Summary
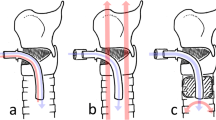
We report a 56 year old woman with a large, left-sided intracerebral hemorrhage. The patient is soporose; the gag and caugh reflexes are almost absent. After insertion of a fine-bore silicone nasogastric feeding tube, a right-sided pneumothorax is detected due to misplacement of the tube into the bronchial system. Over the next few days, the pneumothorax can be successfully treated with a pleural drainage without further complications.
We conclude that the clinical criteria for the proper position of gastric tubes are unreliable. Therefore, a routine chest X-ray is mandatory after placement of each nasogastric tube, in particular, if the patient is uncooperative or unconscious.
Zusammenfassung
Wir berichten über eine 56jährige Patientin mit einer großen intrazerebralen Blutung links parietal. Die Patientin ist soporös; die Schutzreflexe sind abgeschwächt. Beim Versuch, eine Magensonde zu legen, kommt es zur Fehlplazierung in die Lunge mit Pneumothorax rechts, der problemlos mit einer Pleuradrainage behandelt werden kann.
Klinische Kriterien sind zur Beurteilung der korrekten Lage einer Magensonde nicht ausreichend. Eine radiologische Lagekontrolle ist vor allem bei bewußtseinsgetrübten und unkooperativen Patienten nach jeder Anlage einer Magensonde erforderlich.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Eingegangen: 22. Januar 1998 Akzeptiert: 19. Februar 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schwarz, S., Mende, U. & Schwab, S. Pneumothorax nach Fehlplazierung einer Magensonde – Fallbericht. Intensivmed 35, 711–714 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003900050198
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003900050198