Abstract
Introduction
Catheter ablation of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (PAF) has been suggested as first-line treatment for selected patients (pts). However, patient characteristics, procedural data, and complication rate in the group of young patients remain undetermined.
Methods
The German Ablation Registry has been designed as a multi-center prospective registry. AF ablation data were collected from 51 German centers between March 2007 to September 2012 and 2 groups were defined (group A: ≤45 years, group B: >45 years). Data were analyzed according to patient characteristics, procedural data, and complications. To calculate differences between both groups CHI2 or Mann–Whitney–Wilcoxon tests was utilized.
Results
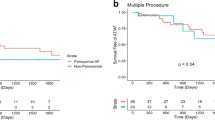
A total of 7243 patients undergoing AF ablation were included (group A: 593, 8.2 %; group B: 6650, 91.8 %). Male gender and PAF were significantly more often present in group A. Patient characteristic revealed decreased co-morbidities in the young. In both groups circumferential pulmonary vein isolation represented the procedural cornerstone, whereas substrate modification was significantly more often performed in group B. Procedure-, and fluoroscopy-time was similar but there was a shorter hospital stay and a favorable complication profile in the young. After 12 months AF recurrence and use of antiarrhythmic drugs were less common in group A.
Conclusion
The young AF ablation patient has typically paroxysmal AF and less comorbidities. In this group, catheter ablation of AF is associated with a lower major complication rate, shorter hospitalization, and a favorable clinical outcome.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AAD:
-
Antiarrhtyhmic drug
- AF:
-
Atrial fibrillation
- CA:
-
Catheter ablation
- CFAE:
-
Complex fractionated atrial electrograms
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- IQR:
-
Interquartile range
- PV:
-
Pulmonary vein
- MACE:
-
Major adverse cardiac events
- MACCE:
-
Major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- RFC:
-
Radiofrequency current
References
Calkins H, Kuck KH, Cappato R, Brugada J, Camm AJ, Chen SA, Crijns HJ, Damiano RJ, Jr., Davies DW, DiMarco J, Edgerton J, Ellenbogen K, Ezekowitz MD, Haines DE, Haissaguerre M, Hindricks G, Iesaka Y, Jackman W, Jalife J, Jais P, Kalman J, Keane D, Kim YH, Kirchhof P, Klein G, Kottkamp H, Kumagai K, Lindsay BD, Mansour M, Marchlinski FE, McCarthy PM, Mont JL, Morady F, Nademanee K, Nakagawa H, Natale A, Nattel S, Packer DL, Pappone C, Prystowsky E, Raviele A, Reddy V, Ruskin JN, Shemin RJ, Tsao HM, Wilber D. (2012) HRS/EHRA/ECAS expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation: recommendations for patient selection, procedural techniques, patient management and follow-up, definitions, endpoints, and research trial design: a report of the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) Task Force on Catheter and Surgical Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation. Developed in partnership with the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA), a registered branch of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Cardiac Arrhythmia Society (ECAS); and in collaboration with the American College of Cardiology (ACC), American Heart Association (AHA), the Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society (APHRS), and the Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS). Endorsed by the governing bodies of the American College of Cardiology Foundation, the American Heart Association, the European Cardiac Arrhythmia Society, the European Heart Rhythm Association, the Society of Thoracic Surgeons, the Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society, and the Heart Rhythm Society. Heart Rhythm 9:632–96 e21
Camm AJ, Kirchhof P, Lip GY, Schotten U, Savelieva I, Ernst S, Van Gelder IC, Al-Attar N, Hindricks G, Prendergast B, Heidbuchel H, Alfieri O, Angelini A, Atar D, Colonna P, De Caterina R, De Sutter J, Goette A, Gorenek B, Heldal M, Hohloser SH, Kolh P, Le Heuzey JY, Ponikowski P, Rutten FH (2010) Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation: the Task Force for the Management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J 31:2369–2429
