Abstract
Background
Renal involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), known as lupus nephritis (LN), is a common and severe complication and a major predictor of poor outcome. Long-term survival in SLE can be improved with early diagnosis and prompt treatment of LN. A number of biochemical markers are currently used to clinically assess disease activity in patients; however, they lack sensitivity and specificity for differentiating renal activity and damage in LN. A reliable clinical biomarker that can forecast LN flare and which could be sequentially followed would help to optimize initiation and escalation of therapy at the time of active or relapsing disease.
Objective
This study was carried out to investigate the value of urinary tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-like weak inducer of apoptosis (uTWEAK) as a biomarker for active lupus nephritis.
Patients and methods
A total of 44 patients with SLE fulfilling the 1997 revised criteria for the classification of SLE as well as 11 age and sex-matched healthy controls were included in this study and subjected to full medical history taking, clinical examination, routine laboratory investigations, measurement of uTWEAK level as well as renal biopsy for patients with active LN.
Results
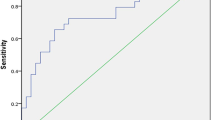
The uTWEAK levels were significantly higher in SLE patients with active LN compared to those without or with inactive renal disease and normal healthy subjects.
Zusammenfassung
Hintergrund
Eine Nierenbeteiligung bei einem systemischen Lupus erythematodes (SLE), die sog. Lupusnephritis (LN), ist eine häufige und schwere Komplikation sowie ein wichtiger Prädiktor für ein schlechtes Outcome. Das Langzeitüberleben bei SLE kann durch eine frühzeitige Diagnose und unmittelbare Behandlung der LN verbessert werden. Derzeit werden mehrere biochemische Marker verwendet, um die Nierenaktivität und -schädigung bei LN zu differenzieren, jedoch mangelt es hierzu an Sensitivität und Spezifität. Ein verlässlicher klinischer Biomarker, der einen LN-Schub voraussagen und fortlaufend verfolgen könnte, würde bei der Optimierung des Therapiebeginns und der -eskalation zum Zeitpunkt der aktiven oder rezidivierenden Krankheit helfen.
Ziel
Diese Studie wurde durchgeführt, um den Wert des Tumornekrosefaktor(TNF)-ähnlichen schwachen Induktors von Apoptose im Urin („urinary TNF-like weak inducer of apoptosis“, uTWEAK) als Biomarker für eine aktive Lupusnephritis zu untersuchen.
Patienten und Methoden
Insgesamt 44 Patienten mit SLE, die die überarbeiteten Kriterien für die SLE-Klassifikation aus dem Jahr 1997 erfüllten, sowie 11 alters- und geschlechtsgematchte gesunde Kontrollpersonen wurden in diese Studie eingeschlossen und unterzogen sich einer vollständigen Anamnese, einer klinischen Untersuchung, Routine-Laboruntersuchungen, Messungen der uTWEAK-Werte und Patienten mit aktiver LN einer Nierenbiopsie.
Ergebnisse
Die uTWEAK-Werte waren bei SLE-Patienten mit aktiver LN signifikant höher im Vergleich zu den Werten der Patienten ohne oder mit inaktiver Nierenerkrankung sowie der gesunden Kontrollpersonen.




Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Spot urine test is a test for proteinuria. Protein-to-creatinine ratio (P/C) in spot urine specimens is a predictor of urine protein excretion in 24-h collections.
