Abstract
Arrhythmia induction during implantation of cardioverter defibrillators (ICD) is a standard procedure. However, controversy exists regarding the need for routine arrhythmia induction before discharge from hospital (pre-hospital discharge (PHD) test). In order to reduce the number of tests we identified risk factors that predict relevant ICD malfunction.
Methods and results
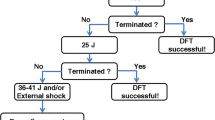
965 patients receiving a first device implantation (n = 724) or device/system replacement (n = 241) between 1998 and 2004 were analysed. During implantation 176 (18%) complications (intraoperative undersensing of induced arrhythmias, unsuccessful arrhythmia-therapy or low DFT safety margin) occurred. Frequent (> 4 times) intraoperative lead repositioning due to low sensing values was present in 44 patients (5%). 9% of the patients with first ICD implantation, 21% with device replacement and 27% with system replacement developed complications during PHD testing with arrhythmia induction. Intraoperative complications, although corrected during implantation, were independent risk factors for malfunction during PHD testing (p < 0.05). Additional predictors for malfunction were intraoperative lead repositioning (> 4 times) and a history of both VF and VT (p < 0.05). Patients without intraoperative complications rarely developed malfunction during PHD testing (3.7% first device, 6.25% system replacement). Only in patients undergoing device replacement was a higher risk for failure (13%) evident. No risk factors could be identified for these subgroups.
Conclusion
Routine arrhythmia induction during PHD is recommended in ICD patients with intraoperative complications, although corrected during implantation, as well as frequent intraoperatives lead repositioning. Patients undergoing device/ system replacement uncomplicated implantation are not generally at low risk for device failure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bardy GH, Lee KL, Mark DB et al (2005) Sudden Cardiac Death in Heart Failure Trial (SCD-HeFT) Investigators. Amiodarone or an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator for congestive heart failure. N Engl J Med 352:225–237
Bhandari AK, Isber N, Estioko M et al (1998) Efficacy of low-energy T wave shocks for induction of ventricular fibrillation in patients with implantable cardioverter defibrillators. J Electrocardiol 3:31–37
Brodsky CM, Chang F, Vlay SC (1999) Multicenter evaluation of implantable cardioverter defibrillator testing after implant: the Post Implant Testing Study (PITS). Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 22:1769–1776
Brunn J, Böcker D, Weber M et al (2000) Is there a need for routine testing of ICD defibrillator capacity? Eur Heart J 21:162–169
Buob A, Siaplaouras S, Tscholl D et al (2004) Clinical value of routine predischarge testing after ICD-implantation. Europace 6:159–164
Glikson M, Friedman P (2001) Routine arrhythmia inductions for ICD follow-up: are they obsolete? Clin Electrophysiol 24:915–920
Glikson M, Luria D, Friedman PA et al (2000) Are routine arrhythmia inductions necessary in patients with pectoral implantable cardioverter defibrillators? J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 11:127–135
Grubb BP, Durzinsky D, Brewster P et al (1997) Sudden cerebral vasoconstriction during induced polymorphic ventricular tachycardia and fibrillation: further observations of a paradoxic response. Pacing Clin Electrophysio 20:1667–1672
Higgins SL, Rich DH, Haygood JR et al (1998) ICD restudy: results and potential benefit from routine predischarge and 2-month evaluation. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 21:410–417
Hoffmann E, Steinbeck G (1998) Experience with pectoral versus abdominal implantation of a small defibrillator. A multicenter comparison in 778 patients. European Jewel Investigators. Eur Heart J 19:1085–1098
Meyer J, Mollhoff T, Seifert T et al (1996) Cardiac output is not affected during intraoperative testing of the automatic implantable cardioverter defibrillator. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 7:211–216
Moss AJ, Zareba W, Hall WJ et al (2002) For the Multicenter Automatic Defibrillator Implantation Trial II Investigators. Prophylactic implantation of a defibrillator in patients with myocardial infarction and reduced ejection fraction. N Engl J Med 346:877–883
Moss AJ, Hall WJ, Cannom DS et al (1996) For the multicenter automatic defibrillator implantation trial investigators. Improved survival with an implantable defibrillator in patients with coronary disease at high risk for ventricular arrhythmia. N Engl J Med 335:1933–1940
Murkin JM, Baird DL, Martzke JS et al (1997) Cognitive dysfunction after ventricular fibrillation during implantable cardiovertor/defibrillator procedures is related to duration of the reperfusion interval. Anesth Analg 84:1186–1192
The Antiarrhythmics Versus Implantable Defibrillator Investigators (1997) N Engl J Med 337:11576–11583
Wichter T, Paul M, Wollmann C et al (2004) Implantable cardioverter/defibrillator therapy in arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy: single-center experience of long-term follow-up and complications in 60 patients. Circulation 109:1503–1508
Wieckhorst A, Buchwald A, Unterberg C (1998) On the necessity of the invasive predischarge test after implantation of a cardioverter-defibrillator. Am J Cardiol 81:933–935
Winters SL, Packer DL, Marchlinski FE et al (2001) North American Society of Electrophysiology and Pacing. Consensus statement on indications, guidelines for use, and recommendations for follow-up of implantable cardioverter defibrillators. North American Society of Electrophysiology and Pacing. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 24:262–269
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Gudula Christ and Ruediger Becker contributed equally to this work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Christ, G., Becker, R., Voss, F. et al. Indications for predismissal testing with arrhythmia-induction in patients receiving an implantable cardioverter defibrillator. Clin Res Cardiol 96, 613–620 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-007-0541-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-007-0541-9