Abstract
Background
SALL4 is a zinc finger transcription factor that exerts its physiological role during embryo-fetal development. Analyses of SALL4 expression have shown its oncogenic role in precursor B-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma, acute and chronic myeloid leukemia, gastrointestinal, breast, and lung cancers. The aim of this study was to determine the immunohistochemical profile of SALL4 in pediatric yolk sac tumors (YSTs).
Methods and results
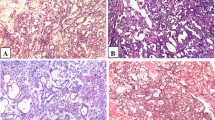
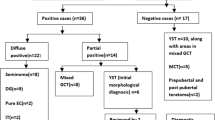
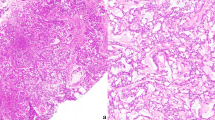
Immunohistochemistry detection of SALL4 was performed in 22 cases of pediatric YSTs and 10 mature teratomas. The percentage of tumor cells stained was scored as 0, 1+ (1–30% cells), 2+ (31–60%), 3+ (61–90%), and 4+ (> 90%). To compare its sensitivity and specificity with Glypican-3 and α-fetoprotein (AFP), we also stained tumors from these cases for Glypican-3 and AFP. In contrast to AFP and glypican-3, SALL4 staining in more than 90% of the tumor cells was seen in all 22 pediatric YSTs (100% sensitivity) (P < 0.001 for both SALL4 vs. AFP and SALL4 vs. glypican-3).
Conclusions
SALL4 is a sensitive marker for pediatric YSTs and it can be used to distinguish them from mature teratomas. SALL4 is likely to become a new and valuable biomarker for the diagnosis of pediatric YST.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hamilton-Dutoit SJ, Lou H, Pallesen G (1990) The expression of placental alkaline phosphatase (PLAP) and PLAP-like enzymes in normal and neoplastic human tissues. An immunohistological survey using monoclonal antibodies. APMIS 98:797–811
Iczkowski KA, Butler SL, Shanks JH et al (2008) Trials of new germ cell immunohistochemical stains in 93 extragonadal and metastatic GCTs. Hum Pathol 39:275–281
Leroy X, Augusto D, Leteurtre E et al (2002) CD30 and CD117 (c-kit) used in combination are useful for distinguishing embryonal carcinoma from seminoma. J Histochem Cytochem 50:283–285
Tickoo SK, Hutchinson B, Bacik J et al (2002) Testicular seminoma: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of 105 cases with special reference to seminomas with atypical features. Int J Surg Pathol 10:23–32
Morinaga S, Ojima M, Sasano N (1983) Human chorionic gonadotropin and alph α-fetoprotein in testicular GCTs. An immunohistochemical study in comparison with tissue concentrations. Cancer 52:1281–1289
Eglen DE, Ulbright TM (1987) The differential diagnosis of yolk sac tumor and seminoma. Usefulness of cytokeratin, alph α-fetoprotein, and α-1-antitrypsin immunoperoxidase reactions. Am J Clin Pathol 88:328–332
Cao D, Li J, Guo CC et al (2009) SALL4 is a novel diagnostic marker for testicular germ cell tumors. Am J Surg Pathol 33:1065–1077
Ota S, Hishinuma M, Yamauchi N et al (2006) Oncofetal protein glypican-3 in testicular germ-cell tumor. Virchows Arch 449:308–314
Zynger DL, Dimov ND, Luan C et al (2006) Glypican 3: a novel marker in testicular germ cell tumors. Am J Surg Pathol 30:1570–1575
Feng S, Huang S, Tong Y et al (2016) RNA-binding protein LIN28 is a sensitive marker of pediatric yolk sac tumors. Pediatr Surg Int 32(8):819–825
Loh YH, Wu Q, Chew JL et al (2006) The Oct4 and Nanog transcription network regulates pluripotency in mouse embryonic stem cells. Nat Genet 38:431–440
Wang J, Rao S, Chu J et al (2006) A protein interaction network for pluripotency of embryonic stem cells. Nature 444:364–368
Wu Q, Chen X, Zhang J et al (2006) Sall4 interacts with Nanog and cooccupies Nanog genomic sites in embryonic stem cells. J Biol Chem 281:24090–24094
Santagata S, Ligon KL, Hornick JL (2007) Embryonic stem cell transcription factor signatures in the diagnosis of primary and metastatic GCTs. Am J Surg Pathol 31:836–845
Ulbright TM (2005) Germ cell tumors of the gonads: a selective review emphasizing problems in differential diagnosis, newly appreciated, and controversial issues. Mod Pathol 18(suppl 2):S61–S79
Grady RW, Ross JH, Kay R (1995) Patterns of metastatic spread in prepubertal yolk sac tumor of the testis. J Urol 153:1259–1261
Clement PB, Young RH (1993) Pathology of extragonadal yolk sac tumors. In: Nogales FF (ed) The human yolk sac and yolk sac tumors. Springer, New York, pp 285–308
Kao CS, Cornejo KM, Ulbright TM, Young RH (2015) Juvenile granulosa cell tumors of the testis: a clinicopathologic study of 70 cases with emphasis on its wide morphologic spectrum. Am J Surg Pathol 39(9):1159–1169
Zynger DL, McCallum JC, Luan C et al (2010) Glypican 3 has a higher sensitivity than α-fetoprotein for testicular and ovarian yolk sac tumour: immunohistochemical investigation with analysis of histological growth patterns. Histopathology 56:750–757
Kao CS, Idrees MT, Young RH et al (2012) Solid pattern yolk sac tumor: a morphologic and immunohistochemical study of 52 cases. Am J Surg Pathol 36:360–367
Miettinen M, Wang Z, McCue PA et al (2014) SALL4 expression in germ cell and non-germ cell tumors: a systematic immunohistochemical study of 3215 cases. Am J Surg Pathol 38:410–420
Gao C, Kong NR, Li A et al (2013) SALL4 is a key transcription regulator in normal human hematopoiesis. Transfusion 53:1037–1049
Al-Baradie R, Yamada K, St Hilaire C et al (2002) Duane radial ray syndrome (Okihiro syndrome) maps to 20q13 and results from mutations in SALL4, a new member of the SAL family. Am J Hum Genet 71:1195–1199
Li A, Yang Y, Gao C et al (2013) A SALL4/MLL/HOXA9 pathway in murine and human myeloid leukemogenesis. J Clin Investig 123:4195–4207
Ardalan Khales S, Abbaszadegan MR, Abdollahi A et al (2015) SALL4 as a new biomarker for early colorectal cancers. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol 141:229–235
Itou J, Matsumoto Y, Yoshikawa K et al (2013) Sal-like 4 (SALL4) suppresses CDH1 expression and maintains cell dispersion in basal-like breast cancer. FEBS Lett 587:3115–3121
Du W, Ni L, Liu B et al (2018) Upregulation of SALL4 by EGFR activation regulates the stamens of CD44-positive lung cancer. Oncogenesis 7:229–235
Acknowledgements
The manuscript had been proofread by Professor Xin-He Lai. School of Biology & Food Science, Shangqiu Normal University, Shangqiu, Henan Province, China.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Ethical statement
This study was conducted in accordance with the guidelines of the human ethics committee at our institute.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, P., Luo, R., Sun, B. et al. SALL4 is a useful marker for pediatric yolk sac tumors. Pediatr Surg Int 36, 727–734 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-020-04652-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-020-04652-w