Abstract
Purpose
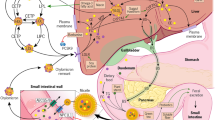
Phytosterols reduce intestinal cholesterol absorption and help to lower LDL-cholesterol. Many Chinese adults are lactose-intolerant and cannot tolerate bovine milk enriched with phytosterol. Soya-milk is a common beverage in Asia and it has beneficial effects on general health. We therefore conducted a randomized double-blind controlled trial to assess the effectiveness of a phytosterols-enriched soya drink in lowering serum LDL-cholesterol level (primary outcome) and other cardiovascular parameters (secondary outcomes).
Methods
One hundred and fifty-nine normocholesterolaemic participants (85 men and 74 women; aged 19–79) were randomized to daily intake of one serving of phytosterols-enriched soya drink (N = 82), equivalent to 2 g of phytosterol per day, or a matched soya drink without phytosterols (N = 77) for 3 weeks. Adverse events, withdrawal and compliance were documented.
Results
Among the treatment group (N = 82), phytosterols-enriched soya drink significantly decreased LDL-cholesterol by 5.96% (SE 1.48, 95% CI − 8.91%, − 3.00%) with a median of 6.74% compared with baseline, resulting in a significant reduction of 4.70% (95% CI − 8.89%, − 0.51%; p = 0.028) with a median of 5.20% compared with placebo (N = 77). In contrast, there were no significant changes in other lipid parameters, blood glucose, blood pressure, body weight or waist circumference. Remarkably, 95% of the participants randomized to the fortified drink reported no adverse events at all.
Conclusions
Daily consumption of a phytosterols-enriched soya drink may be a simple and cost-neutral means of lowering LDL-cholesterol in individuals in China, with massive population and rising incidence of coronary heart disease (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT02881658; date of registration: 14 Aug 2016).

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yusuf S, Hawken S, Ounpuu S, Dans T, Avezum A, Lanas F, McQueen M, Budaj A, Pais P, Varigos J, Lisheng L (2004) Effect of potentially modifiable risk factors associated with myocardial infarction in 52 countries (the INTERHEART study): case–control study. Lancet 364(9438):937–952. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(04)17018-9
Cholesterol Treatment Trialists Collaborators (2012) The effects of lowering LDL cholesterol with statin therapy in people at low risk of vascular disease: meta-analysis of individual data from 27 randomised trials. Lancet 380(9841):581–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60367-5
Davies JT, Delfino SF, Feinberg CE, Johnson MF, Nappi VL, Olinger JT, Schwab AP, Swanson HI (2016) Current and emerging uses of statins in clinical therapeutics: a review. Lipid Insights 9:13–29. https://doi.org/10.4137/LPI.S37450
Jones PJH, Shamloo M, MacKay DS, Rideout TC, Myrie SB, Plat J, Roullet JB, Baer DJ, Calkins KL, Davis HR, Barton Duell P, Ginsberg H, Gylling H, Jenkins D, Lutjohann D, Moghadasian M, Moreau RA, Mymin D, Ostlund RE Jr, Ras RT, Ochoa Reparaz J, Trautwein EA, Turley S, Vanmierlo T, Weingartner O (2018) Progress and perspectives in plant sterol and plant stanol research. Nutr Rev 76(10):725–746. https://doi.org/10.1093/nutrit/nuy032
Jew S, Antoine J, Bourlioux P, Milner J, Tapsell LC, Yang Y, Jones PJH (2015) Nutrient essentiality revisited. J Funct Foods 14:203–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2015.01.024
United States FDA (2018) Health claims: plant sterol/stanol esters and risk of coronary heart disease (CHD), 21 C.F.R. §101.83. https://www.ecfr.gov/cgi-bin/ECFR?SID=9597fbb69b17673c3588a74ae48fd0e2. Accessed 13 July 2018
Clifton PM, Noakes M, Sullivan D, Erichsen N, Ross D, Annison G, Fassoulakis A, Cehun M, Nestel P (2004) Cholesterol-lowering effects of plant sterol esters differ in milk, yoghurt, bread and cereal. Eur J Clin Nutr 58(3):503–509. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601837
Rideout TC, Chan YM, Harding SV, Jones PJ (2009) Low and moderate-fat plant sterol fortified soymilk in modulation of plasma lipids and cholesterol kinetics in subjects with normal to high cholesterol concentrations: report on two randomized crossover studies. Lipids Health Dis 8:45. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-511X-8-45
Abumweis SS, Barake R, Jones PJ (2008) Plant sterols/stanols as cholesterol lowering agents: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Food Nutr Res. https://doi.org/10.3402/fnr.v52i0.1811
Cheung CL, Ho DK, Sing CW, Tsoi MF, Cheng VK, Lee GK, Ho YN, Cheung BM (2017) Randomized controlled trial of the effect of phytosterols-enriched low-fat milk on lipid profile in Chinese. Sci Rep 7:41084. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep41084
Solomons NW (2002) Fermentation, fermented foods and lactose intolerance. Eur J Clin Nutr 56(Suppl 4):S50–S55. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601663
Rizzo G, Baroni L (2018) Soy, soy foods and their role in vegetarian diets. Nutrients. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10010043
Taku K, Melby MK, Kronenberg F, Kurzer MS, Messina M (2012) Extracted or synthesized soybean isoflavones reduce menopausal hot flash frequency and severity: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Menopause 19(7):776–790. https://doi.org/10.1097/gme.0b013e3182410159
Clarkson TB (2002) Soy, soy phytoestrogens and cardiovascular disease. J Nutr 132(3):566S–569S. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/132.3.566S
ICH (2016) Integrated addendum to ICH E6(R1): guideline for good clinical practice E6(E2). https://www.ich.org/products/guidelines/efficacy/efficacy-single/article/integrated-addendum-good-clinical-practice.html. Accessed 01 May 2019
Amending Regulations (EC) No 983/2009 and (EU) No 384/2010 as regards the conditions of use of certain health claims related to the lowering effect of plant sterols and plant stanols on blood LDL-cholesterol Text with EEA relevance (2014). https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2014/686/oj. Accessed 01 May 2019
Thomsen AB, Hansen HB, Christiansen C, Green H, Berger A (2004) Effect of free plant sterols in low-fat milk on serum lipid profile in hypercholesterolemic subjects. Eur J Clin Nutr 58(6):860–870. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601887
Ras RT, Geleijnse JM, Trautwein EA (2014) LDL-cholesterol-lowering effect of plant sterols and stanols across different dose ranges: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled studies. Br J Nutr 112(2):214–219. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114514000750
Ramdath DD, Padhi EM, Sarfaraz S, Renwick S, Duncan AM (2017) Beyond the cholesterol-lowering effect of soy protein: a review of the effects of dietary soy and its constituents on risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Nutrients. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9040324
Taku K, Umegaki K, Sato Y, Taki Y, Endoh K, Watanabe S (2007) Soy isoflavones lower serum total and LDL cholesterol in humans: a meta-analysis of 11 randomized controlled trials. Am J Clin Nutr 85(4):1148–1156. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/85.4.1148
Messina M (2016) Soy and health update: evaluation of the clinical and epidemiologic literature. Nutrients. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8120754
Mandal CC (2015) High cholesterol deteriorates bone health: new insights into molecular mechanisms. Front Endocrinol 6:165. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2015.00165
Murai T (2015) Cholesterol lowering: role in cancer prevention and treatment. Biol Chem 396(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1515/hsz-2014-0194
Sattar N, Preiss D, Murray HM, Welsh P, Buckley BM, de Craen AJ, Seshasai SR, McMurray JJ, Freeman DJ, Jukema JW, Macfarlane PW, Packard CJ, Stott DJ, Westendorp RG, Shepherd J, Davis BR, Pressel SL, Marchioli R, Marfisi RM, Maggioni AP, Tavazzi L, Tognoni G, Kjekshus J, Pedersen TR, Cook TJ, Gotto AM, Clearfield MB, Downs JR, Nakamura H, Ohashi Y, Mizuno K, Ray KK, Ford I (2010) Statins and risk of incident diabetes: a collaborative meta-analysis of randomised statin trials. Lancet 375(9716):735–742. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61965-6
Sabatine MS, Giugliano RP, Keech AC, Honarpour N, Wiviott SD, Murphy SA, Kuder JF, Wang H, Liu T, Wasserman SM, Sever PS, Pedersen TR (2017) Evolocumab and clinical outcomes in patients with cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med 376(18):1713–1722. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1615664
Fonarow GC, Keech AC, Pedersen TR, Giugliano RP, Sever PS, Lindgren P, van Hout B, Villa G, Qian Y, Somaratne R, Sabatine MS (2017) Cost-effectiveness of evolocumab therapy for reducing cardiovascular events in patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. JAMA Cardiol 2(10):1069–1078. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamacardio.2017.2762
QuIlez J, GarcIa-Lorda P, Salas-Salvado J (2003) Potential uses and benefits of phytosterols in diet: present situation and future directions. Clin Nutr 22(4):343–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0261-5614(03)00060-8
Han S, Jiao J, Xu J, Zimmermann D, Actis-Goretta L, Guan L, Zhao Y, Qin L (2016) Effects of plant stanol or sterol-enriched diets on lipid profiles in patients treated with statins: systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep 6:31337. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep31337
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BMYC and CLC designed the study, interpreted the data and wrote the first draft. YPC, YCC, CWS, MFT, VKFC, GKYL were involved in subject enrollment, subject interview and performing physical assessments, BMYC and CLC supervised the whole RCT. All authors have read and approved the final version of the manuscript and its conclusions. The corresponding authors had full access to the data and had final responsibility for the decision to submit for publication.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Yes, there is potential competing interest. All authors declare: grants from The University of Hong Kong, sponsorship from Vitasoy International Holdings Ltd. for the study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chau, YP., Cheng, YC., Sing, CW. et al. The lipid-lowering effect of once-daily soya drink fortified with phytosterols in normocholesterolaemic Chinese: a double-blind randomized controlled trial. Eur J Nutr 59, 2739–2746 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-019-02119-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-019-02119-w