Abstract
Background
Several stressful environmental factors are associated with short-term breast-feeding. A high concentration of sodium in colostrum has predicted early failure.
Aim of the study
We studied the association of growth factors in colostrum and the length of breast-feeding (BF).
Methods
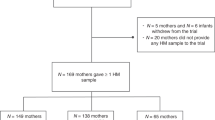
We measured concentrations of TGF-β1 and -β2; epidermal growth factor, total protein, and sodium and compared their concentrations in colostral samples from mothers who either breast-fed their infants exclusively less than 0.5 months (n = 109) or longer than 3.5 months (n = 119).
Results
In the short BF group more mothers smoked and were primiparous more frequently and had less often a university education. They also provided the colostral samples significantly later than did those with long BF. Geometric mean concentration for TGF-β1 was 1.9 times as high in the samples from short BF mothers as in those with long BF; sinificant difference remained in comparisons of samples taken equally long postpartum. Samples from the short BF group showed higher levels for sodium, TGF-β2 and total protein, whereas concentrations of epidermal growth factor were similar between groups.
Conclusions
We thus infer that concentrations of factors in breast milk with an effect on the development and involution of the mammary gland, like TGF-β1 in milk, may be one of many biological factors having an impact on the successful initiation of breast-feeding.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chockalingam A, Paape MJ, Bannerman DD (2005) Increased milk levels of transforming growth factor-alpha, beta1, and beta2 during Escherichia coli-induced mastitis. J Dairy Sci 88:1986–1993
Dewey KG (2001) Maternal and fetal stress are associated with impaired lactogenesis in humans. J Nutr 131:3012–3015
Jonsson S, Pulkkinen MO (1994) Mastitis today: incidence, prevention and treatment. Ann Chir Gynaecol Suppl 208:84–87
Kalliomäki M, Ouwehand A, Arvilommi H, Kero P, Isolauri E (1999) Transforming growth factor-beta in breast milk: a potential regulator of atopic disease at an early age. J Allergy Clin Immunol 104:1251–1257
Lamote I, Meyer E, Massart-Leen AM, Burvenich C (2004) Sex steroids and growth factors in the regulation of mammary gland proliferation, differentiation, and involution. Steroids 69:145–159
Lau C (2001) Effects of stress on lactation. Pediatr Clin North Am 48:221–234
Letterio JJ, Geiser AG, Kulkarni AB, Roche NS, Sporn MB, Roberts AB (1994) Maternal rescue of transforming growth factor-b1 null mice. Science 264:1936–1938
McManaman JL, Neville MC (2003) Mammary physiology and milk secretion. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 55:629–641
Morton JA (1994) The clinical usefulness of breast milk sodium in the assessment of lactogenesis. Pediatrics 93:802–806
Motyl T, Gajkowska B, Wojewodzka U, Wareski P, Rekiel A, Ploszaj T (2001) Expression of apoptosis-related proteins in involuting mammary gland of sow. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 128:635–646
Neville MC (2001) Anatomy and physiology of lactation. Pediatr Clin North Am 48:13–34
Neville MC, McFadden TB, Forsyth I (2002) Hormonal regulation of mammary differentiation and milk secretion. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 7:49–66
Neville MC, Morton J, Umemura S (2001) Lactogenesis. The transition from pregnancy to lactation. Pediatr Clin North Am 48:35–52
Picciano MF (2003) Pregnancy and lactation: physiological adjustments, nutritional requirements and the role of dietary supplements. J Nutr 133(S):1997–2002
Pollard JW (2001) Tumour-stromal interactions. Transforming growth factor-beta isoforms and hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor in mammary gland ductal morphogenesis. Breast Cancer Res 3:230–237
Saarinen KM, Juntunen-Backman K, Järvenpää AL, Kuitunen P, Lope L, Renlund M, Siivola M, Savilahti E (1999) Supplementary feeding in maternity hospitals and the risk of cow’s milk allergy: a prospective study of 6209 infants. J Allergy Clin Immunol 104:457–461
Savilahti E, Siltanen M, Kajosaari M, Vaarala O, Saarinen KM (2005) IgA antibodies, TGF-beta1 and -beta2, and soluble CD14 in the colostrum and development of atopy by age 4. Pediatr Res 58:1300–1305
Widstrom AM, Werner S, Matthiesen AS, Svensson K, Uvnas-Moberg K (1991) Somatostatin levels in plasma in nonsmoking and smoking breast-feeding women. Acta Paediatr Scand 80:13–21
World Health Organization (2000) Mastitis. Causes, management. Geneva
Xie W, Paterson AJ, Chin E, Nabell LM, Kudlow JE (1997) Targeted expression of a dominant negative epidermal growth factor receptor in the mammary gland of transgenic mice inhibits pubertal mammary duct development. Mol Endocrinol 11:1766–1781
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Savilahti, E., Saarinen, K.M. Colostrum TGF-β-1 associates with the duration of breast-feeding. Eur J Nutr 46, 238–242 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-007-0656-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-007-0656-9