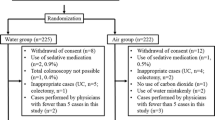
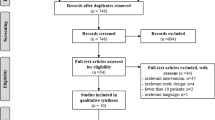
Abstract
Background
Carbon dioxide (CO2) has been used as an alternative to air insufflation at endoscopy with good results; however, uptake of the technique has been poor, possibly due to perceived lack of outcome equivalency. This meta-analysis evaluates the effectiveness of CO2 versus air in reducing pain post-colonoscopy and furthermore examines other key performance indicators (KPIs) such as sedative use, procedure times and polyp detection rates.
Methods
This meta-analysis was performed using the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines. Pubmed, Pubmed Central, Embase and Cochrane Library were searched for randomized studies from 2004 to 2019, reporting outcomes for patients undergoing colonoscopy with air or CO2 insufflation, who reported pain on a numerical or visual analogue scale (VAS). Results were reported as mean differences (MD) or pooled odds ratios (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (95% CI).
Results
Of 3586 citations, 23 studies comprising 3217 patients were analysed. Patients undergoing colonoscopy with air insufflation had 30% higher intraprocedural pain scores than those receiving CO2 (VAS 3.4 versus 2.6, MD -0.7, 95% CI − 1.4–0.0, p = 0.05), with a sustained beneficial effect amongst those in the CO2 group at 30 min, 1–2-h and 6-h post procedure (MD − 0.8, − 0.6 and − 0.2, respectively, p < 0.001 for all), as well as less distension, bloating and flatulence (p < 0.01 for all). There were no differences between the two groups in KPIs such as the sedation required, procedure time, caecal intubation or polyp detection rates.
Conclusions
CO2 insufflation improves patient comfort without compromising colonoscopic performance.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hoff G, Bretthauer M, Huppertz-Hauss G, Kittang E, Stallemo A, Hoie O, Dahler S, Nyhus S, Halvorsen FA, Pallenschat J, Vetvik K, Kristian Sandvei P, Friestad J, Pytte R, Coll P (2006) The Norwegian Gastronet project: continuous quality improvement of colonoscopy in 14 Norwegian centres. Scand J Gastroenterol 41:481–487
Bugajski M, Wieszczy P, Hoff G, Rupinski M, Regula J, Kaminski MF (2018) Modifiable factors associated with patient-reported pain during and after screening colonoscopy. Gut 67:1958–1964
Edwards BK, Ward E, Kohler BA, Eheman C, Zauber AG, Anderson RN, Jemal A, Schymura MJ, Lansdorp-Vogelaar I, Seeff LC, van Ballegooijen M, Goede SL, Ries LA (2010) Annual report to the nation on the status of cancer, 1975-2006, featuring colorectal cancer trends and impact of interventions (risk factors, screening, and treatment) to reduce future rates. Cancer 116:544–573
O'Donoghue D, Sheahan K, MacMathuna P, Stephens RB, Fenlon H, Morrin M, Mooney J, Fahy LE, Mooney T, Smith A (2019) A National Bowel Cancer Screening Programme using FIT: achievements and challenges. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 12:89–94
McLachlan SA, Clements A, Austoker J (2012) Patients’ experiences and reported barriers to colonoscopy in the screening context--a systematic review of the literature. Patient Educ Couns 86:137–146
Carter HG (1952) Explosion in the colon during electrodesiccation of polyps. Am J Surg 84:514–517
Hussein AM, Bartram CI, Williams CB (1984) Carbon dioxide insufflation for more comfortable colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc 30:68–70
