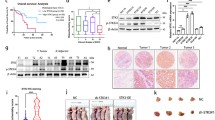
Abstract
Purpose
Pancreatic cancer (PC) is one of the most deadly human malignancies. Curcumin is a natural polyphenolic compound with wide-ranging pharmacological effects. Growing evidence suggests that curcumin has anticancer activity against PC, but the mechanism remains incompletely elucidated. This study aimed to investigate the effects and mechanisms of curcumin on the invasion and migration of PC cells.
Methods
Effect of curcumin on tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI)-2 mRNA expression in PC cells was initially identified using qRT-PCR. Cytotoxicity of curcumin was assessed with MTT assays and IC50 was calculated. Involvement of ERK and JNK pathways, as well as protein expression of TFPI-2 and epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT)-related markers, were detected using immunoblotting. Invasion and migration of PC cells were examined using Transwell assays. TFPI-2 expression was manipulated by transfection with siRNA and shRNA. Rescue assays were used to validate the effect of curcumin on cell invasion and migration via TFPI-2.
Results
Curcumin increased the expression of TFPI-2 mRNA and protein in PC cells and attenuated cell invasion and migration. Curcumin also inhibited ERK and JNK pathways and EMT in PC cells. Knockdown of TFPI-2 partially reversed the inhibition of ERK and JNK pathways and EMT by curcumin. Mechanistically, curcumin upregulated TFPI-2, thereby inhibiting the ERK and JNK pathways, leading to the inhibition of EMT in PC cells.
Conclusion
Collectively, curcumin inhibits ERK- and JNK-mediated EMT through upregulating TFPI-2, which in turn suppresses the migration and invasion of PC cells. These findings provide new insights into the antitumor mechanism of curcumin.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data generated in this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Wu W, He X, Yang L, Wang Q, Bian X, Ye J, Li Y, Li L (2018) Rising trends in pancreatic cancer incidence and mortality in 2000–2014. Clin Epidemiol 10:789–797. https://doi.org/10.2147/CLEP.S160018
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A (2022) Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin 72(1):7–33. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21708
Kempaiah P, Chand HS, Kisiel W (2007) Identification of a human TFPI-2 splice variant that is upregulated in human tumor tissues. Mol Cancer 6:20. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-4598-6-20
Wojtukiewicz MZ, Sierko E, Zimnoch L, Kozlowski L, Kisiel W (2003) Immunohistochemical localization of tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 in human tumor tissue. Thromb Haemost 90(1):140–146
Zhai LL, Wu Y, Huang DW, Tang ZG (2015) Increased matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression and reduced tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 expression correlate with angiogenesis and early postoperative recurrence of pancreatic carcinoma. Am J Transl Res 7(11):2412–2422
Zhai LL, Cai CY, Wu Y, Tang ZG (2015) Correlation and prognostic significance of MMP-2 and TFPI-2 differential expression in pancreatic carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8(1):682–691
Zhai LL, Wu Y, Cai CY, Tang ZG (2015) Upregulated matrix metalloproteinase-2 and downregulated tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 are risk factors for lymph node metastasis and perineural invasion in pancreatic carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther 8:2827–2834. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S90599
Sato N, Parker AR, Fukushima N, Miyagi Y, Iacobuzio-Donahue CA, Eshleman JR, Goggins M (2005) Epigenetic inactivation of TFPI-2 as a common mechanism associated with growth and invasion of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncogene 24(5):850–858. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208050
Tang Z, Geng G, Huang Q, Xu G, Hu H, Chen J, Li J (2011) Expression of tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 in human pancreatic carcinoma and its effect on tumor growth, invasion, and migration in vitro and in vivo. J Surg Res 167(1):62–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2009.06.015
