Abstract
Purpose
Appendectomy is one of the most frequently performed surgeries worldwide, but neurogenic appendicopathy (NA) remains a poorly understood disease with controversial clinical management. The aim of this review was to obtain a clear definition of the disease and summarize its management.
Methods
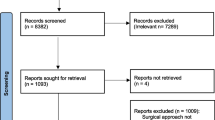
We performed a systematic review of the literature on NA in PubMed, EMBASE, Web of Science, and Cochrane databases from inception to 19/01/2021 according to PRISMA statement standards. Eligibility criteria were original articles examining histopathology, clinical management, and/or follow-up of patients with NA. The literature review is complemented by a clinical case.
Results
In 40 articles, the estimated incidence of NA among appendectomies performed in patients with a suspicion of acute appendicitis (AA) was 10.4% (N = 740, range 1.8-32%). NA more frequently causes recurrent and longer lasting pain compared to AA; however, these diseases are usually not clinically or radiologically distinguishable. Based on our analysis, NA is defined as the presence of three criteria: (1) clinical presentation of AA, (2) absence of acute inflammation on histopathology, and (3) presence of S-100-positive spindle cells or proliferation of Schwann cells. Laparoscopic appendectomy has been shown to be a safe and successful treatment.
Conclusions
NA is a poorly known disease, which may clinically appear as AA but is often related to recurrent and longer lasting abdominal pain. Patients with NA may suffer for years before diagnosis. In cases of typical symptoms, appendectomy should be performed even in cases of macroscopically and radiologically normal-appearing appendices with normal laboratory results.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stewart B, Khanduri P, McCord C, Ohene-Yeboah M, Uranues S, Vega Rivera F, Mock C (2014) Global disease burden of conditions requiring emergency surgery: global disease burden of conditions requiring emergency surgery. Br J Surg 101:e9–e22
Bhangu A, Søreide K, Di Saverio S, Assarsson JH, Drake FT (2015) Acute appendicitis: modern understanding of pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management. Lancet 386:1278–1287
Florence M, Flum DR, Jurkovich GJ, Lin P, Steele SR, Symons RG (2008) Negative appendectomy and imaging accuracy in the Washington state surgical care and outcomes assessment program. Trans Meet Am Surg Assoc 126:198–204
Chamisa I (2009) A clinicopathological review of 324 appendices removed for acute appendicitis in Durban, South Africa: a retrospective analysis. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 91:688–692
Tamini N, Santurro L, Chiappetta MF, Gattuso I, Barbieri C, Fattori L, Gianotti L (2020) Morbidity after negative appendectomy: a single-centre experience on 627 cases. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 46:859–864
Höfler H (1980) Neurogene Appendicopathie? Eine häufige aber selten diagnostizierte Krankheit. Langenbecks Arch Für Chir 351:171–178
Di Sebastiano P, Fink T, di Mola FF, Weihe E, Innocenti P, Friess H, Büchler MW (1999) Neuroimmune appendicitis. Lancet Lond Engl 354:461–466
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG (2010) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Int J Surg 8:336–341
Goossen K, Tenckhoff S, Probst P, Grummich K, Mihaljevic AL, Büchler MW, Diener MK (2018) Optimal literature search for systematic reviews in surgery. Langenbeck's Arch Surg 403:119–129
Murad MH, Sultan S, Haffar S, Bazerbachi F (2018) Methodological quality and synthesis of case series and case reports. BMJ Evid-Based Med 23:60–63
Higgins J, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page M (2019) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 6.0 (updated July 2019). Cochrane. https://training.cochrane.org/handbook/current. Accessed 09 February 2020
Aouad K, Clotteau JE, Prémont M, Lemaigre G (1994) Neurogenic appendicitis. A case. Presse Médicale Paris Fr 23:940–942
Auböck L, Ratzenhofer M (1982) “Extraepithelial enterochromaffin cell—nerve-fibre complexes” in the normal human appendix, and in neurogenic appendicopathy. J Pathol 136:217–226
