Abstract
Purpose
The only effective and safe treatment of celiac disease (CD) continues being strict exclusion of gluten for life, the so-called gluten-free diet (GFD). Although this treatment is highly successful, following strict GFD poses difficulties to patients in family, social and working contexts, deteriorating his/her quality of life. We aimed to review main characteristics of GFD with special emphasis on factors that may interfere with adherence to it.
Methods
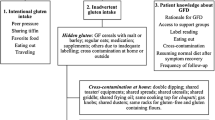
We conducted a search of various databases, such as PubMed, Google Scholar, Embase, and Scielo, with focus on key words such as “gluten-free diet”, “celiac disease”, “gluten” and “gluten-free diet adherence”. Available literature has not reached definitive conclusions on the exact amount of gluten that is harmless to celiac patients, although international agreements establish cutoff points for gluten-free products and advise the use of clinical assessment to tailor the diet according to individual needs. Following GFD must include eliminating gluten as ingredient as well as hidden component and potential cross contamination in foods. There are numerous grains to substitute wheat but composition of most gluten-free products tends to include only a small number of them, especially rice. The diet must be not only free of gluten but also healthy to avoid nutrient, vitamins and minerals deficiencies or excess. Overweight/obesity frequency has increased among celiac patients so weight gain deserves attention during follow up. Nutritional education by a trained nutritionist is of great relevance to achieve long-term satisfactory health status and good compliance.
Conclusions
A balanced GFD should be based on a combination of naturally gluten-free foods and certified processed gluten-free products. How to measure and improve adherence to GFD is still controversial and deserves further study.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Green PH, Lebwohl B, Greywoode R (2015) Celiac disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol 135(5):1099–1106. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2015.01.044
Schuppan D, Zimmer KP (2013) The diagnosis and treatment of celiac disease. Dtsch Arztebl Int 110(49):835–846. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2013.0835
Accomando S, Cataldo F (2004) The global village of celiac disease. Dig Liver Dis 36(7):492–498. doi:10.1016/j.dld.2004.01.026
Leffler DA, Schuppan D (2010) Update on serologic testing in celiac disease. Am J Gastroenterol 105(12):2520–2524. doi:10.1038/ajg.2010.276
Catassi C, Ratsch IM, Gandolfi L, Pratesi R, Fabiani E, El Asmar R, Frijia M, Bearzi I, Vizzoni L (1999) Why is coeliac disease endemic in the people of the Sahara? Lancet 354(9179):647–648
Ciacci C, Cirillo M, Cavallaro R, Mazzacca G (2002) Long-term follow-up of celiac adults on gluten-free diet: prevalence and correlates of intestinal damage. Digestion 66(3):178–185. doi:10.1159/000066757
Ludvigsson JF, Montgomery SM, Ekbom A, Brandt L, Granath F (2009) Small-intestinal histopathology and mortality risk in celiac disease. JAMA 302(11):1171–1178. doi:10.1001/jama.2009.1320
Lee A, Newman JM (2003) Celiac diet: its impact on quality of life. J Am Diet Assoc 103(11):1533–1535. doi:10.1016/S0002-8223(03)01233-1
Parnell ND, Ciclitira PJ (1999) Review article: coeliac disease and its management. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 13(1):1–13
Hallert C, Grant C, Grehn S, Granno C, Hulten S, Midhagen G, Strom M, Svensson H, Valdimarsson T (2002) Evidence of poor vitamin status in coeliac patients on a gluten-free diet for 10 years. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 16(7):1333–1339