Wang W, He Y, Zhai LL, Chen LJ, Yao LC, Wu L, Tang ZG, Ning JZ (2022) m6A RNA demethylase FTO promotes the growth, migration and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells through inhibiting TFPI-2. Epigenetics 17(12):1738–1752. https://doi.org/10.1080/15592294.2022.2061117
Lavergne M, Jourdan ML, Blechet C, Guyetant S, Pape AL, Heuze-Vourc’h N, Courty Y, Lerondel S, Sobilo J, Iochmann S, Reverdiau P (2013) Beneficial role of overexpression of TFPI-2 on tumour progression in human small cell lung cancer. FEBS Open Bio 3:291–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fob.2013.06.004
Wang G, Zeng Y, Chen S, Li D, Li W, Zhou Y, Singer RH, Gu W (2017) Localization of TFPI-2 in the nucleus modulates MMP-2 gene expression in breast cancer cells. Sci Rep 7(1):13575. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-14148-8
Wang G, Huang W, Li W, Chen S, Chen W, Zhou Y, Peng P, Gu W (2018) TFPI-2 suppresses breast cancer cell proliferation and invasion through regulation of ERK signaling and interaction with actinin-4 and myosin-9. Sci Rep 8(1):14402. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-32698-3
Do HTT, Cho J (2020) Involvement of the ERK/HIF-1α/EMT pathway in XCL1-induced migration of MDA-MB-231 and SK-BR-3 breast cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci 22(1):89. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010089
Lee S, Rauch J, Kolch W (2020) Targeting MAPK signaling in cancer: mechanisms of drug resistance and sensitivity. Int J Mol Sci 21(3):1102. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21031102
Xue M, Sun H, Xu R, Wang Y, Guo J, Li X, Cheng Y, Xu C, Tang C, Sun B, Chen L (2020) GADD45B promotes glucose-induced renal tubular epithelial–mesenchymal transition and apoptosis via the p38 MAPK and JNK signaling pathways. Front Physiol 11:1074. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2020.01074
Wu Q, Wu W, Jacevic V, Franca TCC, Wang X, Kuca K (2020) Selective inhibitors for JNK signalling: a potential targeted therapy in cancer. J Enzyme Inhibit Med Chem 35(1):574–583. https://doi.org/10.1080/14756366.2020.1720013
Bimonte S, Barbieri A, Leongito M, Piccirillo M, Giudice A, Pivonello C, de Angelis C, Granata V, Palaia R, Izzo F (2016) Curcumin anticancer studies in pancreatic cancer. Nutrients 8(7):433. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8070433
Nagaraju GP, Benton L, Bethi SR, Shoji M, El-Rayes BF (2019) Curcumin analogs: their roles in pancreatic cancer growth and metastasis. Int J Cancer 145(1):10–19. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.31867
Li L, Aggarwal BB, Shishodia S, Abbruzzese J, Kurzrock R (2004) Nuclear factor-kappaB and IkappaB kinase are constitutively active in human pancreatic cells, and their down-regulation by curcumin (diferuloylmethane) is associated with the suppression of proliferation and the induction of apoptosis. Cancer 101(10):2351–2362. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.20605
Bimonte S, Barbieri A, Palma G, Luciano A, Rea D, Arra C (2013) Curcumin inhibits tumor growth and angiogenesis in an orthotopic mouse model of human pancreatic cancer. Biomed Res Int 2013:810423. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/810423
Jutooru I, Chadalapaka G, Lei P, Safe S (2010) Inhibition of NFkappaB and pancreatic cancer cell and tumor growth by curcumin is dependent on specificity protein down-regulation. J Biol Chem 285(33):25332–25344. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.095240
Youns M, Fathy GM (2013) Upregulation of extrinsic apoptotic pathway in curcumin-mediated antiproliferative effect on human pancreatic carcinogenesis. J Cell Biochem 114(12):2654–2665. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.24612
Kunnumakkara AB, Guha S, Krishnan S, Diagaradjane P, Gelovani J, Aggarwal BB (2007) Curcumin potentiates antitumor activity of gemcitabine in an orthotopic model of pancreatic cancer through suppression of proliferation, angiogenesis, and inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB-regulated gene products. Cancer Res 67(8):3853–3861. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-4257