Valori R, Rey JF, Atkin WS, Bretthauer M, Senore C, Hoff G, Kuipers EJ, Altenhofen L, Lambert R, Minoli G (2012) European guidelines for quality assurance in colorectal cancer screening and diagnosis. First Edition Quality assurance in endoscopy in colorectal cancer screening and diagnosis. Endoscopy 44:SE88–SE105
Janssens F, Deviere J, Eisendrath P, Dumonceau JM (2009) Carbon dioxide for gut distension during digestive endoscopy: technique and practice survey. World J Gastroenterol 15:1475–1479
Bretthauer M, Kalager M, Adami HO, Hoff G (2016) Who is for CO2? Slow adoption of carbon dioxide insufflation in colonoscopy. Ann Intern Med 165:145–146
Iida T, Okamura S, Kakizaki S, Sagawa T, Zhang Y, Kobayashi R, Masuo T, Mori M (2013) Carbon dioxide insufflation reduces the discomfort due to colonoscopy as objectively analyzed by salivary stress markers. Acta Gastro-Enterol Belg 76:219–224
Wong JC, Yau KK, Cheung HY, Wong DC, Chung CC, Li MK (2008) Towards painless colonoscopy: a randomized controlled trial on carbon dioxide-insufflating colonoscopy. ANZ J Surg 78:871–874
Geyer M, Guller U, Beglinger C (2011) Carbon dioxide insufflation in routine colonoscopy is safe and more comfortable: results of a randomized controlled double-blinded trial. Diagn Ther Endosc 2011:378906
Murakami K, Kataoka H, Hayano J, Fukuta H, Mori Y, Nishiwaki H, Mizoshita T, Tanaka M, Okamoto Y, Shimura T, Hirata Y, Mizushima T, Ebi M, Joh T (2016) Autonomic nervous responses in colorectal polypectomy: randomized controlled trial comparing air and carbon dioxide insufflation. Dig Endosc 28:203–209
Amato A, Radaelli F, Paggi S, Baccarin A, Spinzi G, Terruzzi V (2013) Carbon dioxide insufflation or warm-water infusion versus standard air insufflation for unsedated colonoscopy: a randomized controlled trial. Dis Colon Rectum 56:511–518
Bretthauer M, Seip B, Aasen S, Kordal M, Hoff G, Aabakken L (2007) Carbon dioxide insufflation for more comfortable endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: a randomized, controlled, double-blind trial. Endoscopy 39:58–56
Hsu WF, Hu WH, Chen YN, Lai HH, Chen MK, Chang LC, Tu CH, Chou CK, Wang HP, Wu MS, Chiu HM (2014) Carbon dioxide insufflation can significantly reduce toilet use after colonoscopy: a double-blind randomized controlled trial. Endoscopy 46:190–195
Szura M, Pach R, Matyja A, Kulig J (2015) Carbon dioxide insufflation during screening unsedated colonoscopy: a randomised clinical trial. Eur J Cancer Prev 24:37–43
Falt P, Smajstrla V, Fojtik P, Hill M, Urban O (2017) Carbon dioxide insufflation during colonoscopy in inflammatory bowel disease patients: a double-blind, randomized, single-center trial. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 29:355–359
Chen YJ, Lee J, Puryear M, Wong RK, Lake JM, Maydonovitch CL, Belle L, Moawad FJ (2014) A randomized controlled study comparing room air with carbon dioxide for abdominal pain, distention, and recovery time in patients undergoing colonoscopy. Gastroenterol Nurs 37:273–278
Kim SY, Chung JW, Park DK, Kwon KA, Kim KO, Kim YJ, Kim JH (2017) Comparison of carbon dioxide and air insufflation during consecutive EGD and colonoscopy in moderate-sedation patients: a prospective, double-blind, randomized controlled trial. Gastrointest Endosc 85:1255–1262
Chen PJ, Li CH, Huang TY, Shih YL, Chu HC, Chang WK, Hsieh TY (2013) Carbon dioxide insufflation does not reduce pain scores during colonoscope insertion in unsedated patients: a randomized, controlled trial. Gastrointest Endosc 77:79–89
Yamano HO, Yoshikawa K, Kimura T, Yamamoto E, Harada E, Kudou T, Katou R, Hayashi Y, Satou K (2010) Carbon dioxide insufflation for colonoscopy: evaluation of gas volume, abdominal pain, examination time and transcutaneous partial CO2 pressure. J Gastroenterol 45:1235–1240
