Abstract
Purpose
The biologic significance of low-level microsatellite instability (MSI) in sporadic colorectal cancers (CRCs) is not clearly defined. In particular, the relationship of MSI-low to MSI-high and microsatellite stable (MSS) tumours is currently under debate and the prognostic impact of these genetic changes remains unclear. The objective of this study was to investigate whether sporadic MSI-low CRCs have different clinicopathological and molecular features from MSS and MSI-high tumours.
Methods
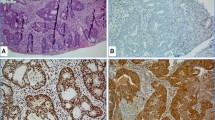
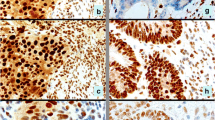
A series of 184 primary sporadic CRCs were divided, according to the level of MSI, into three groups (94 MSS, 22 MSI-low and 68 MSI-high) and were analyzed for baseline clinicopathological features and outcome, allelic losses at 18q, 8p and 4p chromosomes and immunohistochemical expression of MGMT, hMlh1, hMsh2, Fhit, Cox-2, p21 and p27 proteins.
Results
MSI-low tumours were more frequently distal (59.1%) whereas MSS tumours had a strong predilection for distal (72.3%) and MSI-high tumours for proximal location (54.4%; p = 0.003). When compared with MSI-high tumors, MSI-low CRCs were adenocarcinoma, not otherwise specified (p = 0.0138) and well to/moderately differentiated (p = 0.027). MSI-low CRCs also showed specific molecular features including intermediate 18q allelic losses, altered MGMT and Cox-2 expression. Finally, the 5-year overall survival rates were 79% for MSI-low, 40.3% for MSS and 71% for MSI-high CRCs (p = 0.0160 MSS vs. MSI-low groups).
Conclusions
Sporadic MSI-low CRCs display characteristic clinicopathological and genetic features that distinguish them from MSS CRCs.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chapuis PH, Dent OF, Fisher R, Newland RC, Pheils MT, Smyth E, Colquhoun K (1985) A multivariate analysis of clinical and pathological variables in prognosis after resection of large bowel cancer. Br J Surg 72:698–702
Offit K (2000) Genetic prognostic markers for colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 342:124–125
Lengauer C, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B (1997) Genetic instability in colorectal cancers. Nature 386:623–627
Aaltonen LA, Peltomäki P, Leach FS, Sistonen P, Pylkkänen L, Mecklin JP, Järvinen H, Powell SM, Jen J, Hamilton SR et al (1993) Clues to the pathogenesis of familial colorectal cancer. Science 260:812–816
Thibodeau SN, Bren G, Schaid D (1993) Microsatellite instability in cancer of the proximal colon. Science 260:816–819
Umar A, Boland C, Terdiman J, Syngal S, de la Chapelle A, Rüschoff J, Fishel R, Lindor N, Burgart L, Hamelin R, Hamilton S, Hiatt R, Jass J, Lindblom A, Lynch H, Peltomaki P, Ramsey S, Rodriguez-Bigas M, Vasen H, Hawk E, Barrett J, Freedman A, Srivastava S (2004) Revised Bethesda guidelines for hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (Lynch syndrome) and microsatellite instability. J Natl Cancer Inst 96:261–268
Aaltonen LA, Salovaara R, Kristo P, Canzian F, Hemminki A, Peltomäki P, Chadwick RB, Kääriäinen H, Eskelinen M, Järvinen H, Mecklin JP, de la Chapelle A (1998) Incidence of hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer and the feasibility of molecular screening for the disease. N Engl J Med 338:1481–1487
Asaka S, Arai Y, Nishimura Y, Yamaguchi K, Ishikubo T, Yatsuoka T, Tanaka Y, Akagi K (2009) Microsatellite instability-low colorectal cancer acquires a KRAS mutation during the progression from Dukes' A to Dukes' B. Carcinogenesis 30:494–499
Kohonen-Corish MR, Daniel JJ, Chan C, Lin BP, Kwun SY, Dent OF, Dhillon VS, Trent RJ, Chapuis PH, Bokey EL (2005) Low microsatellite instability is associated with poor prognosis in stage C colon cancer. J Clin Oncol 23:2318–2324
Halford SE, Sawyer EJ, Lambros MB, Gorman P, Macdonald ND, Talbot IC, Foulkes WD, Gillett CE, Barnes DM, Akslen LA, Lee K, Jacobs IJ, Hanby AM, Ganesan TS, Salvesen HB, Bodmer WF, Tomlinson IP, Roylance RR (2003) MSI-low, a real phenomenon which varies in frequency among cancer types. J Pathol 201:389–394
Biden KG, Simms LA, Cummings M, Buttenshaw R, Schoch E, Searle J, Gobe G, Jass JR, Meltzer SJ, Leggett BA, Young J (1999) Expression of Bcl-2 protein is decreased in colorectal adenocarcinomas with microsatellite instability. Oncogene 18:1245–1249