Cappato R, Calkins H, Chen SA, Davies W, Iesaka Y, Kalman J, Kim YH, Klein G, Natale A, Packer D, Skanes A, Ambrogi F, Biganzoli E (2010) Updated worldwide survey on the methods, efficacy, and safety of catheter ablation for human atrial fibrillation. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 3:32–38
Neven K, Schmidt B, Metzner A, Otomo K, Nuyens D, De Potter T, Chun KR, Ouyang F, Kuck KH (2010) Fatal end of a safety algorithm for pulmonary vein isolation with use of high-intensity focused ultrasound. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 3:260–265
Hoyt H, Bhonsale A, Chilukuri K, Alhumaid F, Needleman M, Edwards D, Govil A, Nazarian S, Cheng A, Henrikson CA, Sinha S, Marine JE, Berger R, Calkins H, Spragg DD (2011) Complications arising from catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: temporal trends and predictors. Heart Rhythm 8:1869–1874
Guiot A, Jongnarangsin K, Chugh A, Suwanagool A, Latchamsetty R, Myles JD, Jiang Q, Crawford T, Good E, Pelosi F Jr, Bogun F, Morady F, Oral H (2012) Anticoagulant therapy and risk of cerebrovascular events after catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation in the elderly. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 23:36–43
Koester I, Schmidt B, Ouyang F, Chun KRJ, Metzner A, Tilz R, Koektuerk B, Zerm T, Kuck KH (2008) A single centre experience of pulmonary vein isolation in the very elderly-patient characteristics, procedural data and complication rates. Heart Rhythm [PO2-22]
Spragg DD, Dalal D, Cheema A, Scherr D, Chilukuri K, Cheng A, Henrikson CA, Marine JE, Berger RD, Dong J, Calkins H (2008) Complications of catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation: incidence and predictors. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 19:627–631
Zado E, Callans DJ, Riley M, Hutchinson M, Garcia F, Bala R, Lin D, Cooper J, Verdino R, Russo AM, Dixit S, Gerstenfeld E, Marchlinski FE (2008) Long-term clinical efficacy and risk of catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation in the elderly. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 19:621–626
Leong-Sit P, Zado E, Callans DJ, Garcia F, Lin D, Dixit S, Bala R, Riley MP, Hutchinson MD, Cooper J, Gerstenfeld EP, Marchlinski FE (2010) Efficacy and risk of atrial fibrillation ablation before 45 years of age. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 3:452–457
Fuster V, Ryden LE, Cannom DS, Crijns HJ, Curtis AB, Ellenbogen KA, Halperin JL, Le Heuzey JY, Kay GN, Lowe JE, Olsson SB, Prystowsky EN, Tamargo JL, Wann S, Smith SC Jr, Jacobs AK, Adams CD, Anderson JL, Antman EM, Hunt SA, Nishimura R, Ornato JP, Page RL, Riegel B, Priori SG, Blanc JJ, Budaj A, Camm AJ, Dean V, Deckers JW, Despres C, Dickstein K, Lekakis J, McGregor K, Metra M, Morais J, Osterspey A, Zamorano JL (2006) ACC/AHA/ESC 2006 Guidelines for the Management of Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the European Society of Cardiology Committee for Practice Guidelines (Writing Committee to Revise the 2001 Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation): developed in collaboration with the European Heart Rhythm Association and the Heart Rhythm Society. Circulation 114:e257–e354
Camm AJ, Breithardt G, Crijns H, Dorian P, Kowey P, Le Heuzey JY, Merioua I, Pedrazzini L, Prystowsky EN, Schwartz PJ, Torp-Pedersen C, Weintraub W (2011) Real-life observations of clinical outcomes with rhythm- and rate-control therapies for atrial fibrillation RECORDAF (Registry on cardiac rhythm disorders assessing the control of atrial fibrillation). J Am Coll Cardiol 58:493–501
Jais P, Cauchemez B, Macle L, Daoud E, Khairy P, Subbiah R, Hocini M, Extramiana F, Sacher F, Bordachar P, Klein G, Weerasooriya R, Clementy J, Haissaguerre M (2008) Catheter ablation versus antiarrhythmic drugs for atrial fibrillation: the A4 study. Circulation 118:2498–2505
Wazni OM, Marrouche NF, Martin DO, Verma A, Bhargava M, Saliba W, Bash D, Schweikert R, Brachmann J, Gunther J, Gutleben K, Pisano E, Potenza D, Fanelli R, Raviele A, Themistoclakis S, Rossillo A, Bonso A, Natale A (2005) Radiofrequency ablation vs antiarrhythmic drugs as first-line treatment of symptomatic atrial fibrillation: a randomized trial. JAMA 293:2634–2640