Chen SW, Hui CK, Chang JJ, Lee TS, Chan SC, Chien CH, Hu CC, Lin CL, Chen LW, Liu CJ, Yen CL, Hsieh PJ, Liu CK, Su CS, Yu CY, Chien RN (2016) Carbon dioxide insufflation during colonoscopy can significantly decrease post-interventional abdominal discomfort in deeply sedated patients: a prospective, randomized, double-blinded, controlled trial. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 31:808–813
Seo EH, Kim TO, Park MJ, Kim HJ, Shin BC, Woo JG, Heo NY, Park J, Park SH, Yang SY et al (2013) The efficacy and safety of carbon dioxide insufflation during colonoscopy with consecutive esophagogastroduodenoscopy in moderately sedated outpatients: a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. J Clin Gastroenterol 47:e45–e49
Hsu WH, Sun MS, Lo HW, Tsai CY, Tsai YJ (2012) Carbon dioxide insufflation during withdrawal of the colonoscope improved postprocedure discomfort: a prospective, randomized, controlled trial. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 28:265–269
Feisthammel J, Trung KV, Hollenbach M, Mössner J, Hoffmeister A (2018) Is CO2 insufflation an amelioration of routine colonoscopy? Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol 64:193–200
Cleland A, Carryer J, La Grow S (2013) Carbon dioxide insufflation during colonoscopy: a randomised controlled trial. N Z Med J 126:87–94
Fernandez-Calderon M, Munoz-Navas MA, Carrascosa-Gil J, Betes-Ibanez MT, de-la Riva S, Prieto-de-Frias C, Herraiz-Bayod MT, Carretero-Ribon C (2012) Carbon dioxide vs. air insufflation in ileo-colonoscopy and in gastroscopy plus ileo-colonoscopy: a comparative study. Rev Esp Enferm Dig 104:237–241
Diez-Redondo P, Gil-Simon P, Alcaide-Suarez N, Atienza-Sanchez R, Barrio-Andres J, de-la Serna-Higuera C, Perez-Miranda M (2012) Comparison between insufflation with air or carbon dioxide during the colonoscopy in sedated patients with propofol. Rev Esp Enferm Dig 104:411–417
Riss S, Akan B, Mikola B, Rieder E, Karner-Hanusch J, Dirlea D, Mittlbock M, Weiser FA (2009) CO2 insufflation during colonoscopy decreases post-interventional pain in deeply sedated patients: a randomized controlled trial. Wien Klin Wochenschr 121:464–468
Singh R, Neo EN, Nordeen N, Shanmuganathan G, Ashby A, Drummond S, Nind G, Murphy E, Luck A, Tucker G, Tam W (2012) Carbon dioxide insufflation during colonoscopy in deeply sedated patients. World J Gastroenterol 18:3250–3253
Uraoka T, Kato J, Kuriyama M, Hori K, Ishikawa S, Harada K, Takemoto K, Hiraoka S, Fujita H, Horii J, Saito Y, Yamamoto K (2009) CO(2) insufflation for potentially difficult colonoscopies: efficacy when used by less experienced colonoscopists. World J Gastroenterol 15:5186–5192
Mayr M, Miller A, Gauger U, Rösch T (2012) CO2 versus air insufflation for private practice routine colonoscopy: results of a randomized double blind trial. Z Gastroenterol 50:445–448
Bretthauer M, Lynge AB, Thiis-Evensen E, Hoff G, Fausa O, Aabakken L (2005) Carbon dioxide insufflation in colonoscopy: safe and effective in sedated patients. Endoscopy 37:706–709
Hozo SP, Djulbegovic B, Hozo I (2005) Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med Res Methodol 5:13
Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ (2011) Chapter 7: selecting studies and collecting data. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (eds) (Eds) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5.1.0 (updated march 2011) The Cochrane Collaboration