Kupper C (2005) Dietary guidelines and implementation for celiac disease. Gastroenterology 128(4 Suppl 1):S121–S127
Thompson T, Dennis M, Higgins LA, Lee AR, Sharrett MK (2005) Gluten-free diet survey: are Americans with coeliac disease consuming recommended amounts of fibre, iron, calcium and grain foods? J Hum Nutr Diet 18(3):163–169. doi:10.1111/j.1365-277X.2005.00607.x
Saturni L, Ferretti G, Bacchetti T (2010) The gluten-free diet: safety and nutritional quality. Nutrients 2(1):16–34. doi:10.3390/nu20100016
La Vieille S, Dubois S, Hayward S, Koerner TB (2014) Estimated levels of gluten incidentally present in a Canadian gluten-free diet. Nutrients 6(2):881–896. doi:10.3390/nu6020881
Catassi C, Bai JC, Bonaz B, Bouma G, Calabro A, Carroccio A, Castillejo G, Ciacci C, Cristofori F, Dolinsek J, Francavilla R, Elli L, Green P, Holtmeier W, Koehler P, Koletzko S, Meinhold C, Sanders D, Schumann M, Schuppan D, Ullrich R, Vecsei A, Volta U, Zevallos V, Sapone A, Fasano A (2013) Non-celiac gluten sensitivity: the new frontier of gluten related disorders. Nutrients 5(10):3839–3853. doi:10.3390/nu5103839
Ludvigsson JF, Leffler DA, Bai JC, Biagi F, Fasano A, Green PH, Hadjivassiliou M, Kaukinen K, Kelly CP, Leonard JN, Lundin KE, Murray JA, Sanders DS, Walker MM, Zingone F, Ciacci C (2013) The Oslo definitions for coeliac disease and related terms. Gut 62(1):43–52. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2011-301346
Fasano A, Sapone A, Zevallos V, Schuppan D (2015) Nonceliac gluten sensitivity. Gastroenterology 148(6):1195–1204. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2014.12.049
Ontiveros N, Lopez-Gallardo JA, Vergara-Jimenez MJ, Cabrera-Chavez F (2015) Self-reported prevalence of symptomatic adverse reactions to gluten and adherence to gluten-free diet in an Adult Mexican Population. Nutrients 7(7):6000–6015. doi:10.3390/nu7075267
Volta U, Bardella MT, Calabro A, Troncone R, Corazza GR, Study Group for Non-Celiac Gluten S (2014) An Italian prospective multicenter survey on patients suspected of having non-celiac gluten sensitivity. BMC Med 12:85. doi:10.1186/1741-7015-12-85
Sapone A, Bai JC, Ciacci C, Dolinsek J, Green PH, Hadjivassiliou M, Kaukinen K, Rostami K, Sanders DS, Schumann M, Ullrich R, Villalta D, Volta U, Catassi C, Fasano A (2012) Spectrum of gluten-related disorders: consensus on new nomenclature and classification. BMC Med 10:13. doi:10.1186/1741-7015-10-13
Lebwohl B, Ludvigsson JF, Green PH (2015) Celiac disease and non-celiac gluten sensitivity. BMJ 351:h4347. doi:10.1136/bmj.h4347
Inomata N (2009) Wheat allergy. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol 9(3):238–243. doi:10.1097/ACI.0b013e32832aa5bc
Jones SM, Magnolfi CF, Cooke SK, Sampson HA (1995) Immunologic cross-reactivity among cereal grains and grasses in children with food hypersensitivity. J Allergy Clin Immunol 96(3):341–351
Matricardi PM, Bockelbrink A, Beyer K, Keil T, Niggemann B, Gruber C, Wahn U, Lau S (2008) Primary versus secondary immunoglobulin E sensitization to soy and wheat in the Multi-Centre Allergy Study cohort. Clin Exp Allergy J Br Soc Allergy Clin Immunol 38(3):493–500. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2222.2007.02912.x
Tatham AS, Shewry PR (2008) Allergens to wheat and related cereals. Clin Exp Allergy J Br Soc Allergy Clin Immunol 38(11):1712–1726. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2222.2008.03101.x
Halmos EP, Power VA, Shepherd SJ, Gibson PR, Muir JG (2014) A diet low in FODMAPs reduces symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 146(1):67–75 e65. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2013.09.046
