Abstract
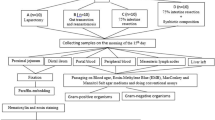
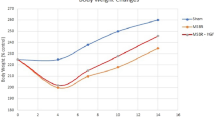
Despite the adaptive process triggered in the remaining intestine by massive bowel resection, bacterial translocation (BT) is frequent under these conditions. Several trophic factors, including growth hormone (GH), are involved in the process of adaptation in short-bowel syndrome (SBS). However, the effect of GH on BT has not been investigated experimentally. The aim of this study was to test the hypothesis that GH administration prevents BT in rats with SBS receiving only parental nutrition (PN). Nineteen adult Wistar rats underwent central venous cannulation and were randomly assigned to one of two groups receiving for 10 days two treatment regimes: PN group (n = 10): fasting, all-in-one PN solution (300 ml · kg · 24 h, 280 kcal/kg · 24 h), 80% gut section including ileocecal valve; GH group (n = 9): fasting, same PN regime and resection plus GH 1 mg/kg s.c). At the end of the experiment, the rats were killed and mesenteric lymph nodes (MLN) and samples of systemic and portal blood were obtained and cultured. Several samples of full-thickness jejunal wall were taken for determining cell proliferation index (PCNA) and mucosal thickness. Jejunal mucosal thickness increased by 30% and PCNA index by 35% in GH-treated rats in comparison with those treated with PN alone. However, contrary to our expectations, BT expressed by positive culture of intestinal flora in portal blood, MLN, or systemic blood was found in 60% of PN and 87% of GH animals (P = 0.1). Translocation to the general circulation expressed by the presence of organisms in systemic blood was detected in 0% of PN and 44% of GH rats (P < 0.05). Although exogenous GH improves gut mucosal structure in rats with SBS treated with PN, it seems to increase rather than decrease mucosal permeability to intestinal bacteria.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eizaguirre, I., Aldazabal, P., Barrena, M. et al. Effect of growth hormone on bacterial translocation in experimental short-bowel syndrome. Pediatr Surg Int 15, 160–163 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003830050545
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003830050545