Bernaschek W (1957) Neurogenic appendicitis with fusiform giant neuroma of the appendix. Zentralbl Chir 82:781–785
Bouchard S, Russo P, Radu AP, Adzick NS (2001) Expression of neuropeptides in normal and abnormal appendices. J Pediatr Surg 36:1222–1226
Chiari H (1952) Neurogenic appendicopathy. J Mt Sinai Hosp N Y 19:30–37
Coronini C, Kovac W, Lassmann G (1957) Die neurogene Appendicopathie, ein vegetativer Test für Klinik und Pathologie. Acta Neuroveg (Wien) 16:250–278
Doberauer W (1955) Neurogenic appendicitis in aged people. Klin Med Osterr Z Wiss Prakt Med 10:209–219
Fein MJ, Hanan JT, Seidler VB (1938) Plexiform neuroma of appendix. Am J Surg 39:27–33
Feyrter F (1958) Pathogenesis of attacks in neurogenic appendicitis (Masson). Bruns Beitr Klin Chir 197:433–437
Franke C, Gerharz CD, Böhner H, Ohmann C, Heydrich G, Krämling HJ, Stock W, Rosen D, Kurpreugsch K, Röher HD (2002) Neurogenic appendicopathy: a clinical disease entity? Int J Color Dis 17:185–191
Güller U, Oertli D, Terracciano L, Harder F (2001) Neurogene Appendicopathie: Ein häufiges, fast unbekanntes Krankheitsbild: Auswertung von 816. Appendices und Literaturübersicht Chir 72:684–689
Grebeldinger S, Radojcic B, Meljnikov I, Mocko-Kacanski M (2012) Neurogenic appendicopathy in pediatric patients: a clinical and histopathological entity. HealthMED 6:950–961
Höfler H, Heitz PU (1982) Neurogenic appendicopathy-an immunocytochemical study. Wien Klin Wochenschr 94:588–591
Höfler H, Kasper M, Heitz PU (1983) The neuroendocrine system of normal human appendix, ileum and colon, and in neurogenic appendicopathy. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol 399:127–140
Isaacson NH (1951) Neuroappendicopathy: review of the literature and report on fifty-two cases. AMA Arch Surg 62:455–466
Kapitonova MY, Aripin YM, Yusoff AR, Rashid AHA, Gupalo SP (2014) Distribution of Schwann cells in human appendix. Ann Anat 196:65
Knoflach JG, Wayand E (1951) Neurogenic appendicitis. Acta Neuroveg (Wien) 2:458–459
Lassmann G (1949) Zum Problem der neurogenen Appendizitis. Mikroskopie 4. Fromme, Vienna 277–290
Lassmann G (1950) Neurogenic appendicitis in the picture of neurovegetative-allergic diseases. Minerva Med 41:880–885
Lassmann G (1952) Terminale nervöse Struktur in der neurogenen Appendicopathie. Acta Neuroveg (Wien) 4:23–30
Maresch R (1928) Über das Vorkommen neuromartiger Bildungen in obliterierten Wurmfortsätzen. Wien Klin Wochenschr 34:181–182
Masson MP (1921) Les lésions nerveuses de l’appendicite chronique. C R Acad Sci:262–264
Michalany J (1976) Appendiceal neuromatosis (neurogenic appendicitis, nervous appendicopathy or the Masson neuro-appendicopathy). AMB Rev Assoc Med Bras 22:380–387
Müller HG (1952) Neurogenic appendicitis in gynecology. Zentralbl Gynakol 74:1653–1661
Naik R, Baliga P, Pai MR (1999) Neurogenic appendicopathy–role of enterochromaffin cells in its pathogenesis. Indian J Pathol Microbiol 42:279–281
Olsen BS, Holck S (1987) Neurogenous hyperplasia leading to appendiceal obliteration: an immunohistochemical study of 237 cases. Histopathology 11:843–849
Parker ML, Corrigan M (1941) The significance of neuromatous lesions in obliterated appendices: a clinicopathologic study. Ann Surg 114:424–440
Partecke LI, Thiele A, Schmidt-Wankel F, Kessler W, Wodny M, Dombrowski F, Heidecke CD, Von Bernstorff W (2013) Appendicopathy–a clinical and diagnostic dilemma. Int J Color Dis 28:1081–1089
Quell M, Horvath W (1987) Neurogenic appendicopathy–long-term results following appendectomy. Chirurg 58:597–600
Ratzenhofer M, Auböck L, Becker H (1969) Elekronen- und fluoreszenzmikroskopische Untersuchungen der Appendicite neurogene. Verh Dt Ges Path 53:218–224
Röper K (1952) Klinische und neurohistologische Studien über den Verlauf der Appendicopathia neuromatosa. Acta Neuroveg (Wien) 4:9–22
Ruiz J, Ríos A, Oviedo MI, Rodríguez JM, Parrilla P (2017) Neurogenic appendicopathy. A report of 8 cases. Rev Esp Enferm Dig 109:180–184
Sesia S, Mayr J, Bruder E, Haecker F-M (2013) Neurogenic appendicopathy: clinical, macroscopic, and histopathological presentation in pediatric patients. Eur J Pediatr Surg 23:238–242