References
Illei GG, Lipsky PE (2004) Biomarkers in systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Rheumatol Rep 6:382–390
Salgado A, Herrera-Diaz C (2012) Lupus nephritis: an overview of recent findings. Autoimmune Dis 2012:1–21
Korbet SM, Lewis EJ, Schwartz MM (2000) Factors predictive of outcome in severe lupus nephritis. Lupus Nephritis Collaborative Study Group. Am J Kidney Dis 35:904–914
Esdaile JM, Joseph L, MacKenzie T, Kashgarian M, Hayslett JP (1994) The benefit of early treatment with immunosuppressive agents in lupus nephritis. J Rheumatol 21:2046–2051
Illei GG, Tackey E, Lapteva L, Lipsky PE (2004) Biomarkers in systemic lupus erythematosus: II. Markers of disease activity. Arthritis Rheum 50:2048–2065
Schwartz N, Michaelson JS, Putterman C (2007) Lipocalin-2, TWEAK, and other cytokines as urinary biomarkers for lupus nephritis. Ann NY Acad Sci 1109:265–274
Mok CC (2010) Biomarkers for lupus nephritis: A critical appraisal. J Biomed Biotechnol 2010:638413
Fiehn C, Hajjar Y, Mueller K, Waldherr R, Ho AD, Andrassy K (2003) Improved clinical outcome of lupus nephritis during the past decade: Importance of early diagnosis and treatment. Ann Rheum Dis 62:435–439
Houssiau FA, Vasconcelos C, D’Cruz D, Sebastiani GD, Garrido ER, Danieli MG, Abramovicz D, Blockmans D, Mathieu A, Direskeneli H, Galeazzi M, Gul A, Levy Y, Petera P, Popovic R, Petrovic R, Sinico RA, Cattaneo R, Font J, Depresseux G, Cosyns J‑P, Crevera R (2004) Early response to immunosuppressive therapy predicts good renal outcome in lupus nephritis. Arthritis Rheum 50:3934–3940
Austin HA, Boumpas DT, Vaughan EM, Balow JE (1995) High-risk features of lupus nephritis: importance of race and clinical and histological factors in 166 patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 10:1620–1628
Schwartz N, Michaelson J, Putterman C (2007) Lipocalin-2,TWEAK, and other cytokines as urinary biomarkers for lupus nephritis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1109:265–274
Maecker H, Varfolomeev E, Kischkel F et al (2005) TWEAK attenuates the transition from innate to adaptive immunity. Cell 123:931–944
Muñoz-García B, Martín-Ventura JL, Martínez E, Sánchez S, Hernández G, Ortega L, Ortiz A, Egido J, Blanco-Colio LM (2006) Fn14 is upregulated in cytokine-stimulated vascular smooth muscle cells and is expressed in human carotid atherosclerotic plaques modulation by atorvastatin. Stroke 37(8):2044–2053
Sanz AB, Santamaria B, Ruiz Ortega M, Egido J, Ortiz A (2008) Mechanisms of renal apoptosis in health and disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 19(9):695–703
Burkly LC, Michaelson JS, Hahm K, Zheng TS (2007) TWEAKing tissue remodeling by a multifunctional cytokine: Role of TWEAK/Fn14 pathway in health and disease. Cytokine 40(1):1–16
Winkles JA (2008) The TWEAK-Fn14 cytokine-receptor axis: discovery, biology and therapeutic targeting. Nat Rev Drug Discov 7(5):411–425
Gao HX, Campbell SR, Burkly LC, Jakubowski A, Jarchum I, Banas B et al (2009) TNFlike weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) induces inflammatory and proliferative effects in human kidney cells. Cytokines 46:24e35
Zhao Z, Burkly LC, Campbell S, Schwartz N, Molano A, Choudhury A, Eisenberg RA, Michaelson JS, Putterman C (2007) TWEAK/Fn14 interactions are instrumental in the pathogenesis of nephritis in the chronic graft-versus-host model of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol 179:7949–7958
Xuejing Z, Jiazhen T, Jun L, Xiangqing X, Shuguang Y, Fuyou L (2012) Urinary TWEAK level as a marker of lupus nephritis activity in 46 cases. J Biomed Biotechnol 2012:359647
Hochberg MC (1997) Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 40(9):1725
Bombardier, C, Gladman, DD, Urowitz, MB et al (1992) Derivation of SLEDAI: a disease activity index for lupus patients. Arthritis and Rheumatism. 35:630
