Abstract
Purpose
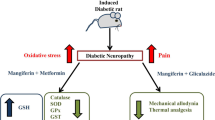
Neuropathic pain is a common diabetic complication. It is characterized by symptoms of spontaneous and stimulus-evoked pain including hyperalgesia and allodynia. l-Arginine is a common precursor of many metabolites of biological interest, in particular, nitric oxide (NO), ornithine, and hence polyamines. In central nervous system, NO, glutamate, and polyamines share an N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor-mediated effect. We hypothesized that a variation in arginine metabolism caused by diabetes may contribute to development and maintenance of neuropathic pain and to the worsening of clinical and biological signs of diabetes.
Methods
We examined whether oral l-arginine supplementation (2.58 ± 0.13 g/l in drinking water for 3 weeks) could improve the development of neuropathic pain and the clinical, biological, and metabolic complications of diabetes in streptozocin (STZ)-induced diabetic (D) rats.
Results
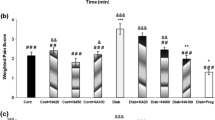
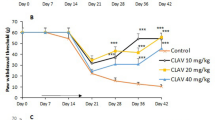
STZ administration induced classical symptoms of type 1 diabetes. Diabetic rats also displayed mechanical hypersensitivity, tactile, and thermal allodynia. Plasma citrulline and NO levels were increased in diabetic hyperalgesic/allodynic rats. l-Arginine supplementation failed to reduce hyperglycaemia, polyphagia, and weight loss. Moreover, it abolished hyperalgesia and allodynia by normalizing NO plasma concentration and increasing plasma agmatine concentration.
Conclusions
l-Arginine supplementation prevented the development of mechanical hyperalgesia, tactile, and thermal allodynia in painful diabetic neuropathy with concomitant reduction of NO and increased agmatine production, offering new therapeutic opportunities for the management of diabetic neuropathic pain.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tavakoli M, Mojaddidi M, Fadavi H, Malik RA (2008) Pathophysiology and treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy. Curr Pain Headache Rep 12:192–197
Said G (2007) Diabetic neuropathy—a review. Nat Clin Pract Neurol 3:331–340. doi:10.1038/ncpneuro0504
Wu EQ, Borton J, Said G, Le TK, Monz B, Rosilio M, Avoinet S (2007) Estimated prevalence of peripheral neuropathy and associated pain in adults with diabetes in France. Curr Med Res Opin 23:2035–2042. doi:10.1185/030079907X210516
Halawa MR, Karawagh A, Zeidan A, Mahmoud AE, Sakr M, Hegazy A (2010) Prevalence of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy among patients suffering from diabetes mellitus in Saudi Arabia. Curr Med Res Opin 26:337–343. doi:10.1185/03007990903471940
Sadosky A, McDermott AM, Brandenburg NA, Strauss M (2008) A review of the epidemiology of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and less commonly studied neuropathic pain conditions. Pain Pract 8:45–56. doi:10.1111/j.1533-2500.2007.00164.x
Attal N, Bouhassira D (2015) Pharmacotherapy of neuropathic pain: which drugs, which treatment algorithms? Pain 156(Suppl 1):S104–S114. doi:10.1097/01.j.pain.0000460358.01998.15
Finnerup NB, Attal N, Haroutounian S, McNicol E, Baron R, Dworkin RH, Gilron I, Haanpaa M, Hansson P, Jensen TS, Kamerman PR, Lund K, Moore A, Raja SN, Rice AS, Rowbotham M, Sena E, Siddall P, Smith BH, Wallace M (2015) Pharmacotherapy for neuropathic pain in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol 14:162–173. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(14)70251-0
Finnerup NB, Sindrup SH, Jensen TS (2010) Recent advances in pharmacological treatment of neuropathic pain. F1000 Med Rep 2:52. doi:10.3410/M2-52
Sang CN, Bennett GJ (2009) Novel therapies for the control and prevention of neuropathic pain. Neurotherapeutics 6:607–608. doi:10.1016/j.nurt.2009.08.004
Pieper GM, Siebeneich W (1997) Diabetes-induced endothelial dysfunction is prevented by long-term treatment with the modified iron chelator, hydroxyethyl starch conjugated-deferoxamine. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 30:734–738
Wu G, Morris SM (2004) Arginine metabolism in mammals. In: Cynober LA (ed) Metabolic and therapeutic aspects of amino acids in clinical nutrition. CRC Press, Boa Raton, pp 153–167
Raghavan SA, Dikshit M (2004) Vascular regulation by the l-arginine metabolites, nitric oxide and agmatine. Pharmacol Res 49:397–414. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2003.10.008
Reyes AA, Karl IE, Klahr S (1994) Role of arginine in health and in renal disease. Am J Physiol 267:F331–F346
Wu G, Morris SM Jr (1998) Arginine metabolism: nitric oxide and beyond. Biochem J 336(Pt 1):1–17
Flynn NE, Meininger CJ, Haynes TE, Wu G (2002) The metabolic basis of arginine nutrition and pharmacotherapy. Biomed Pharmacother 56:427–438
Blantz RC, Satriano J, Gabbai F, Kelly C (2000) Biological effects of arginine metabolites. Acta Physiol Scand 168:21–25
Luiking YC, Engelen MP, Deutz NE (2010) Regulation of nitric oxide production in health and disease. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 13:97–104. doi:10.1097/MCO.0b013e328332f99d
Bennett GJ (2000) Update on the neurophysiology of pain transmission and modulation: focus on the NMDA-receptor. J Pain Symptom Manag 19:S2–S6
Malcangio M, Tomlinson DR (1998) A pharmacologic analysis of mechanical hyperalgesia in streptozotocin/diabetic rats. Pain 76:151–157
Daulhac L, Maffre V, Mallet C, Etienne M, Privat AM, Kowalski-Chauvel A, Seva C, Fialip J, Eschalier A (2011) Phosphorylation of spinal N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor NR1 subunits by extracellular signal-regulated kinase in dorsal horn neurons and microglia contributes to diabetes-induced painful neuropathy. Eur J Pain 15:169 e112–169 e161. doi:10.1016/j.ejpain.2010.06.003
Rondon LJ, Privat AM, Daulhac L, Davin N, Mazur A, Fialip J, Eschalier A, Courteix C (2010) Magnesium attenuates chronic hypersensitivity and spinal cord NMDA receptor phosphorylation in a rat model of diabetic neuropathic pain. J Physiol 588:4205–4215. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2010.197004
Courteix C, Privat AM, Pelissier T, Hernandez A, Eschalier A, Fialip J (2007) Agmatine induces antihyperalgesic effects in diabetic rats and a superadditive interaction with R(−)-3-(2-carboxypiperazine-4-yl)-propyl-1-phosphonic acid, a N-methyl-d-aspartate-receptor antagonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 322:1237–1245. doi:10.1124/jpet.107.123018
Zimmermann M (1983) Ethical guidelines for investigations of experimental pain in conscious animals. Pain 16:109–110
Skogerboe KJ, Labbe RF, Rettmer RL, Sundquist JP, Gargett AM (1990) Chemiluminescent measurement of total urinary nitrogen for accurate calculation of nitrogen balance. Clin Chem 36:752–755
Green LC, Wagner DA, Glogowski J, Skipper PL, Wishnok JS, Tannenbaum SR (1982) Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N]nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem 126:131–138
Schmidt HH, Warner TD, Ishii K, Sheng H, Murad F (1992) Insulin secretion from pancreatic B cells caused by l-arginine-derived nitrogen oxides. Science (New York, NY) 255:721–723
Fekkes D (1996) State-of-the-art of high-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of amino acids in physiological samples. J Chromatogr B Biomed Appl 682:3–22