Lis DM, Stellingwerff T, Shing CM, Ahuja KD, Fell JW (2015) Exploring the popularity, experiences, and beliefs surrounding gluten-free diets in nonceliac athletes. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 25(1):37–45. doi:10.1123/ijsnem.2013-0247
Markets and Markets (2015) Gluten-free products market by type, sales channel and geography: global trends and forecasts to 2018. http://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/gluten-free-products-market-738.html. Accessed Jan 2016
Greco L (1997) From the neolithic revolution to gluten intolerance: benefits and problems associated with the cultivation of wheat. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 24(5):S14–S16 (discussion S16-17)
van den Broeck HC, van Herpen TW, Schuit C, Salentijn EM, Dekking L, Bosch D, Hamer RJ, Smulders MJ, Gilissen LJ, van der Meer IM (2009) Removing celiac disease-related gluten proteins from bread wheat while retaining technological properties: a study with Chinese Spring deletion lines. BMC Plant Biol 9:41. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-9-41
Ang S, Kogulanathan J, Morris GA, Kok MS, Shewry PR, Tatham AS, Adams GG, Rowe AJ, Harding SE (2010) Structure and heterogeneity of gliadin: a hydrodynamic evaluation. Eur Biophys J 39(2):255–261. doi:10.1007/s00249-009-0529-7
Frisoni M, Corazza GR, Lafiandra D, De Ambrogio E, Filipponi C, Bonvicini F, Borasio E, Porceddu E, Gasbarrini G (1995) Wheat deficient in gliadins: promising tool for treatment of coeliac disease. Gut 36(3):375–378
Spaenij-Dekking L, Kooy-Winkelaar Y, van Veelen P, Drijfhout JW, Jonker H, van Soest L, Smulders MJ, Bosch D, Gilissen LJ, Koning F (2005) Natural variation in toxicity of wheat: potential for selection of nontoxic varieties for celiac disease patients. Gastroenterology 129(3):797–806. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2005.06.017
Carroccio A, Di Prima L, Noto D, Fayer F, Ambrosiano G, Villanacci V, Lammers K, Lafiandra D, De Ambrogio E, Di Fede G, Iacono G, Pogna N (2011) Searching for wheat plants with low toxicity in celiac disease: between direct toxicity and immunologic activation. Dig Liver Dis 43(1):34–39. doi:10.1016/j.dld.2010.05.005
Parada A, Araya M (2010) History of gluten and its effects on celiac disease. Rev Med Chil 138(10):1319–1325. doi:10.4067/S0034-98872010001100018
Mitea C, Salentijn EM, van Veelen P, Goryunova SV, van der Meer IM, van den Broeck HC, Mujico JR, Montserrat V, Gilissen LJ, Drijfhout JW, Dekking L, Koning F, Smulders MJ (2010) A universal approach to eliminate antigenic properties of alpha-gliadin peptides in celiac disease. PLoS One 5(12):e15637. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0015637
Auricchio S, De Ritis G, De Vincenzi M, Occorsio P, Silano V (1982) Effects of gliadin-derived peptides from bread and durum wheats on small intestine cultures from rat fetus and coeliac children. Pediatr Res 16(12):1004–1010
Kagnoff MF (2007) Celiac disease: pathogenesis of a model immunogenetic disease. J Clin Invest 117(1):41–49. doi:10.1172/JCI30253
Rescigno M, Urbano M, Valzasina B, Francolini M, Rotta G, Bonasio R, Granucci F, Kraehenbuhl JP, Ricciardi-Castagnoli P (2001) Dendritic cells express tight junction proteins and penetrate gut epithelial monolayers to sample bacteria. Nat Immunol 2(4):361–367. doi:10.1038/86373
Ciccocioppo R, Di Sabatino A, Parroni R, D’Alo S, Pistoia MA, Doglioni C, Cifone MG, Corazza GR (2000) Cytolytic mechanisms of intraepithelial lymphocytes in coeliac disease (CoD). Clin Exp Immunol 120(2):235–240
Di Sabatino A, Ciccocioppo R, Cupelli F, Cinque B, Millimaggi D, Clarkson MM, Paulli M, Cifone MG, Corazza GR (2006) Epithelium derived interleukin 15 regulates intraepithelial lymphocyte Th1 cytokine production, cytotoxicity, and survival in coeliac disease. Gut 55(4):469–477. doi:10.1136/gut.2005.068684
