Abstract
Purpose
Bacterial infections are a factor for morbidity in patients with acute appendicitis (AA). The spreading of multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria is a significant problem in surgery, and the most relevant MDR pathogens are summarized as Enterobacteriaceae, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Enterococci (ESKAPE) bacteria. Data regarding the species and distribution of bacteria in AA are available, but information about the resistances and their relevance is deficient.
Methods
In this retrospective study, we analyzed microbiological swabs of patients with AA. The outcome parameters of patients after laparoscopic appendectomy were analyzed against microbiological results, including antibiotic resistance testing. Positive swabs were compared with bacteria cultivated after alternative abdominal emergency surgery (AES).
Results
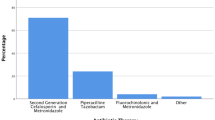
In total, 584 patients with AA were included and had a mean age of 35.5 years. In 216 patients (36.9%), a swab was taken, and in 128 (59.3%) swabs, bacteria could be cultivated. The most frequent organisms were Escherichia coli, Bacteroides species, and Pseudomonas. In 9.4% of the positive AA swabs, MDR germs were cultivated, and all of them were ESKAPE pathogens. Patients with MDR bacteria in AA suffered more infectious complications (p = 0.006) and needed longer hospitalizations (p < 0.009). In AES, aside from appendicitis, a different spectrum containing more MDR bacteria was cultivated (5.9 vs. 20.9%; p < 0.0001).
Conclusions
Although they occur less frequently in appendectomy compared to emergency surgeries for other abdominal diseases, MDR bacteria are traceable in this common disease and contribute to additional morbidity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen BR, Kallehave FL, Andersen HK (2003) Antibiotics versus placebo for prevention of postoperative infection after appendicectomy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2:CD001439. doi:10.1002/14651858.cd001439
Fagenholz PJ, Peev MP, Thabet A, Michailidou M, Chang Y, Mueller PR, Hahn PF, Velmahos GC (2015) Abscess due to perforated appendicitis: factors associated with successful percutaneous drainage. Am J Surg. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2015.07.017
Garg CP, Vaidya BB, Chengalath MM (2009) Efficacy of laparoscopy in complicated appendicitis. Int J Surg 7(3):250–252. doi:10.1016/j.ijsu.2009.04.007
Taguchi Y, Komatsu S, Sakamoto E, Norimizu S, Shingu Y, Hasegawa H (2016) Laparoscopic versus open surgery for complicated appendicitis in adults: a randomized controlled trial. Surg Endosc 30(5):1705–1712. doi:10.1007/s00464-015-4453-x
Bodmann KF, und die Expertenkommission der I (2010) Complicated intra-abdominal infections: pathogens, resistance. Recommendations of the Infectliga on antbiotic therapy. Chirurg 81(1):38–49. doi:10.1007/s00104-009-1822-9
Solomkin JS, Mazuski JE, Bradley JS, Rodvold KA, Goldstein EJ, Baron EJ, O’Neill PJ, Chow AW, Dellinger EP, Eachempati SR, Gorbach S, Hilfiker M, May AK, Nathens AB, Sawyer RG, Bartlett JG (2010) Diagnosis and management of complicated intra-abdominal infection in adults and children: guidelines by the Surgical Infection Society and the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Surg Infect 11(1):79–109. doi:10.1089/sur.2009.9930
Gorter RR, Eker HH, Gorter-Stam MA, Abis GS, Acharya A, Ankersmit M, Antoniou SA, Arolfo S, Babic B, Boni L, Bruntink M, van Dam DA, Defoort B, Deijen CL, DeLacy FB, Go PM, Harmsen AM, van den Helder RS, Iordache F, Ket JC, Muysoms FE, Ozmen MM, Papoulas M, Rhodes M, Straatman J, Tenhagen M, Turrado V, Vereczkei A, Vilallonga R, Deelder JD, Bonjer J (2016) Diagnosis and management of acute appendicitis. EAES consensus development conference 2015. Surg Endosc. doi:10.1007/s00464-016-5245-7
