Abstract
Background
Cognitive decline (CD) and delirium (PD) are commonly observed complications after bypass heart surgery. In this study we aimed to investigate whether certain genetic factors (alleles of the SOAT-1 gene) play a role in their appearance.
Patients and methods
We examined 137 patients receiving coronary bypass surgery with a neuropsychiatric test battery consisting of the Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE), the Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale (BPRS), the Wechsler's Memory Scale-Revised (WMS-R) on admission and one month after surgery, and the Delirium Rating Scale postoperatively, when indicated, and genotyped them in relation to the SOAT–1 genotypes (AA positive group with augmented protection of the nerve cells against stress and the AA negative group – AC and CC subgroups – with diminished protection against stress).
Results
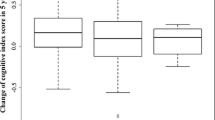
We noted a significant decline in test results postoperatively and a high frequency of delirium (29.92% of the patients). None of these complications could be associated to the SOAT-1 genotypes.
Conclusions
Our study confirmed the expected cognitive decline and highly frequent delirium after bypass heart surgery and excluded the possible role of SOAT-1 genotype polymorphisms in their genesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Elsasser A, Mollmann H, Nef HM, Hamm CW (2006) How to revascularize patients with diabetes mellitus: Bypass or stents and drugs? Clin Res Cardiol 95(4):195–203
Newman Mark F, Croughwell Nada D, Blumenthal James A et al (1995) Predictors of cognitive decline after cardiac operation. Ann Thorac Surg 59:1326–1330
Bucerius J, Gummert JF, Borger MA et al (2004) Predictors of delirium after cardiac surgery: effect of beating- heart (off pump) surgery. J Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery 127(1):7–9
Jung W, Meyerfeldt U, Birkemeyer R (2006) Atrial arrhythmias after cardiac surgery in patients with diabetes mellitus. Clin Res Cardiol 95(Suppl 1):i88–i97
Rolfson DB, Mac Elhaney JE, Rockwood H et al (1999) Incidence and risk factors for delirium and other adverse outcomes in older adults after coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Can J Cardiol 15(7):771–776
Tardiff BE, Newman MF , Saunders AM et al (1997) Preliminary report of a genetic basis for cognitive decline after cardiac operations. Ann Thorac Surg 64:715–720
Steed L, Kong R, Stygall J et al (2001) The role of apolipoprotein E in cognitive decline after cardiac operation. Ann of Thorac Surg 71:823–826
Lelis RG, Krieger JE, Pereira AC, Schmidt AP, Carmona MJ, Olivaira SA, Auler JO Jr (2006) Apolipoprotein E4 genotype imcreases the risk of postoperative cognitive dysfunction in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass graft surgery. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino) 47(4):451–456
Askar FZ, Cetin HY, Kumral E et al (2005) Apolipoprotein E epsilon 4 allele and neurobehavioral status after on- pump coronary artery bypass grafting. J Card Surg 20(5):501–505
Tagarakis GI, Tsolaki-Tagaraki F, Tsolaki M, Diegeler A, Papassotiropoulos A (2007) The role of apolipoprotein E in cognitive decline and delirium after bypass heart operations. Am J of Alzheimers Dis and Other Demen. June-July (in press)
Wollmer MA, Streffer JR, Tsolaki M, Grimaldi LM, Lutjohann D, Thal D, von Bergmann H, Nitsch RM, Hock C, Papassotiropoulos A (2003) Genetic association of acyl-coenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferase with cerebrospinal fluid cholesterol levels, brain amyloid load and risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Psychiatry 8(6):635–638
Puglielli L, Konopka G, Pack-Chung E, Ingano LA, Berezovska O, Hyman BT et al (2001) Acyl-coenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferase modulates the generation of the amyloid betapeptide. Nat Cell Biol 3:905–912
Zhao FG, Wang YH, Yang JF, Ma OZ, Tang Z, Dong XM, Chan P (2005) Association between acyl- coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase gene and risk for Alzheimer’s Disease in Chinese. Neuroscience Letters 388(1):17–20
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, Mac Hugh RR (1975) Mini Mental State: a practical method for grading the state of patients for the clinician. Journal of Psychiatric Research 12:189–198
Kessler J, Markowitsch HJ, Denzler P (1990) Der Mini Mental Status Test. Beltz, Weinheim
Wechsler D (1987) Wechsler Memory Scale Revised, S CP San Antonio, Texas: The Psychological Corporation – Harcourt Brace Jovanovich
Haerting C, Markowitsch HJ, Neufeld H, Calabrese P, Deisinger K, Kessler J (2000) Wechsler Gedächtnis Test – Revidierte Fassung (WMS-R), Huber, Bern
Ventura MA, Green MF, Shaner A, Liberman RP (1993) Training and quality assurance with the brief psychiatric rating scale: “The drift buster”. International Journal of Methods in Psychiatric Research 3:221– 244
Trzepacz PT, Baker RW, Greenhouse J (1988) A symptom rating scale for delirium. Psychiatry Research 23(1):89–97
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tagarakis, G.I., Tsolaki-Tagaraki, F., Tsolaki, M. et al. The role of SOAT-1 polymorphisms in cognitive decline and delirium after bypass heart surgery. Clin Res Cardiol 96, 600–603 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-007-0539-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-007-0539-3