Salvati VM, Mazzarella G, Gianfrani C, Levings MK, Stefanile R, De Giulio B, Iaquinto G, Giardullo N, Auricchio S, Roncarolo MG, Troncone R (2005) Recombinant human interleukin 10 suppresses gliadin dependent T cell activation in ex vivo cultured coeliac intestinal mucosa. Gut 54(1):46–53. doi:10.1136/gut.2003.023150
Burgess SJ, Maasho K, Masilamani M, Narayanan S, Borrego F, Coligan JE (2008) The NKG2D receptor: immunobiology and clinical implications. Immunol Res 40(1):18–34. doi:10.1007/s12026-007-0060-9
Meresse B, Chen Z, Ciszewski C, Tretiakova M, Bhagat G, Krausz TN, Raulet DH, Lanier LL, Groh V, Spies T, Ebert EC, Green PH, Jabri B (2004) Coordinated induction by IL15 of a TCR-independent NKG2D signaling pathway converts CTL into lymphokine-activated killer cells in celiac disease. Immunity 21(3):357–366. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2004.06.020
Pagliari D, Cianci R, Frosali S, Landolfi R, Cammarota G, Newton EE, Pandolfi F (2013) The role of IL-15 in gastrointestinal diseases: a bridge between innate and adaptive immune response. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 24(5):455–466. doi:10.1016/j.cytogfr.2013.05.004
Hue S, Mention JJ, Monteiro RC, Zhang S, Cellier C, Schmitz J, Verkarre V, Fodil N, Bahram S, Cerf-Bensussan N, Caillat-Zucman S (2004) A direct role for NKG2D/MICA interaction in villous atrophy during celiac disease. Immunity 21(3):367–377. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2004.06.018
Maiuri L, Ciacci C, Auricchio S, Brown V, Quaratino S, Londei M (2000) Interleukin 15 mediates epithelial changes in celiac disease. Gastroenterology 119(4):996–1006
Benahmed M, Meresse B, Arnulf B, Barbe U, Mention JJ, Verkarre V, Allez M, Cellier C, Hermine O, Cerf-Bensussan N (2007) Inhibition of TGF-beta signaling by IL-15: a new role for IL-15 in the loss of immune homeostasis in celiac disease. Gastroenterology 132(3):994–1008. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2006.12.025
Meresse B, Verdier J, Cerf-Bensussan N (2008) The cytokine interleukin 21: a new player in coeliac disease? Gut 57(7):879–881. doi:10.1136/gut.2007.141994
Daum S, Bauer U, Foss HD, Schuppan D, Stein H, Riecken EO, Ullrich R (1999) Increased expression of mRNA for matrix metalloproteinases-1 and -3 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 in intestinal biopsy specimens from patients with coeliac disease. Gut 44(1):17–25
Junker Y, Zeissig S, Kim SJ, Barisani D, Wieser H, Leffler DA, Zevallos V, Libermann TA, Dillon S, Freitag TL, Kelly CP, Schuppan D (2012) Wheat amylase trypsin inhibitors drive intestinal inflammation via activation of toll-like receptor 4. J Exp Med 209(13):2395–2408. doi:10.1084/jem.20102660
Hopper AD, Cross SS, Hurlstone DP, McAlindon ME, Lobo AJ, Hadjivassiliou M, Sloan ME, Dixon S, Sanders DS (2007) Pre-endoscopy serological testing for coeliac disease: evaluation of a clinical decision tool. BMJ 334(7596):729. doi:10.1136/bmj.39133.668681.BE
Oberhuber G, Granditsch G, Vogelsang H (1999) The histopathology of coeliac disease: time for a standardized report scheme for pathologists. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 11(10):1185–1194
Ludvigsson JF, Green PH (2011) Clinical management of coeliac disease. J Intern Med 269(6):560–571. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2796.2011.02379.x
do Nascimento AB, Fiates GM, Dos Anjos A, Teixeira E (2013) Analysis of ingredient lists of commercially available gluten-free and gluten-containing food products using the text mining technique. Int J Food Sci Nutr 64(2):217–222. doi:10.3109/09637486.2012.718744
Santos V, Benassi M, Visentainer J, Matioli G (2010) Quinoa and flaxseed: potential ingredients in the production of bread with functional quality. Braz Arch Biol Tech 53(4):981–986