Davies HO, Alkhamesi NA, Dawson PM (2010) Peritoneal fluid culture in appendicitis: review in changing times. Int J Surg 8(6):426–429. doi:10.1016/j.ijsu.2010.06.016
Coccolini F, D’Amico G, Sartelli M, Catena F, Montori G, Ceresoli M, Manfredi R, Di Saverio S, Ansaloni L (2016) Antibiotic resistance evaluation and clinical analysis of acute appendicitis; report of 1431 consecutive worldwide patients: a cohort study. Int J Surg 26:6–11. doi:10.1016/j.ijsu.2015.12.063
Boucher HW, Talbot GH, Bradley JS, Edwards JE, Gilbert D, Rice LB, Scheld M, Spellberg B, Bartlett J (2009) Bad bugs, no drugs: no ESKAPE! An update from the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis 48(1):1–12. doi:10.1086/595011
Dimopoulos G, Kollef MH, Cohen J (2016) In 2035, will all bacteria be multiresistant? Yes Intensive Care Med. doi:10.1007/s00134-016-4310-y
Lodise TP, McKinnon PS, Levine DP, Rybak MJ (2007) Impact of empirical-therapy selection on outcomes of intravenous drug users with infective endocarditis caused by methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 51(10):3731–3733. doi:10.1128/AAC.00101-07
Pletz MW, Eckmann C, Hagel S, Heppner HJ, Huber K, Kämmerer W, Schmitz FJ, Wilke M, Grabein B (2015) Current strategies against multi-drug resistant organisms. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 140(13):975–981. doi:10.1055/s-0041-102452
McNamara MJ, Pasquale MD, Evans SR (1993) Acute appendicitis and the use of intraperitoneal cultures. Surg Gynecol Obstet 177(4):393–397
Gladman MA, Knowles CH, Gladman LJ, Payne JG (2004) Intra-operative culture in appendicitis: traditional practice challenged. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 86(3):196–201. doi:10.1308/003588404323043346
Kokoska ER, Silen ML, Tracy TF Jr, Dillon PA, Kennedy DJ, Cradock TV, Weber TR (1999) The impact of intraoperative culture on treatment and outcome in children with perforated appendicitis. J Pediatr Surg 34(5):749–753
Lob SH, Badal RE, Bouchillon SK, Hawser SP, Hackel MA, Hoban DJ (2013) Epidemiology and susceptibility of Gram-negative appendicitis pathogens: SMART 2008-2010. Surg Infect 14(2):203–208. doi:10.1089/sur.2012.034
Delgado-Rodriguez M, Sillero-Arenas M, Medina-Cuadros M, Martinez-Gallego G (1997) Nosocomial infections in surgical patients: comparison of two measures of intrinsic patient risk. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 18(1):19–23
Charlson ME, Pompei P, Ales KL, MacKenzie CR (1987) A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation. J Chronic Dis 40(5):373–383
Linder MM, Wacha H, Feldmann U, Wesch G, Streifensand RA, Gundlach E (1987) The Mannheim peritonitis index. An instrument for the intraoperative prognosis of peritonitis. Chirurg 58(2):84–92
Bhangu A, Soreide K, Di Saverio S, Assarsson JH, Drake FT (2015) Acute appendicitis: modern understanding of pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management. Lancet 386(10000):1278–1287. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00275-5
Foo FJ, Beckingham IJ, Ahmed I (2008) Intra-operative culture swabs in acute appendicitis: a waste of resources. Surgeon 6(5):278–281
Sartelli M, Weber DG, Ruppé E, Bassetti M, Wright BJ, Ansaloni L, Catena F, Coccolini F, Abu-Zidan FM, Coimbra R, Moore EE, Moore FA, Maier RV, De Waele JJ, Kirkpatrick AW, Griffiths EA, Eckmann C, Brink AJ, Mazuski JE, May AK, Sawyer RG, Mertz D, Montravers P, Kumar A, Roberts JA, Vincent JL, Watkins RR, Lowman W, Spellberg B, Abbott IJ, Adesunkanmi AK, Al-Dahir S, Al-Hasan MN, Agresta F, Althani AA, Ansari S, Ansumana R, Augustin G, Bala M, Balogh ZJ, Baraket O, Bhangu A, Beltrán MA, Bernhard M, Biffl WL, Boermeester MA, Brecher SM, Cherry-Bukowiec JR, Buyne OR, Cainzos MA, Cairns KA, Camacho-Ortiz A, Chandy SJ, Che Jusoh A, Chichom-Mefire A, Colijn C, Corcione F, Cui Y, Curcio D, Delibegovic S, Demetrashvili Z, De Simone B, Dhingra S, Diaz JJ, Di