Wright CM, Dent OF, Newland RC, Barker M, Chapuis PH, Bokey EL, Young JP, Leggett BA, Jass JR, Macdonald GA (2005) Low level microsatellite instability may be associated with reduced cancer specific survival in sporadic stage C colorectal carcinoma. Gut 54:103–108
Sarli L, Bottarelli L, Bader G, Iusco D, Pizzi S, Costi R, D'adda T, Bertolani M, Roncoroni L, Bordi C (2004) Association between recurrence of sporadic colorectal cancer, high level of microsatellite instability, and loss of heterozygosity at chromosome 18q. Dis Colon Rectum 47:1467–1482
Wright CM, Dent OF, Barker M, Newland RC, Chapuis PH, Bokey EL, Young JP, Leggett BA, Jass JR, Macdonald GA (2000) Prognostic significance of extensive microsatellite instability in sporadic clinicopathological stage C colorectal cancer. Br J Surg 87:1197–1202
Halling KC, French AJ, McDonnell SK, Burgart LJ, Schaid DJ, Peterson BJ, Moon-Tasson L, Mahoney MR, Sargent DJ, O'Connell MJ, Witzig TE, Farr GHJ, Goldberg RM, Thibodeau SN (1999) Microsatellite instability and 8p allelic imbalance in stage B2 and C colorectal cancers. J Natl Cancer Inst 91:1295–1303
Ward R, Meagher A, Tomlinson I, O'Connor T, Norrie M, Wu R, Hawkins N (2001) Microsatellite instability and the clinicopathological features of sporadic colorectal cancer. Gut 48:821–829
Mori Y, Selaru FM, Sato F, Yin J, Simms LA, Xu Y, Olaru A, Deacu E, Wang S, Taylor JM, Young J, Leggett B, Jass JR, Abraham JM, Shibata D, Meltzer SJ (2003) The impact of microsatellite instability on the molecular phenotype of colorectal tumors. Cancer Res 63:4577–4582
Guda K, Upender MB, Belinsky G, Flynn C, Nakanishi M, Marino JN, Ried T, Rosenberg DW (2004) Carcinogen-induced colon tumors in mice are chromosomally stable and are characterized by low-level microsatellite instability. Oncogene 23:3813–3821
Rudzki Z, Zazula M, Okon K, Stachura J (2003) Low-level microsatellite instability colorectal carcinomas: do they really belong to a “gray zone” between high-level microsatellite instability and microsatellite-stable cancers? Int J Colorectal Dis 18:216–221
Jass JR, Biden KG, Cummings MC, Simms LA, Walsh M, Schoch E, Meltzer SJ, Wright C, Searle J, Young J, Leggett BA (1999) Characterisation of a subtype of colorectal cancer combining features of the suppressor and mild mutator pathways. J Clin Pathol 52:455–460
Whitehall VL, Walsh MD, Young J, Leggett BA, Jass JR (2001) Methylation of O-6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase characterizes a subset of colorectal cancer with low-level DNA microsatellite instability. Cancer Res 61:827–830
Kominami K, Nagasaka T, Cullings HM, Hoshizima N, Sasamoto H, Young J, Leggett BA, Tanaka N, Matsubara N (2009) Methylation in p14(ARF) is frequently observed in colorectal cancer with low-level microsatellite instability. J Int Med Res 37:1038–1045
Tomlinson I, Halford S, Aaltonen L, Hawkins N, Ward R (2002) Does MSI-low exist? J Pathol 197:6–13
Cheng JD, Werness BA, Babb JS, Meropol NJ (1999) Paradoxical correlation of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors p21 waf1/cip1 and p27kip1 in metastatic colorectal carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 5:1057–1062
McKay JA, Douglas JJ, Ross VG, Curran S, Loane JF, Ahmed FY, Cassidy J, McLeod HL, Murray GI (2002) Analysis of key cell-cycle checkpoint proteins in colorectal tumours. J Pathol 196:386–393
Sarli L, Bottarelli L, Azzoni C, Campanini N, Di Cola G, Bader G, Iusco D, Salvemini C, Caruso G, Donadei E, Pizzi S, D'Adda T, Costi R, Roncoroni L, Bordi C (2004) Abnormal Fhit protein expression and high frequency of microsatellite instability in sporadic colorectal cancer. Eur J Cancer 40:1581–1588
Sheehan KM, O'Connell F, O'Grady A, Conroy RM, Leader MB, Byrne MF, Murray FE, Kay EW (2004) The relationship between cyclooxygenase-2 expression and characteristics of malignant transformation in human colorectal adenomas. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 16:619–625
Jass JR, Sobin LH (1989) Histological typing of intestinal tumours. Springer, Berlin
Sobin LH, Wittekind CH (eds) (1997) TNM classification of malignant tumours, 5th edn. Wiley-Liss, New York
Jen J, Kim H, Piantadosi S, Liu ZF, Levitt RC, Sistonen P, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, Hamilton SR (1994) Allelic loss of chromosome 18q and prognosis in colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 331:213–221