Bisht S, Mizuma M, Feldmann G, Ottenhof NA, Hong SM, Pramanik D, Chenna V, Karikari C, Sharma R, Goggins MG, Rudek MA, Ravi R, Maitra A, Maitra A (2010) Systemic administration of polymeric nanoparticle-encapsulated curcumin (NanoCurc) blocks tumor growth and metastases in preclinical models of pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 9(8):2255–2264. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-0172
Li W, Sun L, Lei J, Wu Z, Ma Q, Wang Z (2020) Curcumin inhibits pancreatic cancer cell invasion and EMT by interfering with tumor-stromal crosstalk under hypoxic conditions via the IL-6/ERK/NF-κB axis. Oncol Rep 44(1):382–392. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2020.7600
Li W, Jiang Z, Xiao X, Wang Z, Wu Z, Ma Q, Cao L (2018) Curcumin inhibits superoxide dismutase-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB pathway in pancreatic cancer cells. Int J Oncol 52(5):1593–1602. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2018.4295
Zhao Z, Li C, Xi H, Gao Y, Xu D (2015) Curcumin induces apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells through the induction of forkhead box O1 and inhibition of the PI3K/Akt pathway. Mol Med Rep 12(4):5415–5422. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2015.4060
Sun XD, Liu XE, Huang DS (2013) Curcumin reverses the epithelial–mesenchymal transition of pancreatic cancer cells by inhibiting the Hedgehog signaling pathway. Oncol Rep 29(6):2401–2407. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2013.2385
Cao L, Xiao X, Lei J, Duan W, Ma Q, Li W (2016) Curcumin inhibits hypoxia-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer cells via suppression of the hedgehog signaling pathway. Oncol Rep 35(6):3728–3734. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2016.4709
Basha R, Connelly SF, Sankpal UT, Nagaraju GP, Patel H, Vishwanatha JK, Shelake S, Tabor-Simecka L, Shoji M, Simecka JW, El-Rayes B (2016) Small molecule tolfenamic acid and dietary spice curcumin treatment enhances antiproliferative effect in pancreatic cancer cells via suppressing Sp1, disrupting NF-kB translocation to nucleus and cell cycle phase distribution. J Nutr Biochem 31:77–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2016.01.003
Glienke W, Maute L, Wicht J, Bergmann L (2010) Curcumin inhibits constitutive STAT3 phosphorylation in human pancreatic cancer cell lines and downregulation of survivin/BIRC5 gene expression. Cancer Invest 28(2):166–71. https://doi.org/10.3109/07357900903287006
Sahu RP, Batra S, Srivastava SK (2009) Activation of ATM/Chk1 by curcumin causes cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human pancreatic cancer cells. Br J Cancer 100(9):1425–1433. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6605039
Díaz Osterman CJ, Gonda A, Stiff T, Sigaran U, Valenzuela MM, Ferguson Bennit HR, Moyron RB, Khan S, Wall NR (2016) Curcumin induces pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell death via reduction of the inhibitors of apoptosis. Pancreas 45(1):101–109. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPA.0000000000000411
Ma J, Fang B, Zeng F, Pang H, Zhang J, Shi Y, Wu X, Cheng L, Ma C, Xia J, Wang Z (2014) Curcumin inhibits cell growth and invasion through up-regulation of miR-7 in pancreatic cancer cells. Toxicol Lett 231(1):82–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2014.09.014
Sarkar S, Dubaybo H, Ali S, Goncalves P, Kollepara SL, Sethi S, Philip PA, Li Y (2013) Down-regulation of miR-221 inhibits proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells through up-regulation of PTEN, p27(kip1), p57(kip2), and PUMA. Am J Cancer Res 3(5):465–477
Bao B, Ali S, Banerjee S, Wang Z, Logna F, Azmi AS, Kong D, Ahmad A, Li Y, Padhye S, Sarkar FH (2012) Curcumin analogue CDF inhibits pancreatic tumor growth by switching on suppressor microRNAs and attenuating EZH2 expression. Cancer Res 72(1):335–345. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-2182
Giordano A, Tommonaro G (2019) Curcumin and Cancer. Nutrients 11(10):2376. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11102376