Meinertz T, Kirch W, Rosin L, Pittrow D, Willich SN, Kirchhof P (2011) Management of atrial fibrillation by primary care physicians in Germany: baseline results of the ATRIUM registry. Clin Res Cardiol 100:897–905
Pappone C, Vicedomini G, Giuseppe A, Manguso F, Saviano M, Baldi M, Petretta A, Giannelli L, Calovic Z, Guluta V, Tavazzi L, Santinelli V. (2011) Radiofrequency catheter ablation and antiarrhythmic drug therapy: a prospective, randomized 4-year follow-up trial—the APAF study. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol
Cleland JG, Coletta AP, Buga L, Ahmed D, Clark AL (2010) Clinical trials update from the American College of Cardiology meeting 2010: DOSE, ASPIRE, CONNECT, STICH, STOP-AF, CABANA, RACE II, EVEREST II, ACCORD, and NAVIGATOR. Eur J Heart Fail 12:623–629
Calkins H, Reynolds MR, Spector P, Sondhi M, Xu Y, Martin A, Williams CJ, Sledge I (2009) Treatment of atrial fibrillation with antiarrhythmic drugs or radiofrequency ablation: two systematic literature reviews and meta-analyses. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 2:349–361
Morillo C, Verma A, Kuck KH, Champagne J, Nair G, Sterns L, Beresh H, Connolly S, Natale A (2012) Radiofrequency ablation Vs antiarrhythmic drugs as first-line treatment of symptomatic atrial fibrillation: (raaft 2): a randomized trial. Heart Rhythm Boston LB02-1
Jons C, Hansen PS, Johannessen A, Hindricks G, Raatikainen P, Kongstad O, Walfridsson H, Pehrson S, Almroth H, Hartikainen J, Petersen AK, Mortensen LS, Nielsen JC (2009) The medical antiarrhythmic treatment or radiofrequency ablation in paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (MANTRA-PAF) trial: clinical rationale, study design, and implementation. Europace 11:917–923
Cosedis Nielsen J, Johannessen A, Raatikainen P, Hindricks G, Walfridsson H, Kongstad O, Pehrson S, Englund A, Hartikainen J, Mortensen LS, Hansen PS (2012) Radiofrequency ablation as initial therapy in paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 367:1587–1595
Namdar M, Chierchia GB, Westra S, Sorgente A, Meir ML, Bayrak F, Rao JY, Ricciardi D, de Asmundis C, Sarkozy A, Smeets J, Brugada P (2012) Isolating the pulmonary veins as first-line therapy in patients with lone paroxysmal atrial fibrillation using the cryoballoon. Europace 14:197–203
Wasmer K, Kobe J, Dechering D, Milberg P, Pott C, Vogler J, Stypmann J, Waltenberger J, Monnig G, Breithardt G, Eckardt L (2013) CHADS(2) and CHA(2)DS (2)-VASc score of patients with atrial fibrillation or flutter and newly detected left atrial thrombus. Clin Res Cardiol 102(2):139–144. doi:10.1007/s00392-012-0507-4
Fichtner S, Deisenhofer I, Kindsmuller S, Dzijan-Horn M, Tzeis S, Reents T, Wu J, Luise Estner H, Jilek C, Ammar S, Kathan S, Hessling G, Ladwig KH (2012) Prospective assessment of short- and long-term quality of life after ablation for atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 23:121–127
Humphries KH, Kerr CR, Connolly SJ, Klein G, Boone JA, Green M, Sheldon R, Talajic M, Dorian P, Newman D (2001) New-onset atrial fibrillation: sex differences in presentation, treatment, and outcome. Circulation 103:2365–2370
de Vos CB, Pisters R, Nieuwlaat R, Prins MH, Tieleman RG, Coelen RJ, van den Heijkant AC, Allessie MA, Crijns HJ (2010) Progression from paroxysmal to persistent atrial fibrillation clinical correlates and prognosis. J Am Coll Cardiol 55:725–731
Ouyang F, Tilz R, Chun J, Schmidt B, Wissner E, Zerm T, Neven K, Kokturk B, Konstantinidou M, Metzner A, Fuernkranz A, Kuck KH (2010) Long-term results of catheter ablation in paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: lessons from a 5-year follow-up. Circulation 122:2368–2377
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest influenced by the article’s content.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix 1
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chun, K.R.J., Schmidt, B., Kuck, KH. et al. Catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation in the young: insights from the German Ablation Registry. Clin Res Cardiol 102, 459–468 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-013-0553-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-013-0553-6