Sajid MS, Caswell J, Bhatti MI, Sains P, Baig MK, Miles WF (2015) Carbon dioxide insufflation vs conventional air insufflation for colonoscopy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of published randomized controlled trials. Colorectal Dis 17:111–123
Wu J, Hu B (2012) The role of carbon dioxide insufflation in colonoscopy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endoscopy 44:128–136
Wang WL, Wu ZH, Sun Q, Wei JF, Chen XF, Zhou DK, Zhou L, Xie HY, Zheng SS (2012) Meta-analysis: the use of carbon dioxide insufflation vs. room air insufflation for gastrointestinal endoscopy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 35:1145–1154
Memon MA, Memon B, Yunus RM, Khan S (2016) Carbon dioxide versus air insufflation for elective colonoscopy: a meta-analysis and systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 26:102–116
Lo SK, Fujii-Lau LL, Enestvedt BK, Hwang JH, Konda V, Manfredi MA, Maple JT, Murad FM, Pannala R, Woods KL, Banerjee S (2016) The use of carbon dioxide in gastrointestinal endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc 83:857–865
Gabel G, Vogler S, Martens H (1991) Short-chain fatty acids and CO2 as regulators of Na+ and cl- absorption in isolated sheep rumen mucosa. J Comp Physiol B 161:419–426
Rutter MD, Chattree A, Barbour JA, Thomas-Gibson S, Bhandari P, Saunders BP, Veitch AM, Anderson J, Rembacken BJ, Loughrey MB, Pullan R, Garrett WV, Lewis G, Dolwani S (2015) British Society of Gastroenterology/Association of Coloproctologists of Great Britain and Ireland guidelines for the management of large non-pedunculated colorectal polyps. Gut 64:1847–1873
Early DS, Lightdale JR, Vargo JJ 2nd, Acosta RD, Chandrasekhara V, Chathadi KV, Evans JA, Fisher DA, Fonkalsrud L, Hwang JH, Khashab MA, Muthusamy VR, Pasha SF, Saltzman JR, Shergill AK, Cash BD, DeWitt JM, Committee ASoP (2018) Guidelines for sedation and anesthesia in GI endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc 87:327–337
Zhang Z, Wu Y, Sun G, Zhang J, Li J, Qiu C, Zheng X, Wang B, Yang L, Wang X (2018) Bayesian network meta-analysis: efficacy of air insufflation, CO2 insufflation, water exchange, and water immersion in colonoscopy. Dig Endosc 30:321–331
(2019) Trial protocol: comparisons of SWI, WWI and CI in potentially difficult colonoscopy. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03571061. Shenzhen People’s Hospital, China. Accessed 2 June 2019
Anderson J (2019) Water immersion and polyp detection: a randomized controlled trial - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.gov.
Cheng C-L (2019) Right colon polyp miss rates of water exchange and carbon dioxide insufflation colonoscopy - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.gov.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Figure 1
Forest plots for meta-analysis results of effects of CO2 versus air insufflation during colonoscopy on key performance indicators. A) Sedative approach – propofol. B) Sedative approach – midazolam. C) Procedure time. D) Caecal intubation time. E) Polyp detection rate. F) Polypectomy rate (PNG 129 kb)
ESM 1
(PNG 127 kb)
ESM 2
(PNG 202 kb)
ESM 3
(PNG 163 kb)
ESM 4
(PNG 129 kb)
ESM 5
(PNG 129 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rogers, A.C., Van De Hoef, D., Sahebally, S.M. et al. A meta-analysis of carbon dioxide versus room air insufflation on patient comfort and key performance indicators at colonoscopy. Int J Colorectal Dis 35, 455–464 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-019-03470-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-019-03470-4