Abstract
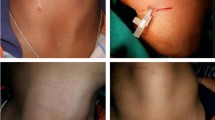
Branchial cleft anomalies are the second most common head and neck congenital lesions in children. It may sometimes be a part of branchio-oto-renal (BOR) syndrome, so in patients with branchial cleft anomalies associated with a complaint of auricular deformity or a similar history and findings in other family members, we should take an additional examination to find the possibility of BOR syndrome. Complete excision is essential for good prognosis. For the management of branchial cleft anomalies, various methods have been reported. Endoscopically assisted dissection technique and transoral robot-assisted surgery were used in the management of fistula and allowed excellent visualization of the pharyngeal component of the lesion and a minimally invasive approach. It is essential for the surgeon to fully comprehend the congenital lesions to attain the correct preoperative diagnosis and plan for an appropriate surgical approach to prevent the most common complication and recurrence in these lesions. The following sections discuss the anatomy, common presentation, auxiliary examination, differential diagnosis, the current principles of surgical treatment and prognosis for second branchial cleft anomalies in children, and discussed the branchio-oto-renal syndrome.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mohamed K, Badawy MK (2010) Pediatric neck masses. Clin Pediatr Emerg Med 11(2):73–80
Waldhausen JH (2006) Branchial cleft and arch anomalies in children. Semin Pediatr Surg 15(2):64–69
Goff CJ, Allred C, Glade RS (2012) Current management of congenital branchial cleft cysts, sinuses, and fistulae. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 20(6):533–539
Jaka RC, Singh G (2007) Complete congenital third branchial fistula on right side. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 137(3):518–519
Doshi J, Anari S (2007) Branchial cyst side predilection: fact or fiction? Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 116(2):112–114
Bailey H (1929) Branchial cysts and other essays on surgical subjects in the facio-cervical region. Lewis, London
Prosser JD, Myer CM IIIrd (2015) Branchial cleft anomalies and thymic cysts. Otolaryngol Clin N Am 48(1):1–14
Sahu S, Kumar A, Ramakrishnan TS (2011) Branchial fistula: an imaging perspective. Med J Armed Forces India 67(3):262–264
Can IH, Dogan S, Donmez M, Dogan M, Samim EE (2012) A different type of branchial fistula as part of a branchio-oto-renal syndrome. J Pediatr Surg 47(2):404–407
Senel E, Kocak H, Akbiyik F, Saylam G, Gulleroglu BN, Senel S (2009) From a branchial fistula to a branchiootorenal syndrome: a case report and review of the literature. J Pediatr Surg 44(3):623–625
Maddalozzo J, Rastatter JC, Dreyfuss HF, Jaffar R, Bhushan B (2012) The second branchial cleft fistula. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 76(7):1042–1045
Bajaj Y, Ifeacho S, Tweedie D, Jephson CG, Albert DM et al (2011) Branchial anomalies in children. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 75(8):1020–1023
Adams A, Mankad K, Offiah C, Childs L (2016) Branchial cleft anomalies: a pictorial review of embryological development and spectrum of imaging findings. Insights Imaging 7(1):69–76
Guldfred LA, Philipsen BB, Siim C (2012) Branchial cleft anomalies: accuracy of pre-operative diagnosis, clinical presentation and management. J Laryngol Otol 126(6):598–604
Stern JS, Ginat DT, Nicholas JL, Ryan ME (2015) Imaging of pediatric head and neck masses. Otolaryngol Clin N Am 48(1):225–246
Kajosaari L, Makitie A, Salminen P, Klockars T (2014) Second branchial cleft fistulae: patient characteristics and surgical outcome. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 78(9):1503–1507
Shekdar KV, Mirsky DM, Kazahaya K, Bilaniuk LT (2012) Magnetic resonance imaging of the pediatric neck: an overview. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 20(3):573–603
Augustine AJ, Pai KR, Govindarajan R (2001) Clinics in diagnostic imaging (66). Right complete branchial fistula. Singap Med J 42(10):494–495
Ryu CW, Lee JH, Lee HK, Lee DH, Choi CG, Kim SJ (2006) Clinical usefulness of multidetector CT fistulography of branchial cleft fistula. Clin Imaging 30(5):339–342
Rattan KN, Rattan S, Parihar D, Gulia JS, Yadav SP (2006) Second branchial cleft fistula: is fistulogram necessary for complete excision. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 70(6):1027–1030
Al-Mufarrej F, Stoddard D, Bite U (2017) Branchial arch anomalies: recurrence, malignant degeneration and operative complications. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 97:24–29
Schroeder JW Jr, Mohyuddin N, Maddalozzo J (2007) Branchial anomalies in the pediatric population. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 137(2):289–295
Yilmaz I, Cakmak O, Ozgirgin N, Boyvat F, Demirhan B (2004) Complete fistula of the second branchial cleft: case report of catheter-aided total excision. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 68(8):1109–1113
Acierno SP, Waldhausen JH (2007) Congenital cervical cysts, sinuses and fistulae. Otolaryngol Clin N Am 2007 40(1):161–176
Barrett G, Toynton S (2013) Endoscopically assisted branchial fistula excision. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 77(6):1048–1050
Suslu N, Suslu AE, Akyol U, Yilmaz T (2013) Minimally invasive endoscope-assisted surgery for bilateral branchial cleft fistula. Laryngoscope 123(9):2296–2299
Guerrissi JO (2002) Innovation and surgical techniques: endoscopic resection of cervical branchiogenic cysts. J Craniofac Surg 13(3):478–482
Gaszynska E, Gaszynski T, Arkuszewski P (2012) Diagnosis and treatment of cervical branchial cleft cysts based on the material from the Department of Cranio-Maxillofacial Surgery, Medical University in Lodz and literature review. Pol Przegl Chir 84:547–550
Teng SE, Paul BC, Brumm JD, Fritz M, Fang Y, Myssiorek D (2016) Endoscope-assisted approach to excision of branchial cleft cysts. Laryngoscope 126(6):1339–1342
Rassekh CH, Kazahaya K, Livolsi VA, Loevner LA, Cowan AT, Weinstein GS (2016) Transoral robotic surgery-assisted excision of a congenital cervical salivary duct fistula presenting as a branchial cleft fistula. Head Neck 38(2):E49–E53
Song CM, Ji YB, Kim KR, Tae K (2015) Robot-assisted excision of branchial cleft cysts using a postauricular facelift approach. Auris Nasus Larynx 42(5):424–427
Kim BH, Kwon SK, Hah JH(2007) Chemocauterization of second branchial cleft fistula using trichloroacetic acid: a preliminary report. Auris Nasus Larynx 45:143–146 (pii:S0385814616304205)
LaRiviere CA, Waldhausen JH (2012) Congenital cervical cysts, sinuses, and fistulae in pediatric surgery. Surg Clin N Am 92(3):583–597
Keogh IJ, Khoo SG, Waheed K, Timon C (2007) Complete branchial cleft fistula: diagnosis and surgical management. Revue de Laryngologie Otologie Rhinologie 128(1–2):73–76
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the assistance of all those who participated in this project.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 81172562 and 81372903).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, LF., Zhou, SH., Chen, Qq. et al. Second branchial cleft anomalies in children: a literature review. Pediatr Surg Int 34, 1251–1256 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-018-4348-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-018-4348-8