvin K, Tilkian A (1984) Cyclical variation of the heart rate in sleep apnoea syndrome. Mechanisms, and usefulness of 24 h electrocardiography as a screening technique. Lancet 1:126–131
Guzik P, Schmidt G (2002) A phenomenon of heart–rate turbulence, its evaluation, and prognostic value. Card Electrophysiol Rev 6:256–261
Hallstrom AP, Stein PK, Schneider R, Hodges M, Schmidt G, Ulm K (2004) Structural relationships between measures based on heart beat intervals: potential for improved risk assessment. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 51:1414–1420
Harbison J, O’Reilly P, McNicholas WT (2000) Cardiac rhythm disturbances in the obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: effects of nasal continuous positive airway pressure therapy. Chest 118:591–595
He J, Kryger MH, Zorick FJ, Conway W, Roth T (1988) Mortality and apnea index in obstructive sleep apnea. Experience in 385 male patients. Chest 94:9–14
Hung J, Whitford EG, Parsons RW, Hillman DR (1990) Association of sleep apnoea with myocardial infarction in men. Lancet 336:261–264
Kleiger RE, Miller JP, Bigger JT Jr, Moss AJ (1987) Decreased heart rate variability and its association with increased mortality after acute myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol 59:256–262
Malone S, Liu PP, Holloway R, Rutherford R, Xie A, Bradley TD (1991) Obstructive sleep apnoea in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy: effects of continuous positive airway pressure. Lancet 338:1480–1484
Narkiewicz K, Montano N, Cogliati C, van de Borne PJ, Dyken ME, Somers VK (1998) Altered cardiovascular variability in obstructive sleep apnea. Circulation 98:1071–1077
Nieto FJ, Young TB, Lind BK, Shahar E, Samet JM, Redline S, D’Agostino RB, Newman AB, Lebowitz MD, Pickering TG (2000) Association of sleep–disordered breathing, sleep apnea, and hypertension in a large community–based study. Sleep Heart Health Study. JAMA 283:1829–1836
Parish JM, Somers VK (2004) Obstructive sleep apnea and cardiovascular disease. Mayo Clin Proc 79:1036–1046
Peker Y, Hedner J, Norum J, Kraiczi H, Carlson J (2002) Increased incidence of cardiovascular disease in middle–aged men with obstructive sleep apnea: a 7– year follow–up. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 166:159–165
Peled N, Abinader EG, Pillar G, Sharif D, Lavie P (1999) Nocturnal ischemic events in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome and ischemic heart disease: effects of continuous positive air pressure treatment. J Am Coll Cardiol 34:1744–1749
Penzel T (2003) Is heart rate variability the simple solution to diagnose sleep apnoea? Eur Respir J 22:870–871
Peppard PE, Young T, Palta M, Skatrud J (2000) Prospective study of the association between sleep–disordered breathing and hypertension. N Engl J Med 342:1378–1384
Rechtschaffen A, Kales A (1968) A manual of standardised terminology: Techniques and scoring systems for sleep stages of human subjects. National Institute of Health, Washington; Publication No. 204
Roche F, Gaspoz JM, Court–Fortune I, Minini P, Pichot V, Duverney D, Costes F, Lacour JR, Barthelemy JC (1999) Screening of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome by heart rate variability analysis. Circulation 100:1411–1415
Schäfer H, Berner S, Ewig S, Hasper E, Tasci S, Lüderitz B (1998) Cardiovascular morbidity in patients with obstructive sleep apnea in relation to their severity of respiratory disorder. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 123:1127–1133
Schmidt G, Malik M, Barthel P, Schneider R, Ulm K, Rolnitzky L, Camm AJ, Bigger T Jr, Schömig A (1999) Heart–rate turbulence after ventricular premature beats as a predictor of mortality after acute myocardial infarction. Lancet 353:1390–1396
Schwab JO, Shlevkov N, Grunwald K, Schrickel JW, Yang A, Lickfett L, Lewalter T, Lüderitz B (2004) Influence of the point of origin on heart rate turbulence after stimulated ventricular and atrial premature beats. Basic Res Cardiol 99:56–60
Shiomi T, Guilleminault C, Sasanabe R, Hirota I, Maekawa M, Kobayashi T (1996) Augmented very low frequency component of heart rate variability during obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep 19:370–377
Somers VK, Dyken ME, Clary MP, Abboud FM (1995) Sympathetic neural mechanisms in obstructive sleep apnea. J Clin Invest 96:1897–1904
Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology (1996) Heart rate variability: standards of measurement, physiological interpretation and clinical use. Circulation 93:1043–1065
Tsuji H, Venditti FJ Jr, Manders ES, Evans JC, Larson MG, Feldman CL, Levy D (1996) Determinants of heart rate variability. J Am Coll Cardiol 28:1539–1546
Young T, Peppard P, Palta M, Hla KM, Finn L, Morgan B, Skatrud J (1997) Population– based study of sleep–disordered breathing as a risk factor for hypertension. Arch Intern Med 157:1746–1752
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, A., Schäfer, H., Manka, R. et al. Influence of obstructive sleep apnea on heart rate turbulence. Basic Res Cardiol 100, 439–445 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-005-0536-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-005-0536-5