Weening JJ, D’Agati VD, Schwartz MM, Seshan SV, Alpers CE, Appel GB, Balow JE et al (2004) International Society of Nephrology Working Group on the Classification of Lupus Nephritis and Renal Pathology Society Working Group on the Classification of Lupus Nephritis : Classification of glomerulonephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus revisited. Kidney Int 65(5):521–530
Bombardier, C, Gladman, DD, Urowitz, MB et al (1992) Derivation of SLEDAI: a disease activity index for lupus patients. Arthritis Rheum 35:630–640
Gladman DD, Ibanez D, Urowitz MB (2002) Systemic lupus erythematosis disease activity index 2000. J Rheumatol 29:288–291
Schwartz N, Rubinstein T, Burkly LC, Collins CE, Blanco I, Su L, Hojaili B, Mackay M, Aranow C, Stohl W, Rovin BH, Michaelson JS, Putterman C (2009) Urinary TWEAK as a biomarker of lupus nephritis: a multicenter cohort study. Arthritis Res Ther 11(5):R143
Zhu X, Tan J, Li J, Xu X, Yuan S, Liu F (2012) Urinary TWEAK Level as a marker of Lupus Nephritis activity in 46 cases. J Biomed Biotechnol 2012(359647):1–7
Pitashny M, Schwartz N, Qing X, Hojaili B, Aranow C, Mackay M, Putterman C (2007) Urinary lipocalin-2 is associated with renal disease activity in human lupus nephritis. Arthritis Rheum 56(6):1894–1903
Marchini M, Antonioli R, Lleo A, Barili M, Caronni M, Origgi L et al (2003) HLA class II antigens associated with lupus nephritis in Italian SLE patients. Hum Immunol 64:462–468
Harley JB, Alarcon-Riquelme ME, Criswell LA, Jacob CO, Kimberly RP, Moser KL et al (2008) Genome-wide association scan in women with systemic lupus erythematosus identifies susceptibility variants in ITGAM, PXK, KIAA1542 and other loci. Nat Genet 40:204–210
Lee YH, Woo JH, Choi SJ, Ji JD, Song GG (2009) Association of programmed cell death 1 polymorphisms and systemic lupus erythematosus: a meta-analysis. Lupus 18:9–15
Gladman DD, Ibanez D, Urowltz MB (2002) Systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity index 2000. J Rheumatol 29(2):288–291
Schwartz N, Rubinstein T, Burkly LC et al (2009) Urinary TWEAK as a biomarker of lupus nephritis: a multicenter cohort study. Arthritis Res Ther 11(5):R143
El-shehaby A, Darweesh H, El-Khatib M, Momtaz M, Marzouk S, El-Shaarawy N, Emad Y (2011) Correlations of urinary biomarkers, TNF-LikeWeak Inducer of Apoptosis (TWEAK), Osteoprotegerin (OPG), Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1), and IL-8 with lupus nephritis. J Clin Immunol 31(5):848–856
Schwartz N, Su L, Burkly LC, Mackay M, Aranow C, Kollaros M, Michaelson JS, Rovin B, Putterman C (2006) Urinary TWEAK and the activity of lupus nephritis. J Autoimmun 27(4):242–250
Dhaun N, Kluth D (2009) TWEAK: a novel biomarker for lupus nephritis? Arthritis Res Ther 11:133
Elsayed M, Elhefnawy KA, Qassem AA, Amr GE (2015) Urinary tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis (tweak) as a marker for lupus nephritis activity. Int J Sci Res 4(2):1615–1619
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
H. A. Taha, M. N. Salem, M. Abd El-Fattah El-Feqi, N. N. Eesa and R. A. Mohamed declare that they have no competing interests.
All studies on humans described in this manuscript were carried out with the approval of the responsible ethics committee and in accordance with national and the Helsinki Declaration of 1975 (in its current revised form). Informed consent was obtained from all patients included in the study.
Additional information
Redaktion
U. Müller-Ladner, Bad Nauheim
U. Lange, Bad Nauheim
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salem, M.N., Taha, H.A., Abd El-Fattah El-Feqi, M. et al. Urinary TNF-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) as a biomarker of lupus nephritis. Z Rheumatol 77, 71–77 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00393-016-0184-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00393-016-0184-1
Keywords
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Lupus nephritis
- Biomarkers
- Cytokine
- Tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis