Summary
Background: In hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy (HOCM) therapy, surgical myectomy and DDD pacemaker implantation are considered to be established extensions to medical treatment. As an alternative procedure for reducing the left ventricular outflow track gradient (LVOTG), percutaneous transluminal septal myocardial ablation (PTSMA) by alcohol-induced septal branch occlusion has been introduced. We report on the acute results and the short-term clinical course following 66 PTSMA interventions in symptomatic patients (pts.) with HOCM.
Methods: In pts. who were symptomatic despite adequate drug therapy (31 women, 35 men; mean age 52.9 ± 15.0 years, range: 16–86) 66 PTSMA interventions were performed (4 pts. with a re-intervention). Septal branches were included by injection of 3.5±1.8 (1.5–11.0) ml ethanol (96%). In the first 30 pts. the target vessel was determined by probatory balloon occlusion (PBO) alone, in the following 36 by additional myocardial contrast echocardiography (MCE). In-hospital follow-up of LVOTG and clinical course were determined.
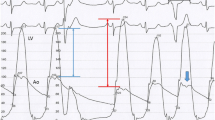
Reults: The invasively determined LVOTG could be reduced by > 50% or eliminated in 54 interventions (82%) with a mean reduction from 71.2 ± 34.4 (4–174) to 18.0 ± 21.5 (0–105) mm Hg at rest and from 145.7 ± 42.3 (68–257) to 63.7 ± 49.3 (0–185) mm Hg post extrasystole (p < 0.0001). All pts. experienced angina pectoris with the first 24 hours. The creatine kinase peak was 690 ± 364 (201–1810) U/l after 11.0 ± 5.4 (4–24) hours. 45 pts. (68%) developed trifascicular block, requiring temporary, or in 9 cases (14%) permanent, (DDD) pacemaker implantation. Two pts. (3%) died 9 and 2 days after a successful intervention, due to uncontrollable ventricular fibrillation associated with betasympathomimetic and theophylline treatment for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in one case, and fulminant pulmonary embolism in the other. The remaining pts. were discharged after 11.1 ± 4.6 (5–24) days, following an uncomplicated hospital course. The introduction of MCE was associated with a higher percentage of short-term success (92% vs. 70%, p < 0.015.
Conclusion: PTSMA in HOCM is a promising non-surgical technique for septal myocardial reduction with a consecutive reduction of the LVOTG. MCE has shown to be a useful addition to PBO for selection of the target vessel. Possible complications are trifascicular blocks requiring permanent pacemaker implantation and tachycardiac rhythm disturbances. Prospective long-term observations of larger populations and a comparison with the established forms of therapy are necessary in order to determine the definitive significance of PTSMA.
Zusammenfassung
Hintergrund: Die chirurgische Myotomie-Myektomie und die DDD-Schrittmacherimplantation gelten als Therapieoptionen für medikamentös nicht hinreichend behandelbare Patienten (Pat.) mit hypertroph-obstruktiver Kardiomyopathie (HOCM). Als alternative nichtchirurgische Strategie wurde die perkutane transluminale septale Myokardablation (PTSMA) zur Reduktion der septalen Hypertrophie bzw. des Gradienten über dem linksventrikulären Ausflußtrakt (LVOTG) entwickelt. Wir berichten über Akutergebnisse und Hospitalverlauf der ersten 66 Patienten.
Methoden: Bei 66 trotz Medikation symptomatischen Patienten (4 Pat. mit 2 Interventionen; 31 Frauen, 35 Männer; mittleren Alters 52,9& plusmn; 15,0 (16–86 Jahre) mit HOCM wurde die Indikation zur PTSMA gestellt. Die Intervention erfolgte durch Injektion von 3,5 ± 1,8 (1,5–11) ml 96%igen Alkohols. Bei den ersten 30 Interventionen wurde das Zielgefäß durch probatorische Ballonokklusion (PBO) ermittelt, bei den folgenden Eingriffen mittels zusätzlicher Myokard-Kontrastechokardiographie (MCE). Das hämodynamische Akutergebnis und der klinische Verlauf wurden erfaßt.
Ergebnisse: Die invasiv gemessenen LVOTG konnten bei 54 Interventionen (82%) um mehr als 50% gesenkt oder ganz beseitigt werden mit einer Reduktion von im Mittel 71,2 ± 34,4 (4–174) auf 18,0 ± 21,5 (0–105) mm Hg in Ruhe bzw. von 145,7 ± 42,3 (68–257) auf 63,7 ± 49,3 (0–185) mm Hg postextrasystolisch (p < 0,0001). Alle Patienten klagten über mäßige, pektanginöse Beschwerden. Der CK-Gipfel betrug 690 ± 364 (201–1810) U/l nach 11,0 ± 5,4 (4–24) h. Ein trifaszikulärer Block entwickelte sich nach 45 Eingriffen (68%); in 9 Fällen (14%) mußte ein permanenter DDD-Schrittmacher implantiert werden. Zwei Patienten (3%) verstarben 9 bzw. 2 Tage nach primär effektiver PTSMA infolge intraktablen Kammerflimmerns, assoziiert mit einer beta-mimetischen und Theophyllin-Therapie wg. schwerer chronischer obstruktiver Atemwegserkrankung (COLD) in einem und an einer fulminanten Lungenembolie im zweiten Fall. Die übrigen Patienten wurden nach 11,1 ± 4,6 (5–24) die bzw. unauffälligem Hospitalverlauf entlassen. Die Einführung der MCE war mit einer höheren Rate akut erfolgreicher Eingriffe assoziiert (92% vs. 70%, p < 0,015).
Schlußfolgerung: Die PTSMA ist eine vielversprechende Option für medikamentös nicht hinreichend behandelbare Patienten mit HOCM. Zur Auswahl des Zielgefäßes hat sich die MCE als Zusatz zur PBO als hilfreich erwiesen. Komplikationsmöglichkeiten sind vor allem bradykarde (aufgrund einer permanenten trifaszikulären Blockierung mit der Notwendigkeit der DDD-Schrittmacher-Implantation) Rhythmusprobleme. Langzeitbeobachtungen, möglichst in Form eines prospektiv angelegten Registers und bei größeren Patientengruppen, sind notwendig zur Definition des Stellenwerts im Vergleich zu den etablierten Behandlungsverfahren.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Eingegangen: 10. Oktober 1997 / Akzeptiert: 15. Dezember 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Faber, L., Seggewiß, H., Faßbender, D. et al. Perkutane transluminale septale Myokardablation bei hypertroph-obstruktiver Kardiomyopathie: Akutergebnisse bei 66 Patienten unter Berücksichtigung der Myokard-Kontrastechkardiographie. Z Kardiol 87, 191–201 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003920050171
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003920050171