Rahaie S, Gharibzahedi SM, Razavi SH, Jafari SM (2014) Recent developments on new formulations based on nutrient-dense ingredients for the production of healthy-functional bread: a review. J Food Sci Technol 51(11):2896–2906. doi:10.1007/s13197-012-0833-6
Alvarez-Jubete L, Arendt EK, Gallagher E (2009) Nutritive value and chemical composition of pseudocereals as gluten-free ingredients. Int J Food Sci Nutr 60(Suppl 4):240–257. doi:10.1080/09637480902950597
Schuppan D, Junker Y, Barisani D (2009) Celiac disease: from pathogenesis to novel therapies. Gastroenterology 137(6):1912–1933. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2009.09.008
Mukherjee R, Kelly CP, Schuppan D (2012) Nondietary therapies for celiac disease. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am 22(4):811–831. doi:10.1016/j.giec.2012.09.001
Nasr I, Leffler DA, Ciclitira PJ (2012) Management of celiac disease. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am 22(4):695–704. doi:10.1016/j.giec.2012.07.012
Lundin KE, Nilsen EM, Scott HG, Loberg EM, Gjoen A, Bratlie J, Skar V, Mendez E, Lovik A, Kett K (2003) Oats induced villous atrophy in coeliac disease. Gut 52(11):1649–1652
Chartrand LJ, Russo PA, Duhaime AG, Seidman EG (1997) Wheat starch intolerance in patients with celiac disease. J Am Diet Assoc 97(6):612–618. doi:10.1016/S0002-8223(97)00156-9
Peraaho M, Kaukinen K, Paasikivi K, Sievanen H, Lohiniemi S, Maki M, Collin P (2003) Wheat-starch-based gluten-free products in the treatment of newly detected coeliac disease: prospective and randomized study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 17(4):587–594. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2036.2003.01425.x
Collin P, Thorell L, Kaukinen K, Maki M (2004) The safe threshold for gluten contamination in gluten-free products. Can trace amounts be accepted in the treatment of coeliac disease? Aliment Pharmacol Ther 19(12):1277–1283. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2036.2004.01961.xAPT1961
Akobeng AK, Thomas AG (2008) Systematic review: tolerable amount of gluten for people with coeliac disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 27(11):1044–1052. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2036.2008.03669.x
Hischenhuber C, Crevel R, Jarry B, Maki M, Moneret-Vautrin DA, Romano A, Troncone R, Ward R (2006) Review article: safe amounts of gluten for patients with wheat allergy or coeliac disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 23(5):559–575. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2036.2006.02768.x
Ciclitira PJ, Ellis HJ, Fagg NL (1984) Evaluation of a gluten free product containing wheat gliadin in patients with coeliac disease. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 289(6437):83
Kaukinen K, Collin P, Holm K, Rantala I, Vuolteenaho N, Reunala T, Maki M (1999) Wheat starch-containing gluten-free flour products in the treatment of coeliac disease and dermatitis herpetiformis. A long-term follow-up study. Scand J Gastroenterol 34(2):163–169
Catassi C, Rossini M, Ratsch IM, Bearzi I, Santinelli A, Castagnani R, Pisani E, Coppa GV, Giorgi PL (1993) Dose dependent effects of protracted ingestion of small amounts of gliadin in coeliac disease children: a clinical and jejunal morphometric study. Gut 34(11):1515–1519
Catassi C, Fabiani E, Iacono G, D’Agate C, Francavilla R, Biagi F, Volta U, Accomando S, Picarelli A, De Vitis I, Pianelli G, Gesuita R, Carle F, Mandolesi A, Bearzi I, Fasano A (2007) A prospective, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to establish a safe gluten threshold for patients with celiac disease. Am J Clin Nutr 85(1):160–166.