Farges MC, Berard MP, Raul F, Cezard JP, Joly B, Davot P, Vasson MP, Cynober L (1999) Oral administration of a glutamine-enriched diet before or after endotoxin challenge in aged rats has limited effects. J Nutr 129:1799–1806
Randall LO, Selitto JJ (1957) A method for measurement of analgesic activity on inflamed tissue. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 111:409–419
Courteix C, Eschalier A, Lavarenne J (1993) Streptozocin-induced diabetic rats: behavioural evidence for a model of chronic pain. Pain 53:81–88
El-Lithy GM, El-Bakly WM, Matboli M, Abd-Alkhalek HA, Masoud SI, Hamza M (2016) Prophylactic l-arginine and ibuprofen delay the development of tactile allodynia and suppress spinal miR-155 in a rat model of diabetic neuropathy. Transl Res J Lab Clin Med 177(85–97):e81. doi:10.1016/j.trsl.2016.06.005
Piatti PM, Monti LD, Valsecchi G, Magni F, Setola E, Marchesi F, Galli-Kienle M, Pozza G, Alberti KG (2001) Long-term oral l-arginine administration improves peripheral and hepatic insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 24:875–880
Hans CP, Chaudhary DP, Bansal DD (2003) Effect of magnesium supplementation on oxidative stress in alloxanic diabetic rats. Magnes Res 16:13–19
Ward DT, Yau SK, Mee AP, Mawer EB, Miller CA, Garland HO, Riccardi D (2001) Functional, molecular, and biochemical characterization of streptozotocin-induced diabetes. J Am Soc Nephrol 12:779–790
Squadrito F, Calapai G, Cucinotta D, Altavilla D, Zingarelli B, Ioculano M, Urna G, Sardella A, Campo GM, Caputi AP (1993) Anorectic activity of NG-nitro-l-arginine, an inhibitor of brain nitric oxide synthase, in obese Zucker rats. Eur J Pharmacol 230:125–128
Rodriguez T, Alvarez B, Busquets S, Carbo N, Lopez-Soriano FJ, Argiles JM (1997) The increased skeletal muscle protein turnover of the streptozotocin diabetic rat is associated with high concentrations of branched-chain amino acids. Biochem Mol Med 61:87–94
Lariviere F, Kupranycz DB, Chiasson JL, Hoffer LJ (1992) Plasma leucine kinetics and urinary nitrogen excretion in intensively treated diabetes mellitus. Am J Physiol 263:E173–E179
Bruins MJ, Soeters PB, Lamers WH, Deutz NE (2002) l-Arginine supplementation in pigs decreases liver protein turnover and increases hindquarter protein turnover both during and after endotoxemia. Am J Clin Nutr 75:1031–1044
Brosnan JT, Man KC, Hall DE, Colbourne SA, Brosnan ME (1983) Interorgan metabolism of amino acids in streptozotocin-diabetic ketoacidotic rat. Am J Physiol 244:E151–E158
Kohli R, Meininger CJ, Haynes TE, Yan W, Self JT, Wu G (2004) Dietary l-arginine supplementation enhances endothelial nitric oxide synthesis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Nutr 134:600–608
Grill V, Bjorkman O, Gutniak M, Lindqvist M (1992) Brain uptake and release of amino acids in nondiabetic and insulin-dependent diabetic subjects: important role of glutamine release for nitrogen balance. Metabolism 41:28–32
Jabecka A, Ast J, Bogdaski P, Drozdowski M, Pawlak-Lemaska K, Cielewicz AR, Pupek-Musialik D (2012) Oral l-arginine supplementation in patients with mild arterial hypertension and its effect on plasma level of asymmetric dimethylarginine, l-citruline, l-arginine and antioxidant status. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 16:1665–1674
Chien WY, Yang KD, Eng HL, Hu YH, Lee PY, Wang ST, Wang PW (2005) Increased plasma concentration of nitric oxide in type 2 diabetes but not in nondiabetic individuals with insulin resistance. Diabetes Metab 31:63–68
Ghosh A, Sherpa ML, Bhutia Y, Pal R, Dahal S (2011) Serum nitric oxide status in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Sikkim. Int J App Basic Med Res 1:31–35
