Abstract
Objectives
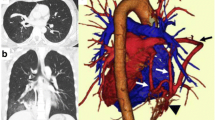
The purpose of this retrospective study was to evaluate the efficacy of anatomic thoracoscopic pulmonary segmentectomy performed based on three-dimensional computed tomography bronchography and angiography (3D-CTBA) in children and infants.
Methods
Totally, 22 patients received thoracoscopic segmentectomy from October 2019 to February 2020. The procedures were performed virtual segmentectomy based on 3D-CTBA. The preoperative planning depended on the 3D-CTBA result.
Results
All of the 22 cases ( 1 left S1, 1 right S3, 1 left S1 + 2, 1 left S1 + 2 + 3, 1 left S4 + 5, 1 right S6, 1 right S10, 1 left S10, 2 right S9 + 10, 3 left S9 + 10, 1 right S7 + 8 + 9 + 10, 8 left S7 + 8 + 9 + 10) were received thoracoscopic segmentectomy successfully. The mean procedure length was 76.6 ± 17.2 min, and the intraoperative blood loss was 16.5 ± 2.8 ml. The mean duration of chest tube insertion was 3.2 ± 0.7 days, and the mean hospital stay was 8.2 ± 2.8 days. Postoperative complications included infection (n = 1), atelectasis (n = 1), hydropneumothorax (n = 1) and pneumothorax (n = 1). No recurrence or mortality was observed during the short-term follow-up period of 3 months.
Conclusions
Based on the 3D-CTBA technique, the specific pulmonary segments invaded by the lesions and the relationship between the corresponding pulmonary vessels and bronchi can be acknowledged before the operation, which is of positive significance for the resection of complex pulmonary segments and good preoperative surgical planning. It’s worth popularizing in the pediatric population.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oizumi H, Kanauchi N, Kato H et al (2011) Anatomic thoracoscopic pulmonary segmentectomy under 3-dimensional multidetector computed tomography simulation: a report of 52 consecutive cases. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 141(3):678–682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2010.08.027
Saji H, Inoue T, Kato Y et al (2013) Virtual segmentectomy based on high-quality three-dimensional lung modeling from computed tomography images. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 17(2):227–232. https://doi.org/10.1093/icvts/ivt120
Hagiwara M, Shimada Y, Kato Y et al (2014) High-quality 3-dimensional image simulation for pulmonary lobectomy and segmentectomy: results of preoperative assessment of pulmonary vessels and short-term surgical outcomes in consecutive patients undergoing video-assisted thoracic surgery. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 46(6):e120–e126. https://doi.org/10.1093/ejcts/ezu375
Yang CF, D’Amico TA (2012) Thoracoscopic segmentectomy for lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg 94(2):668–681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.athoracsur.2012.03.080 ((epub 2012 Jun 27))
Okada M, Tsutani Y, Ikeda T et al (2012) Radical hybrid video-assisted thoracic segmentectomy: long-term results of minimally invasive anatomical sublobar resection for treating lung cancer. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 14(1):5–11. https://doi.org/10.1093/icvts/ivr065 ((epub 2011 Nov 17))
Eguchi T, Takasuna K, Kitazawa A et al (2012) Three-dimensional imaging navigation during a lung segmentectomy using an iPad. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 41(4):893–897. https://doi.org/10.1093/ejcts/ezrl27
Miyajima M, Watanabe A, Uehara M et al (2011) Total thoracoscopic lung segmentectomy of anterior basal segment of the right lower lobe (RS8) for NSCLC stage IA (case report). J Cardiothorac Surg 24(6):115. https://doi.org/10.1186/1749-8090-6-115
Iwano S, Yokoi K, Taniguchi T et al (2013) Planning of segmentectomy using three-dimensional computed tomography angiography with a virtual safety margin: technique and initial experience. Lung Cancer 81(3):410–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2013.06.001 ((epub 2013 Jul 6))
Nakamoto K, Omori K, Nezu K et al (2010) Superselective segmentectomy for deep and small pulmonary nodules under the guidance of three-dimensional reconstructed computed tomographic angiography. Ann Thorac Surg 89(3):877–883. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.athoracsur.2009.11.037
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest:
Authors Zheng Tan, Lijun-Yang, Chen Zou, Jian-gen Yu, Jian-hua Li, Liang Liang, Qiang Shu declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, Z., Lijun-Yang, Zou, C. et al. The application of virtual segmentectomy based on three-dimensional computed tomography and angiography in thoracoscopic segmentectomy for children and infants. Pediatr Surg Int 37, 1207–1214 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-021-04899-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-021-04899-x