Summary
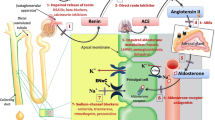
Hyperkalemia is a frequent disturbance. When hyperkalemia is associated with a rapid rise of the serum potassium concentration, the risk of cardiac impairment is greatest. Usually the cooperative action of several causative factors is required to bring about a hyperkalemia. They are often iatrogenic. Increasing age, diabetes mellitus, disorders of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone-system, high-dose antibiotics, and immunsuppressive treatments may result in hyperkalemia. The most important pathogenetic mechanisms are (1) renal insufficiency, (2) hyporeninemic hypoaldeosteronism, (3) tubular disorders, and (4) cellular disorders.
Zusammenfassung
Hyperkaliämie ist eine häufige und weiter zunehmende Erkrankung. Besonders der schnelle Anstieg der Kaliumkonzentration ist eine potentiell lebensbedrohliche Elektrolytstörung. Die Genese ist meist durch das Zusammentreffen mehrerer Faktoren bedingt. Diese sind nicht selten iatrogen verursacht. Zunehmendes Alter des Patienten, Diabetes mellitus, Störungen des Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosteron-Systems, antibiotische Hochdosistherapie und Immunsuppressiva sind Ursachen einer Hyperkaliämie. Pathophysiologisch stehen vier Mechanismen im Vordergrund: 1. Nierenfunktionsstörung, 2. Hyporeninämischer Hypoaldosteronismus, 3. tubuläre Störungen, 4. zelluläre Störungen.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Eingegangen: 30. August 1998 Akzeptiert: 3. September 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Franz, T., Gross, P. Neue Aspekte der Hyperkaliämie. Intensivmed 36, 361–366 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003900050252
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003900050252