Hu C, Li M, Guo T, Wang S, Huang W, Yang K, Liao Z, Wang J, Zhang F, Wang H (2019) Anti-metastasis activity of curcumin against breast cancer via the inhibition of stem cell-like properties and EMT. Phytomedicine 58:152740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2018.11.001
Li M, Guo T, Lin J, Huang X, Ke Q, Wu Y, Fang C, Hu C (2022) Curcumin inhibits the invasion and metastasis of triple negative breast cancer via Hedgehog/Gli1 signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol 283:114689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2021.114689
Wang L, Wang C, Tao Z, Zhao L, Zhu Z, Wu W, He Y, Chen H, Zheng B, Huang X, Yu Y, Yang L, Liang G, Cui R, Chen T (2019) Curcumin derivative WZ35 inhibits tumor cell growth via ROS-YAP-JNK signaling pathway in breast cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 38(1):460. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-019-1424-4
Chen QY, Zheng Y, Jiao DM, Chen FY, Hu HZ, Wu YQ, Song J, Yan J, Wu LJ, Lv GY (2014) Curcumin inhibits lung cancer cell migration and invasion through Rac1-dependent signaling pathway. J Nutr Biochem 25(2):177–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2013.10.004
Lai YH, He RY, Chou JL, Chan MW, Li YF, Tai CK (2014) Promoter hypermethylation and silencing of tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Transl Med 12:237. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-014-0237-7
Wong CM, Ng YL, Lee JM, Wong CC, Cheung OF, Chan CY, Tung EK, Ching YP, Ng IO (2007) Tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 as a frequently silenced tumor suppressor gene in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 45(5):1129–1138. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.21578
Hepworth EMW, Hinton SD (2021) Pseudophosphatases as regulators of MAPK signaling. Int J Mol Sci 22(22):12595. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212595
Asl ER, Amini M, Najafi S, Mansoori B, Mokhtarzadeh A, Mohammadi A, Lotfinejad P, Bagheri M, Shirjang S, Lotfi Z, Rasmi Y, Baradaran B (2021) Interplay between MAPK/ERK signaling pathway and microRNAs: a crucial mechanism regulating cancer cell metabolism and tumor progression. Life Sci 278:119499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119499
Waters AM, Khatib TO, Papke B, Goodwin CM, Hobbs GA, Diehl JN, Yang R, Edwards AC, Walsh KH, Sulahian R, McFarland JM, Kapner KS, Gilbert TSK, Stalnecker CA, Javaid S, Barkovskaya A, Grover KR, Hibshman PS, Blake DR, Schaefer A, Nowak KM, Klomp JE, Hayes TK, Kassner M, Tang N, Tanaseichuk O, Chen K, Zhou Y, Kalkat M, Herring LE, Graves LM, Penn LZ, Yin HH, Aguirre AJ, Hahn WC, Cox AD, Der CJ (2021) Targeting p130Cas- and microtubule-dependent MYC regulation sensitizes pancreatic cancer to ERK MAPK inhibition. Cell Rep 35(13):109291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109291
Xu JC, Chen TY, Liao LT, Chen T, Li QL, Xu JX, Hu JW, Zhou PH, Zhang YQ (2021) NETO2 promotes esophageal cancer progression by inducing proliferation and metastasis via PI3K/AKT and ERK pathway. Int J Biol Sci 17(1):259–270. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.53795
Jiang T, Wu H, Lin M, Yin J, Tan L, Ruan Y, Feng M (2021) B4GALNT1 promotes progression and metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma through JNK/c-Jun/Slug pathway. Carcinogenesis 42(4):621–630. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgaa141
Liu M, Zhang Y, Yang J, Cui X, Zhou Z, Zhan H, Ding K, Tian X, Yang Z, Fung KA, Edil BH, Postier RG, Bronze MS, Fernandez-Zapico ME, Stemmler MP, Brabletz T, Li YP, Houchen CW, Li M (2020) ZIP4 increases expression of transcription factor ZEB1 to promote integrin α3β1 signaling and inhibit expression of the gemcitabine transporter ENT1 in pancreatic cancer cells. Gastroenterology 158(3):679-692.e1. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2019.10.038
Xing M, Yang Y, Huang J, Fang Y, Jin Y, Li L, Chen X, Zhu X, Ma C (2022) TFPI inhibits breast cancer progression by suppressing ERK/p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Genes Genomics 44(7):801–812. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-022-01258-5
Stavik B, Skretting G, Sletten M, Sandset PM, Iversen N (2010) Overexpression of both TFPIα and TFPIβ induces apoptosis and expression of genes involved in the death receptor pathway in breast cancer cells. Mol Carcinogen 49(11):951–963. https://doi.org/10.1002/mc.20679