Vural P, Cevik A, Curgunlu A, Canbaz M (2002) Effects of diabetes mellitus and acute hypertension on plasma nitric oxide and endothelin concentrations in rats. Clin Chim Acta 320:43–47
Boger RH, Bode-Boger SM (2001) The clinical pharmacology of l-arginine. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 41:79–99. doi:10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.41.1.79
Tangphao O, Chalon S, Moreno H Jr, Hoffman BB, Blaschke TF (1999) Pharmacokinetics of l-arginine during chronic administration to patients with hypercholesterolaemia. Clin Sci (Lond) 96:199–207
Wu G, Bazer FW, Davis TA, Kim SW, Li P, Marc Rhoads J, Carey Satterfield M, Smith SB, Spencer TE, Yin Y (2009) Arginine metabolism and nutrition in growth, health and disease. Amino Acids 37:153–168. doi:10.1007/s00726-008-0210-y
Piletz JE, Aricioglu F, Cheng JT, Fairbanks CA, Gilad VH, Haenisch B, Halaris A, Hong S, Lee JE, Li J, Liu P, Molderings GJ, Rodrigues AL, Satriano J, Seong GJ, Wilcox G, Wu N, Gilad GM (2013) Agmatine: clinical applications after 100 years in translation. Drug Discov Today. doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2013.05.017
Raasch W, Regunathan S, Li G, Reis DJ (1995) Agmatine, the bacterial amine, is widely distributed in mammalian tissues. Life Sci 56:2319–2330
Todorovic SM (2016) Painful diabetic neuropathy: prevention or suppression? Int Rev Neurobiol 127:211–225. doi:10.1016/bs.irn.2016.03.005
Behse F, Buchthal F, Carlsen F (1977) Nerve biopsy and conduction studies in diabetic neuropathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 40:1072–1082
Bischoff A (1980) Morphology of diabetic neuropathy. Horm Metab Res Suppl 9:18–28
Said G (1983) Etiology of peripheral neuropathies. Presse Med 12:669–671
Sun W, Miao B, Wang XC, Duan JH, Wang WT, Kuang F, Xie RG, Xing JL, Xu H, Song XJ, Luo C, Hu SJ (2012) Reduced conduction failure of the main axon of polymodal nociceptive C-fibres contributes to painful diabetic neuropathy in rats. Brain J Neurol 135:359–375. doi:10.1093/brain/awr345
Malmberg AB, Yaksh TL (1993) Spinal nitric oxide synthesis inhibition blocks NMDA-induced thermal hyperalgesia and produces antinociception in the formalin test in rats. Pain 54:291–300
Meller ST, Cummings CP, Traub RJ, Gebhart GF (1994) The role of nitric oxide in the development and maintenance of the hyperalgesia produced by intraplantar injection of carrageenan in the rat. Neuroscience 60:367–374
Fairbanks CA, Schreiber KL, Brewer KL, Yu CG, Stone LS, Kitto KF, Nguyen HO, Grocholski BM, Shoeman DW, Kehl LJ, Regunathan S, Reis DJ, Yezierski RP, Wilcox GL (2000) Agmatine reverses pain induced by inflammation, neuropathy, and spinal cord injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:10584–10589
Horvath G, Kekesi G, Dobos I, Szikszay M, Klimscha W, Benedek G (1999) Effect of intrathecal agmatine on inflammation-induced thermal hyperalgesia in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 368:197–204
Harima A, Shimizu H, Takagi H (1991) Analgesic effect of l-arginine in patients with persistent pain. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 1:529–533
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Eric Chapuy for his technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rondón, L.J., Farges, M.C., Davin, N. et al. l-Arginine supplementation prevents allodynia and hyperalgesia in painful diabetic neuropathic rats by normalizing plasma nitric oxide concentration and increasing plasma agmatine concentration. Eur J Nutr 57, 2353–2363 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-017-1508-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-017-1508-x