Leffler D, Schuppan D, Pallav K, Najarian R, Goldsmith JD, Hansen J, Kabbani T, Dennis M, Kelly CP (2013) Kinetics of the histological, serological and symptomatic responses to gluten challenge in adults with coeliac disease. Gut 62(7):996–1004. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2012-302196
Food and Drug Administration (2011) Health hazard assessment for gluten exposure in individuals with celiac disease: determination of tolerable daily intake levels and levels of concern for gluten. Office of Food Safety/Center of Food Safety and Applied Nutrition, Food and Drug Administration, USA
Food and Agriculture Organization/World Health Organization (FAO/WHO) (2008) Codex Committee on Nutrition and Foods for Special Dietary Uses. Codex standard for foods for special dietary use for persons intolerant to gluten. World Health Organization, Rome
Minister of Justice Canada (2015) Food and drug regulations. C.R.C., c. 870. B part. Foods. Foods for special dietary use
Food and Drug Administration (2013) Food labeling: gluten-free labeling of foods. Final Rule 78(150):47154–47179
Ministerio de Salud Argentina (2015) Directrices para la Autorización de un Alimento Libre de Gluten. Programa Federal de control de Alimentos. Conal, Acta 106, Abril 14, 2015. Buenos Aires, Argentina
Food Standards in Australia and New Zealand (2012) Nutrition information user guide to standard 1.2.8, Nutrition information requirements. Part B, Nutrition Claims, Australia
Instituto de Salud Pública (1997) Reglamento Sanitario de los Alimentos (RSA), Articulos 516–518. ISP, Santiago
Gibert A, Espadaler M, Angel Canela M, Sanchez A, Vaque C, Rafecas M (2006) Consumption of gluten-free products: should the threshold value for trace amounts of gluten be at 20, 100 or 200 p.p.m.? Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 18(11):1187–1195. doi:10.1097/01.meg.0000236884.21343.e4
Gibert A, Kruizinga AG, Neuhold S, Houben GF, Canela MA, Fasano A, Catassi C (2012) Might gluten traces in wheat substitutes pose a risk in patients with celiac disease? A population-based probabilistic approach to risk estimation. Am J Clin Nutr 97(1):109–116. doi:10.3945/ajcn.112.047985
Theethira TG, Dennis M (2015) Celiac disease and the gluten-free diet: consequences and recommendations for improvement. Dig Dis 33(2):175–182. doi:10.1159/000369504
Diamanti A, Capriati T, Basso MS, Panetta F, Di Ciommo Laurora VM, Bellucci F, Cristofori F, Francavilla R (2014) Celiac disease and overweight in children: an update. Nutrients 6(1):207–220. doi:10.3390/nu6010207
Mariani P, Viti MG, Montuori M, La Vecchia A, Cipolletta E, Calvani L, Bonamico M (1998) The gluten-free diet: a nutritional risk factor for adolescents with celiac disease? J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 27(5):519–523
Wild D, Robins GG, Burley VJ, Howdle PD (2010) Evidence of high sugar intake, and low fibre and mineral intake, in the gluten-free diet. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 32(4):573–581. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2036.2010.04386.x
Norsa L, Shamir R, Zevit N, Verduci E, Hartman C, Ghisleni D, Riva E, Giovannini M (2013) Cardiovascular disease risk factor profiles in children with celiac disease on gluten-free diets. World J Gastroenterol 19(34):5658–5664. doi:10.3748/wjg.v19.i34.5658
Kabbani TA, Goldberg A, Kelly CP, Pallav K, Tariq S, Peer A, Hansen J, Dennis M, Leffler DA (2012) Body mass index and the risk of obesity in coeliac disease treated with the gluten-free diet. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 35(6):723–729. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2036.2012.05001.x