Subbiah V, Baik C, Kirkwood JM (2020) Clinical development of BRAF plus MEK inhibitor combinations. Trends Cancer 6(9):797–810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trecan.2020.05.009
Del Bufalo D, Di Martile M, Valentini E, Manni I, Masi I, D’Amore A, Filippini A, Nicoletti C, Zaccarini M, Cota C, Castro MV, Quezada MJ, Rosanò L, Lopez-Bergami P, D’Aguanno S (2022) Bcl-2-like protein-10 increases aggressive features of melanoma cells. Explor Target Antitumor Ther 3(1):11–26. https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2022.00068
Tan X, Chen D, Guo S, Wang Y, Zou Y, Wu Z, Zhou F, Qin Z, Liu Z, Cao Y, Lin C, Yuan G, Yao K (2021) Molecular stratification by BCL2A1 and AIM2 provides additional prognostic value in penile squamous cell carcinoma. Theranostics 11(3):1364–1376. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.51725
Józefiak A, Larska M, Pomorska-Mól M, Ruszkowski JJ (2021) The IGF-1 signaling pathway in viral infections. Viruses 13(8):1488. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13081488
Xu Z, Maiti D, Kisiel W, Duh EJ (2006) Tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 is upregulated by vascular endothelial growth factor and suppresses growth factor-induced proliferation of endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 26(12):2819–2825. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.ATV.0000248731.55781.87
Huang L, Chen S, Fan H, Ji D, Chen C, Sheng W (2021) GINS2 promotes EMT in pancreatic cancer via specifically stimulating ERK/MAPK signaling. Cancer Gene Ther 28(7–8):839–849. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-020-0206-7
Zheng J, Shi Z, Yang P, Zhao Y, Tang W, Ye S, Xuan Z, Chen C, Shao C, Wu Q, Sun H (2022) ERK-Smurf1-RhoA signaling is critical for TGFβ-drived EMT and tumor metastasis. Life Sci Alliance 5(10):e202101330. https://doi.org/10.26508/lsa.202101330
Sun XY, Li HZ, Xie DF, Gao SS, Huang X, Guan H, Bai CJ, Zhou PK (2022) LPAR5 confers radio resistance to cancer cells associated with EMT activation via the ERK/Snail pathway. J Transl Med 20(1):456. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-022-03673-4
Tam SY, Wu VWC, Law HKW (2020) JNK pathway mediates low oxygen level induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition and stemness maintenance in colorectal cancer cells. Cancers (Basel) 12(1):224. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12010224
Pang B, Wu N, Guan R, Pang L, Li X, Li S, Tang L, Guo Y, Chen J, Sun D, Sun H, Dai J, Bai J, Ji G, Liu P, Liu A, Wang Q, Xiao S, Fu S, Jin Y (2017) Overexpression of RCC2 enhances cell motility and promotes tumor metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma by inducing epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Clin Cancer Res 23(18):5598–5610. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-2909
Wang JF, Zhao K, Chen YY, Qiu Y, Zhu JH, Li BP, Wang Z, Chen JQ (2021) NKCC1 promotes proliferation, invasion and migration in human gastric cancer cells via activation of the MAPK-JNK/EMT signaling pathway. J Cancer 12(1):253–263. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.49709
Funding
This work was supported by the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. LGF19H290004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LLZ, TFJ, and DLY contributed to conception and design of the study. LLZ, WBL, LJC, and WW performed the experimental work. LLZ, WBL, LJC, and TFJ performed the statistical analysis. LLZ, WBL, LJC, WW, and TFJ wrote the draft of the manuscript. All authors contributed to manuscript revision, read, and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
Not applicable.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhai, LL., Li, WB., Chen, LJ. et al. Curcumin inhibits the invasion and migration of pancreatic cancer cells by upregulating TFPI-2 to regulate ERK- and JNK-mediated epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Eur J Nutr 63, 639–651 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-023-03296-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-023-03296-5