Simard LC (1935) On the frequency of nervous lesions of the vermiform appendix: ‘neuro-appendicopathy’. Can Med Assoc J 33:518–521
Tatekawa H, Tanikake M, Yoshida S, Sato F, Kurata Y, Hayakawa K, Matsuo K, Tamaki N, Hino Y, Urata Y (2011) Multidetector CT findings of neurogenic appendicopathy. Eur J Radiol Extra 77:e47–e53
Triska H (1951) Remote sequels of appendectomy with special reference to neurogenic appendicitis. Wien Med Wochenschr 101:611–613
Wolf G, Stadler H, Höfler H (1981) Das klinische Bild der “neurogenen Appendikopathie”. Acta Chir Austriaca 13:25–29
Zdichavsky M, Gögele H, Blank G, Kraulich M, Meile T, von Feilitzsch M, Wichmann D, Königsrainer A (2013) Histological characterization of appendectomy specimens with intraoperative appearance of vascular injection. Surg Endosc 27:849–853
Jaschinski T, Mosch C, Eikermann M, Neugebauer EAM (2015) Laparoscopic versus open appendectomy in patients with suspected appendicitis: a systematic review of meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials. BMC Gastroenterol 15:48–57
Van den Broek WT, Bijnen AB, van Eerten PV, de Ruiter P, Gouma DJ (2000) Selective use of diagnostic laparoscopy in patients with suspected appendicitis. Surg Endosc 14:938–941
Van den Broek WT, Bijnen AB, de Ruiter P, Gouma DJ (2001) A normal appendix found during diagnostic laparoscopy should not be removed: diagnostic laparoscopy for suspected appendicitis. Br J Surg 88:251–254
Teh SH, O’Ceallaigh S, Mckeon JG, O’Donohoe MK, Tanner WA, Keane FB (2000) Should an appendix that looks ‘normal’ be removed at diagnostic laparoscopy for acute right iliac fossa pain? Eur J Surg 166:388–389
Roberts JK, Behravesh M, Dmitrewski J (2008) Macroscopic findings at appendicectomy are unreliable: implications for laparoscopy and malignant conditions of the appendix. Int J Surg Pathol 16:386–390
Chiarugi M, Buccianti P, Decanini L, Balestri R, Lorenzetti L, Franceschi M, Cavina E (2001) ‘What you see is not what you get’. A plea to remove a “normal” appendix during diagnostic laparoscopy. Acta Chir Belg 101:243–245
Singhal V, Jadhav V (2007) Acute appendicitis: are we over diagnosing it? Ann R Coll Surg Engl 89:766–769
Phillips AW, Jones AE, Sargen K (2009) Should the macroscopically normal appendix be removed during laparoscopy for acute right iliac fossa pain when no other explanatory pathology is found? Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 19:392–394
Emre A, Akbulut S, Bozdag Z, Yilmaz M, Kanlioz M, Emre R, Sahin N (2013) Routine histopathologic examination of appendectomy specimens: retrospective analysis of 1255 patients. Int Surg 98:354–362
Van Rossem CC, Treskes K, Loeza DL, van Geloven AAW (2014) Laparoscopic appendectomy for chronic right lower quadrant abdominal pain. Int J Color Dis 29:1199–1202
Roumen RMH, Groenendijk RPR, Sloots CEJ, Duthoi KES, Scheltinga MRM, Bruijninckx CMA (2007) Randomized clinical trial evaluating elective laparoscopic appendicectomy for chronic right lower-quadrant pain. Br J Surg 95:169–174
Greason KL, Rappold JF, Liberman MA (1998) Incidental laparoscopic appendectomy for acute right lower quadrant abdominal pain: its time has come. Surg Endosc 12:223–225
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BE conceived the presented idea. All authors participated in the conception and design of the paper. SP and OB performed the data acquisition, analysis, and interpretation. The manuscript was drafted by SP and then critically revised by OB and BE. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Statement to comply with ethical requirements
The presented patient and his legal guardian provided informed consent. Due to the nature of this paper, an approval from the local ethics committee was otherwise not required.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOC 63 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peisl, S., Burckhardt, O. & Egger, B. Neurogenic appendicopathy: an underestimated disease—systematic review of the literature. Int J Colorectal Dis 36, 1995–2005 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-021-03901-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-021-03901-1