Samowitz WS, Slattery ML, Potter JD, Leppert MF (1999) BAT-26 and BAT-40 instability in colorectal adenomas and carcinomas and germline polymorphisms. Am J Pathol 154:1637–1641
Arribas R, Ribas M, Risques RA, Masramon L, Tórtola S, Marcuello E, Aiza G, Miró R, Capellà G, Peinado MA (1999) Prospective assessment of allelic losses at 4p14-16 in colorectal cancer: two mutational patterns and a locus associated with poorer survival. Clin Cancer Res 5:3454–3459
Mueller JD, Haegle N, Keller G, Mueller E, Saretzky G, Bethke B, Stolte M, Hofler H (1998) Loss of heterozygosity and microsatellite instability in de novo versus ex-adenoma carcinomas of the colorectum. Am J Pathol 153:1977–1984
Beckmann MW, Picard F, An HX, van Roeyen CR, Dominik SI, Mosny DS, Schnurch HG, Bender HG, Niederacher D (1996) Clinical impact of detection of loss of heterozygosity of BRCA1 and BRCA2 markers in sporadic breast cancer. Br J Cancer 73:1220–1226
Huang L, Jiang T, Yuan F, Li GL, Cui Y, Liu EZ, Wang ZC (2008) Correlation of chromosome 1p and 19q status and expression of MGMT, p53 and Ki-67 in diffuse gliomas of WHO grade II and III: a clinicopathological study. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 35:367–379
Sarli L, Bottarelli L, Azzoni C, Campanini N, Di Cola G, Barilli AL, Marchesi F, Mazzeo A, Salvemini C, Morari S, Di Mauro D, Donadei E, Necchi F, Roncoroni L, Bordi C (2006) Loss of p27 expression and microsatellite instability in sporadic colorectal cancer. Surg Oncol 15:97–106
Ogino S, Kawasaki T, Kirkner GJ, Ogawa A, Dorfman I, Loda M, Fuchs CS (2006) Down-regulation of p21 (CDKN1A/CIP1) is inversely associated with microsatellite instability and CpG island methylator phenotype (CIMP) in colorectal cancer. J Pathol 210:147–154
Lim HY, Joo HJ, Choi JH, Yi JW, Yang MS, Cho DY, Kim HS, Nam DK, Lee KB, Kim HC (2000) Increased expression of cyclooxygenase-2 protein in human gastric carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 6:519–525
Tuppurainen K, Makinen JM, Junttila O, Liakka A, Kyllönen AP, Tuominen H, Karttunen TJ, Mäkinen MJ (2005) Morphology and microsatellite instability in sporadic serrated and non-serrated colorectal cancer. J Pathol 207:285–294
Kim YH, Min BH, Choi HK, Kim SJ, Kim KM, Kim JY, Chang DK, Son HJ, Rhee PL, Kim JJ, Rhee JC, Chun HK (2009) Sporadic colorectal carcinomas with low-level microsatellite instability in Korea: do they form a distinct subgroup with distinguished clinicopathological features? J Surg Oncol 99:351–355
Esteller M, Risques RA, Toyota M, Capella G, Moreno V, Peinado MA, Baylin SB, Herman JG (2001) Promoter hypermethylation of the DNA repair gene O(6)-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase is associated with the presence of G:C to A:T transition mutations in p53 in human colorectal tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 61:4689–4692
Brabender J, Usadel H, Metzger R, Schneider PM, Park J, Salonga D, Tsao-Wei DD, Groshen S, Lord RV, Takebe N, Schneider S, Hölscher AH, Danenberg KD, Danenberg PV (2003) Quantitative O(6)-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase methylation analysis in curatively resected non-small cell lung cancer: associations with clinical outcome. Clin Cancer Res 9:223–227
Dietmaier W, Wallinger S, Bocker T, Kullmann F, Fishel R, Rüschoff J (1997) Diagnostic microsatellite instability: definition and correlation with mismatch repair protein expression. Cancer Res 57:4749–4756
Oliart S, Martínez-Santos C, Moreno-Azcoita M, Cerquella C, Nejda N, Daimiel L, Iglesias D, Fernández-Peralta AM, González-Aguilera JJ (2006) Do MSI-L sporadic colorectal tumors develop through “mild mutator pathway”? Am J Clin Oncol 29:364–370
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 210 kb)
Supplementary Table 1
Clinicopathological characteristics of MSI-low CRCs according to the types of microsatellite instable (DOC 78 kb)
Supplementary Table 2
Comparison of clinicopathological characteristics of MSI-low CRCs according to the type of microsatellite instable (MYC-L vs. other markers) (DOC 46 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azzoni, C., Bottarelli, L., Cecchini, S. et al. Sporadic colorectal carcinomas with low-level microsatellite instability: a distinct subgroup with specific clinicopathological and molecular features. Int J Colorectal Dis 26, 445–453 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-011-1133-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-011-1133-8