Rubio-Tapia A, Hill ID, Kelly CP, Calderwood AH, Murray JA (2013) ACG clinical guidelines: diagnosis and management of celiac disease. Am J Gastroenterol 108(5):656–676. doi:10.1038/ajg.2013.79ajg201379
Dickey W, Kearney N (2006) Overweight in celiac disease: prevalence, clinical characteristics, and effect of a gluten-free diet. Am J Gastroenterol 101(10):2356–2359. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00750.x
Botero-Lopez JE, Araya M, Parada A, Mendez MA, Pizarro F, Espinosa N, Canales P, Alarcon T (2011) Micronutrient deficiencies in patients with typical and atypical celiac disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 53(3):265–270. doi:10.1097/MPG.0b013e3181f988fc
McGough N, Cummings JH (2005) Coeliac disease: a diverse clinical syndrome caused by intolerance of wheat, barley and rye. Proc Nutr Soc 64(4):434–450. doi:10.1079/PNS2005461
Dahele A, Ghosh S (2001) Vitamin B12 deficiency in untreated celiac disease. Am J Gastroenterol 96(3):745–750. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2001.03616.x
Oyarzún A, Nakash T, Ayala J, Lucero Y, Araya M (2015) Following gluten free diet: less available, higher cost and poor nutritional profile of gluten-free school snacks. Int J Celiac Dis 3(3):102–107
Wierdsma NJ, van Bokhorst-de van der Schueren MA, Berkenpas M, Mulder CJ, van Bodegraven AA (2013) Vitamin and mineral deficiencies are highly prevalent in newly diagnosed celiac disease patients. Nutrients 5(10):3975–3992. doi:10.3390/nu5103975
Salazar Quero JC, Espin Jaime B, Rodriguez Martinez A, Arguelles Martin F, Garcia Jimenez R, Rubio Murillo M, Pizarro Martin A (2015) Nutritional assessment of gluten-free diet. Is gluten-free diet deficient in some nutrient? An Pediatr (Barc) 83(1):33–39. doi:10.1016/j.anpedi.2014.08.011
See J, Murray JA (2006) Gluten-free diet: the medical and nutrition management of celiac disease. Nutr Clin Pract 21(1):1–15. doi: 10.1177/011542650602100101
Koerner TB, Cleroux C, Poirier C, Cantin I, La Vieille S, Hayward S, Dubois S (2013) Gluten contamination of naturally gluten-free flours and starches used by Canadians with celiac disease. Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess 30(12):2017–2021. doi:10.1080/19440049.2013.840744
Crowe JP, Falini NP (2001) Gluten in pharmaceutical products. Am J Health Syst Pharm 58(5):396–401
Leffler DA, Dennis M, Edwards George JB, Jamma S, Magge S, Cook EF, Schuppan D, Kelly CP (2009) A simple validated gluten-free diet adherence survey for adults with celiac disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 7(5):530–536, 536 e531–532. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2008.12.032
Vahedi K, Mascart F, Mary JY, Laberenne JE, Bouhnik Y, Morin MC, Ocmant A, Velly C, Colombel JF, Matuchansky C (2003) Reliability of antitransglutaminase antibodies as predictors of gluten-free diet compliance in adult celiac disease. Am J Gastroenterol 98(5):1079–1087. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2003.07284.x
Hall NJ, Rubin G, Charnock A (2009) Systematic review: adherence to a gluten-free diet in adult patients with coeliac disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 30(4):315–330. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2036.2009.04053.x
