Abstract
Purpose
Treatment for high-risk neuroblastoma is still challenging. The purpose of the present study was to determine whether thalidomide suppresses etoposide-induced NF-κB activation and thus potentiates apoptosis in murine neuroblastoma.
Methods
A murine neuroblastoma cell line, C1300, and A/J mice were used in this study. We evaluated NF-κB activation after using etoposide with or without thalidomide by quantitative analysis of NF-κB by ELISA and by Western blot analysis of IκB phosphorylation in vitro and in vivo. Induction of apoptosis was evaluated by Western blot analysis of the apoptotic signals caspase-3, 8, and 9 in vitro and by TUNEL assays in vivo. We also evaluated the efficacy of the combination of etoposide and thalidomide by assessing tumor growth and mouse survival in vivo.
Results
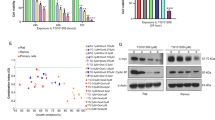
Etoposide activated NF-κB in C1300 cells. This activation was suppressed by thalidomide and IκB was re-upregulated. The apoptotic signals were enhanced by the combination of thalidomide and etoposide compared with etoposide alone in vitro, which was consistent with TUNEL assays. The combination of etoposide and thalidomide also slowed tumor growth and mouse survival.
Conclusion
Thalidomide potentiates etoposide-induced apoptosis in murine neuroblastoma by suppressing NF-κB.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maris JM, Hogarty MD, Bagatell R, Cohn SL (2007) Neuroblastoma. Lancet (London England) 369(9579):2106–2120. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(07)60983-0
Shohet J, Foster J (2017) Neuroblastoma. BMJ (Clinical Research Ed) 357:j1863. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.j1863
Wang CY, Mayo MW, Korneluk RG, Goeddel DV, Baldwin AS Jr (1998) NF-kappaB antiapoptosis: induction of TRAF1 and TRAF2 and c-IAP1 and c-IAP2 to suppress caspase-8 activation. Science 281(5383):1680–1683
Wadgaonkar R, Phelps KM, Haque Z, Williams AJ, Silverman ES, Collins T (1999) CREB-binding protein is a nuclear integrator of nuclear factor-kappaB and p53 signaling. J Biol Chem 274(4):1879–1882
Baldwin AS Jr (1996) The NF-kappa B and I kappa B proteins: new discoveries and insights. Annu Rev Immunol 14:649–683. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.immunol.14.1.649
Viatour P, Merville M-P, Bours V, Chariot A (2005) Phosphorylation of NF-κB and IκB proteins: implications in cancer and inflammation. Trends Biochem Sci 30(1):43–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2004.11.009
Huang TT, Wuerzberger-Davis SM, Seufzer BJ, Shumway SD, Kurama T, Boothman DA, Miyamoto S (2000) NF-kappaB activation by camptothecin. A linkage between nuclear DNA damage and cytoplasmic signaling events. J Biol Chem 275(13):9501–9509
Piret B, Piette J (1996) Topoisomerase poisons activate the transcription factor NF-kappaB in ACH-2 and CEM cells. Nucleic Acids Res 24(21):4242–4248
Wang CY, Cusack JC Jr, Liu R, Baldwin AS Jr (1999) Control of inducible chemoresistance: enhanced anti-tumor therapy through increased apoptosis by inhibition of NF-kappaB. Nat Med 5(4):412–417. https://doi.org/10.1038/7410
Karin M, Yamamoto Y, Wang QM (2004) The IKK NF-kappa B system: a treasure trove for drug development. Nat Rev Drug Discov 3(1):17–26. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd1279
Cusack JC, Liu R, Baldwin AS (1999) NF- kappa B and chemoresistance: potentiation of cancer drugs via inhibition of NF-kappa B. Drug Resist Updat 2(4):271–273. https://doi.org/10.1054/drup.1999.0094
Nakanishi C, Toi M (2005) Nuclear factor-kappaB inhibitors as sensitizers to anticancer drugs. Nat Rev Cancer 5(4):297–309. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc1588
Patel NM, Nozaki S, Shortle NH, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Newton TR, Rice S, Gelfanov V, Boswell SH, Goulet RJ Jr, Sledge GW Jr, Nakshatri H (2000) Paclitaxel sensitivity of breast cancer cells with constitutively active NF-kappaB is enhanced by IkappaBalpha super-repressor and parthenolide. Oncogene 19(36):4159–4169. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203768
Notarbartolo M, Poma P, Perri D, Dusonchet L, Cervello M, D’Alessandro N (2005) Antitumor effects of curcumin, alone or in combination with cisplatin or doxorubicin, on human hepatic cancer cells. Analysis of their possible relationship to changes in NF-kB activation levels and in IAP gene expression. Cancer Lett 224(1):53–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2004.10.051
Ammann JU, Haag C, Kasperczyk H, Debatin KM, Fulda S (2009) Sensitization of neuroblastoma cells for TRAIL-induced apoptosis by NF-kappaB inhibition. Int J Cancer 124(6):1301–1311. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.24068
Bian X, Opipari AW Jr, Ratanaproeksa AB, Boitano AE, Lucas PC, Castle VP (2002) Constitutively active NFkappa B is required for the survival of S-type neuroblastoma. J Biol Chem 277(44):42144–42150. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M203891200
D’Amato RJ, Loughnan MS, Flynn E, Folkman J (1994) Thalidomide is an inhibitor of angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91(9):4082–4085
