Abstract
Purpose
To assess the efficacy of transcatheter arterial embolization (TAE) plus propranolol treatment for infantile hepatic hemangioma (IHH).
Methods
A retrospective study of symptomatic IHH and hemodynamic changes in IHH was conducted between 2016 and 2019.
Results
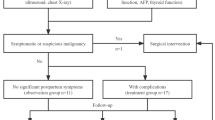
There were five boys and seven girls with diffuse lesions (n = 7) and multifocal lesions (n = 5). Hepatomegaly and abdominal distension (n = 6) were the predominant clinical presentations. Seven patients (58.3%) had multiple cutaneous hemangiomas. Pulmonary arterial hypertension, heart failure (n = 4), and hypothyroidism (n = 4) were observed. A total of 17 TAE procedures were performed in 12 IHH cases, with a technical success rate of 100%. All patients received standard propranolol orally, and one patient was orally administered metacortandracin. Two patients died of heart failure and multiple organ dysfunction caused by an enlarged liver. In addition, one patient was not reexamined after discharge. Of the remaining nine children, the average follow-up time was 10.78 months (range 2–28 months), and they all responded well to TAE combined with oral propranolol.
Conclusion
TAE combined with propranolol is safe and effective for the treatment of IHH, demonstrating low complication rates.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Iacobas I et al (2018) Guidance document for hepatic hemangioma (infantile and congenital) evaluation and monitoring. J Pediatr 203:294-300 e2
Sondhi V et al (2012) Successful management of multi-focal hepatic infantile hemangioendothelioma using TACE/surgery followed by maintenance metronomic therapy. BMJ Case Rep. https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr.12.2011.5456
Zavras N et al (2020) Infantile hepatic hemangioma: current state of the art, controversies, and perspectives. Eur J Pediatr 179(1):1–8
Razon MJ et al (1998) Increased apoptosis coincides with onset of involution in infantile hemangioma. Microcirculation 5(2–3):189–195
Lerut J, Iesari S (2018) Vascular tumours of the liver: a particular story. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol 3:62
Rialon KL et al (2015) Risk factors for mortality in patients with multifocal and diffuse hepatic hemangiomas. J Pediatr Surg 50(5):837–841
Macdonald A et al (2020) Historical and contemporary management of infantile hepatic hemangioma: a 30-year single-center experience. Ann Surg 275(1):e250–e255
Chatmethakul T et al (2016) Infantile hepatic hemangioendothelioma: an uncommon cause of persistent pulmonary hypertension in a newborn infant. AJP Rep 6(3):e260–e263
Varrasso G et al (2017) Propranolol as first-line treatment for life-threatening diffuse infantile hepatic hemangioma: a case report. Hepatology 66(1):283–285
Tsai MC, Liu HC, Yeung CY (2019) Efficacy of infantile hepatic hemangioma with propranolol treatment: a case report. Medicine (Baltimore) 98(4):e14078
Krowchuk DP et al (2019) Clinical practice guideline for the management of infantile hemangiomas. Pediatrics 143(1):e20183475
Wang L et al (2020) Infantile hepatic hemangioendothelioma associated with pulmonary artery hypertension and cardiac insufficiency successfully treated with transcatheter arterial embolization and propranolol: a case report. Medicine 99(24):e20728
Adams DM et al (2016) Efficacy and safety of sirolimus in the treatment of complicated vascular anomalies. Pediatrics 137(2):e20153257
Tian R et al (2020) Propranolol for infantile hepatic hemangioendothelioma: clinical evaluation of drug efficacy and safety using a single-center patient cohort. Ann Hepatol 19(5):530–534
Lekwuttikarn R, Josephs S, Teng JM (2019) Successful medical management of life-threatening hepatic hemangioma in neonates. Pediatrics 144(4):e20191339
Ji Y, Chen S, Yang K, Xiang B, Jiang X, Xu X, Li L, Qiu T, Zhou J, Dai S, Zhang X, Lu G, Kong F, Yang G, Qiu Q (2021) Screening for infantile hepatic hemangioma in patients with cutaneous infantile hemangioma: a multicenter prospective study. J Am Acad Dermatol 84(5):1378–1384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2020.11.062
Ozdemir ZC et al (2017) Beta blocker and steroid therapy in the treatment of infantile hepatic hemangioendothelioma. Drug Discov Ther 11(3):161–164
Sarialioglu F et al (2017) A new perspective for infantile hepatic hemangioma in the age of propranolol: experience at Baskent University. Exp Clin Transplant 15(2):74–78
Wang T et al (2015) Infantile hepatic hemangioendothelioma associated with congestive heart failure: two case reports with different outcomes. Medicine 94(52):e2344
Brown J, Arora R, Sethuraman U (2018) Distributive shock in a neonate with diffuse infantile hepatic hemangioma. J Emerg Med 54(1):e1–e3
Yang K et al (2019) Efficacy of propranolol treatment in infantile hepatic haemangioma. J Paediatr Child Health 55(10):1194–1200
Al Tasseh F et al (2017) Diffuse hepatic hemangioma with single cutaneous hemangioma: an alerting occurrence. Clin Case Rep 5(6):887–890
Aly MM et al (2015) Therapeutic superiority of combined propranolol with short steroids course over propranolol monotherapy in infantile hemangioma. Eur J Pediatr 174(11):1503–1509
deLorimier AA et al (1967) Hepatic-artery ligation for hepatic hemangiomatosis. N Engl J Med 277(7):333–337
Dong W et al (2019) Invasive management of symptomatic hepatic hemangioma. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 31(9):1079–1084
Warmann S et al (2003) Interventional treatment of infantile hepatic hemangioendothelioma. J Pediatr Surg 38(8):1177–1181
Huang Y et al (2014) Proapoptotic effect and the mechanism of action of pingyangmycin on cavernous hemangiomas. Exp Ther Med 7(2):473–477
Gaba RC, Schwind RM, Ballet S (2018) Mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, efficacy, and safety of transarterial therapies using ethiodized oil: preclinical review in liver cancer models. J Vasc Interv Radiol 29(3):413–424
Acknowledgements
I would particularly like to acknowledge my team members for their wonderful collaboration and patient support. We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.cn) for English language editing.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors made substantial contributions to conception and design, or acquisition of data, or analysis and interpretation of data; drafted the article or revised it critically for important intellectual content; and made final approval of the version to be published.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Li, J., Song, D. et al. Clinical evaluation of transcatheter arterial embolization combined with propranolol orally treatment of infantile hepatic hemangioma. Pediatr Surg Int 38, 1149–1155 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-022-05143-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-022-05143-w