Biagi F, Bianchi PI, Marchese A, Trotta L, Vattiato C, Balduzzi D, Brusco G, Andrealli A, Cisaro F, Astegiano M, Pellegrino S, Magazzu G, Klersy C, Corazza GR (2012) A score that verifies adherence to a gluten-free diet: a cross-sectional, multicentre validation in real clinical life. Br J Nutr 108(10):1884–1888. doi:10.1017/S0007114511007367
Comino I, Real A, Vivas S, Siglez MA, Caminero A, Nistal E, Casqueiro J, Rodriguez-Herrera A, Cebolla A, Sousa C (2012) Monitoring of gluten-free diet compliance in celiac patients by assessment of gliadin 33-mer equivalent epitopes in feces. Am J Clin Nutr 95(3):670–677. doi:10.3945/ajcn.111.026708
Moron B, Bethune MT, Comino I, Manyani H, Ferragud M, Lopez MC, Cebolla A, Khosla C, Sousa C (2008) Toward the assessment of food toxicity for celiac patients: characterization of monoclonal antibodies to a main immunogenic gluten peptide. PLoS One 3(5):e2294. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002294
Moron B, Cebolla A, Manyani H, Alvarez-Maqueda M, Megias M, Thomas Mdel C, Lopez MC, Sousa C (2008) Sensitive detection of cereal fractions that are toxic to celiac disease patients by using monoclonal antibodies to a main immunogenic wheat peptide. Am J Clin Nutr 87(2):405–414.
Moreno ML, Cebolla A, Munoz-Suano A, Carrillo-Carrion C, Comino I, Pizarro A, Leon F, Rodriguez-Herrera A, Sousa C (2015) Detection of gluten immunogenic peptides in the urine of patients with coeliac disease reveals transgressions in the gluten-free diet and incomplete mucosal healing. Gut. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2015-310148
Di Sabatino A, Corazza GR (2009) Coeliac disease. Lancet 373(9673):1480–1493. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60254-3
Hallert C, Granno C, Grant C, Hulten S, Midhagen G, Strom M, Svensson H, Valdimarsson T, Wickstrom T (1998) Quality of life of adult coeliac patients treated for 10 years. Scand J Gastroenterol 33(9):933–938
Vilagut G, Ferrer M, Rajmil L, Rebollo P, Permanyer-Miralda G, Quintana JM, Santed R, Valderas JM, Ribera A, Domingo-Salvany A, Alonso J (2005) The Spanish version of the Short Form 36 Health Survey: a decade of experience and new developments. Gac Sanit 19(2):135–150. doi: 10.1590/S0213-91112005000200007
Hauser W, Gold J, Stein J, Caspary WF, Stallmach A (2006) Health-related quality of life in adult coeliac disease in Germany: results of a national survey. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 18(7):747–754. doi:10.1097/01.meg.0000221855.19201.e8
Zarkadas M, Cranney A, Case S, Molloy M, Switzer C, Graham ID, Butzner JD, Rashid M, Warren RE, Burrows V (2006) The impact of a gluten-free diet on adults with coeliac disease: results of a national survey. J Hum Nutr Diet 19(1):41–49. doi:10.1111/j.1365-277X.2006.00659.x
Nachman F, Maurino E, Vazquez H, Sfoggia C, Gonzalez A, Gonzalez V, Plancer del Campo M, Smecuol E, Niveloni S, Sugai E, Mazure R, Cabanne A, Bai JC (2009) Quality of life in celiac disease patients: prospective analysis on the importance of clinical severity at diagnosis and the impact of treatment. Dig Liver Dis 41(1):15–25. doi:10.1016/j.dld.2008.05.011
Sverker A, Hensing G, Hallert C (2005) ‘Controlled by food’- lived experiences of coeliac disease. J Hum Nutr Diet 18(3):171–180. doi:10.1111/j.1365-277X.2005.00591.x
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bascuñán, K.A., Vespa, M.C. & Araya, M. Celiac disease: understanding the gluten-free diet. Eur J Nutr 56, 449–459 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-016-1238-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-016-1238-5