Summary
Background
The incidence of myocardial contusion (MC) after blunt chest trauma has been reported in 8.2 to 75% of trauma patients. We performed this study to report on the incidence of myocardial contusion in order to determine the frequency and to describe the type of complications in these patients.
Methods
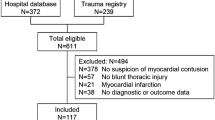
We conducted a retrospective analysis over a period of 3 years. There were 123 patients with a blunt chest trauma who were admitted to our hospital.
Results
Myocardial contusion occurred in 22 of our patients with blunt chest trauma (17.8%). In all these patients typical ECG-changes could be found during hospitalization (100%). The incidence of further pathological findings in the 22 patients were 23% for auscultation, 27% for cardiac enzymes (MB fraction) as well as 27% for the echocardiography. Cardiac complications, such as arrhythmia, cardiac failure or tamponade occurred in 17 patients (77%).
Conclusions
Early diagnosis of myocardial contusion in patients with blunt chest trauma is important to prevent and to treat possible complications. ECG controls have the highest sensivity to detect a MC, whereas cardiac enzymes and echocardiography seem to be poor markers of blunt myocardial injury.
Zusammenfassung
Hintergrund
Die Inzidenz einer Myokardkontusion (MK) nach einem stumpfen Thoraxtrauma liegt in der Literatur zwischen 8,2 und 75% der Trauma-Patienten. Wir haben diese Untersuchung durchgeführt, um die Inzidenz in unserem Patientengut zu bestimmen und um die Häufigkeit und die Art von Komplikationen bei diesen Patienten zu analysieren.
Methoden
Es wurde eine retrospektive Analyse über 3 Jahre vorgenommen. Wir untersuchten dabei 123 Patienten mit einem stumpfem Thoraxtrauma, die unserer Abteilung in diesem Zeitraum zugewiesen wurden.
Ergebnisse
Eine Myokardkontusion trat bei 22 unserer 123 Patienten mit stumpfem Thoraxtrauma auf. Bei allen diesen Patienten konnten während des Krankenhausaufenthaltes die typischen EKG-Veränderungen festgestellt werden (100%). Die Inzidenz weiterer pathologischer Befunde bei diesen 22 Patienten lag bei 23% für die Auskultation, 27% wiesen erhöhte CK-MB Werte auf und ebenfalls 27% einen pathologischen Echokardiographie-Befund. Kardiale Komplikationen wie Arrhythmien, Herzinsuffizienz und Tamponade traten bei 17 Patienten auf (77%).
Schlussfolgerungen
Eine frühe Diagnose ist bei Patienten mit stumpfem Thoraxtrauma wichtig, um mögliche Komplikationen zu behandeln oder sogar zu verhindern. EKG-Kontrollen haben die höchste Sensitivität, um eine MK zu diagnostizieren, wogegen “Herzenzyme“ und die Echokardiographie weniger sensitive Marker einer Myokardkontusion zu sein scheinen.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Präsentiert während des 6. Deutschen Interdisziplinären Kongresses für Intensivmedizin und Notfallmedizin (DIVI) in Hamburg
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Litmathe, J., Boeken, U., Gramsch-Zabel, H. et al. Auftreten einer Myokardkontusion bei 123 Patienten mit stumpfem Thoraxtrauma: Diagnostik und Ergebnisse. Intensivmed 40, 585–589 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00390-003-0402-3
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00390-003-0402-3