Carlo I, Dillip A, Di Saverio S, Doyle MP, Dorj G, Dogjani A, Dupont H, Eachempati SR, Enani MA, Egiev VN, Elmangory MM, Ferrada P, Fitchett JR, Fraga GP, Guessennd N, Giamarellou H, Ghnnam W, Gkiokas G, Goldberg SR, Gomes CA, Gomi H, Guzmán-Blanco M, Haque M, Hansen S, Hecker A, Heizmann WR, Herzog T, Hodonou AM, Hong SK, Kafka-Ritsch R, Kaplan LJ, Kapoor G, Karamarkovic A, Kees MG, Kenig J, Kiguba R, Kim PK, Kluger Y, Khokha V, Koike K, Kok KY, Kong V, Knox MC, Inaba K, Isik A, Iskandar K, Ivatury RR, Labbate M, Labricciosa FM, Laterre PF, Latifi R, Lee JG, Lee YR, Leone M, Leppaniemi A, Li Y, Liang SY, Loho T, Maegele M, Malama S, Marei HE, Martin-Loeches I, Marwah S, Massele A, McFarlane M, Melo RB, Negoi I, Nicolau DP, Nord CE, Ofori-Asenso R, Omari AH, Ordonez CA, Ouadii M, Pereira Júnior GA, Piazza D, Pupelis G, Rawson TM, Rems M, Rizoli S, Rocha C, Sakakhushev B, Sanchez-Garcia M, Sato N, Segovia Lohse HA, Sganga G, Siribumrungwong B, Shelat VG, Soreide K, Soto R, Talving P, Tilsed JV, Timsit JF, Trueba G, Trung NT, Ulrych J, van Goor H, Vereczkei A, Vohra RS, Wani I, Uhl W, Xiao Y, Yuan KC, Zachariah SK, Zahar JR, Zakrison TL, Corcione A, Melotti RM, Viscoli C, Viale P (2016) Antimicrobials: a global alliance for optimizing their rational use in intra-abdominal infections (AGORA). World J Emerg Surg 11:33. doi:10.1186/s13017-016-0089-y
Bayhan G, Tanır G, Karaman I, Ozkan S (2013) Comamonas testosteroni: an unusual bacteria associated with acute appendicitis. Balkan Med J 30(4):447–448. doi:10.5152/balkanmedj.2013.9135
Gul M, Ciragil P, Bulbuloglu E, Aral M, Alkis S, Ezberci F (2007) Comamonas testosteroni bacteremia in a patient with perforated acute appendicitis. Short communication. Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung 54(3):317–321. doi:10.1556/AMicr.54.2007.3.6
Lob SH, Badal RE, Hackel MA, Sahm DF (2016) Epidemiology and antimicrobial susceptibility of Gram-negative pathogens causing intra-abdominal infections in pediatric patients in Europe-SMART 2011-2014. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. doi:10.1093/jpids/piv109
Mazuski JE (2007) Antimicrobial treatment for intra-abdominal infections. Expert Opin Pharmacother 8(17):2933–2945. doi:10.1517/14656566.8.17.2933
Dworniczek E, Piwowarczyk J, Bania J, Kowalska-Krochmal B, Walecka E, Seniuk A, Dolna I, Gosciniak G (2012) Enterococcus in wound infections: virulence and antimicrobial resistance. Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung 59(2):263–269. doi:10.1556/AMicr.59.2012.2.11
Mangram AJ, Horan TC, Pearson ML, Silver LC, Jarvis WR (1999) Guideline for Prevention of Surgical Site Infection, 1999. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Hospital Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee. Am J Infect Control 27(2):97–132 quiz 133-134; discussion 196
Harbarth S, Uckay I (2004) Are there patients with peritonitis who require empiric therapy for Enterococcus? Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 23(2):73–77. doi:10.1007/s10096-003-1078-0
Burnett RJ, Haverstock DC, Dellinger EP, Reinhart HH, Bohnen JM, Rotstein OD, Vogel SB, Solomkin JS (1995) Definition of the role of Enterococcus in intraabdominal infection: analysis of a prospective randomized trial. Surgery 118(4):716–721 discussion 721-713
Moawad MR, Dasmohapatra S, Justin T, Keeling N (2006) Value of intraoperative abdominal cavity culture in appendicectomy: a retrospective study. Int J Clin Pract 60(12):1588–1590. doi:10.1111/j.1742-1241.2005.00774.x
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 43 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reinisch, A., Malkomes, P., Habbe, N. et al. Bad bacteria in acute appendicitis: rare but relevant. Int J Colorectal Dis 32, 1303–1311 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-017-2862-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-017-2862-0