Gockel HR, Lugering A, Heidemann J, Schmidt M, Domschke W, Kucharzik T, Lugering N (2004) Thalidomide induces apoptosis in human monocytes by using a cytochrome c-dependent pathway. J Immunol (Baltimore, Md: 1950) 172 (8):5103–5109
Liu WM, Strauss SJ, Chaplin T, Shahin S, Propper DJ, Young BD, Joel SP, Malpas JS (2004) s-Thalidomide has a greater effect on apoptosis than angiogenesis in a multiple myeloma cell line. Hematol J 5(3):247–254
Singhal S, Mehta J, Desikan R, Ayers D, Roberson P, Eddlemon P, Munshi N, Anaissie E, Wilson C, Dhodapkar M, Zeddis J, Barlogie B (1999) Antitumor activity of thalidomide in refractory multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med 341(21):1565–1571. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm199911183412102
de Souza CM, Araujo e Silva AC, de Jesus Ferraciolli C, Moreira GV, Campos LC, dos Reis DC, Lopes MT, Ferreira MA, Andrade SP, Cassali GD (2014) Combination therapy with carboplatin and thalidomide suppresses tumor growth and metastasis in 4T1 murine breast cancer model. Biomed Pharmacother 68(1):51–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2013.08.004
Qiao Z, Yuan J, Shen J, Wang C, He Z, Hu Y, Zhang M, Xu C (2015) Effect of thalidomide in combination with gemcitabine on human pancreatic carcinoma SW-1990 cell lines in vitro and in vivo. Oncol Lett 9(5):2353–2360. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2015.3064
Rezvani H, Haghighi S, Ghadyani M, Attarian H (2012) Efficacy of taxotere, thalidomide, and prednisolone in patients with hormone-resistant metastatic prostate cancer. Urol J 9(4):673–677
Lv J, Liu N, Liu KW, Ding AP, Wang H, Qiu WS (2012) A Randomised controlled phase II trial of the combination of XELOX with thalidomide for the first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancer Biol Med 9(2):111–114. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.2095-3941.2012.02.005
Lee SM, Hackshaw A (2013) A potential new enriching trial design for selecting non-small-cell lung cancer patients with no predictive biomarker for trials based on both histology and early tumor response: further analysis of a thalidomide trial. Cancer Med 2(3):360–366. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.74
Pinter M, Wichlas M, Schmid K, Plank C, Muller C, Wrba F, Peck-Radosavljevic M (2008) Thalidomide in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma as antiangiogenic treatment approach: a phase I/II trial. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 20(10):1012–1019. https://doi.org/10.1097/MEG.0b013e3283036740
Keifer JA, Guttridge DC, Ashburner BP, Baldwin AS Jr (2001) Inhibition of NF-kappa B activity by thalidomide through suppression of IkappaB kinase activity. J Biol Chem 276(25):22382–22387. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M100938200
Ziegler MM, Ishizu H, Nagabuchi E, Takada N, Arya G (1997) A comparative review of the immunobiology of murine neuroblastoma and human neuroblastoma. Cancer 79(9):1757–1766
Watt F, Watanabe R, Yang W, Ågren N, Arvidsson Y, Funa K (2006) A novel MASH1 enhancer with N-myc and CREB-binding sites is active in neuroblastoma. Cancer Gene Ther 14:287. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7701012
Haruki K, Shiba H, Fujiwara Y, Furukawa K, Iwase R, Uwagawa T, Misawa T, Ohashi T, Yanaga K (2013) Inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB enhances the antitumor effect of tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma in mice. Surgery 154(3):468–478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surg.2013.05.037 154 (3 :468–478.
Majumdar S, Lamothe B, Aggarwal BB (2002) Thalidomide suppresses NF-kappa B activation induced by TNF and H2O2, but not that activated by ceramide, lipopolysaccharides, or phorbol ester. J Immunol (Baltimore: 1950) 168(6):2644–2651
Mezzanzanica D, Balladore E, Turatti F, Luison E, Alberti P, Bagnoli M, Figini M, Mazzoni A, Raspagliesi F, Oggionni M, Pilotti S, Canevari S (2004) CD95-mediated apoptosis is impaired at receptor level by cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein (long form) in wild-type p53 human ovarian carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 10(15):5202–5214. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-03-0537
Bernard D, Quatannens B, Vandenbunder B, Abbadie C (2001) Rel/NF-kappaB transcription factors protect against tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis by up-regulating the TRAIL decoy receptor DcR1. J Biol Chem 276(29):27322–27328. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M011183200
Chen X, Kandasamy K, Srivastava RK (2003) Differential roles of RelA (p65) and c-Rel subunits of nuclear factor kappa B in tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand signaling. Cancer Res 63(5):1059–1066
Lee R, Collins T (2001) Nuclear factor-kappaB and cell survival: IAPs call for support. Circ Res 88(3):262–264
Liston P, Fong WG, Korneluk RG (2003) The inhibitors of apoptosis: there is more to life than Bcl2. Oncogene 22(53):8568–8580. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207101
Wright CW, Duckett CS (2005) Reawakening the cellular death program in neoplasia through the therapeutic blockade of IAP function. J Clin Investig 115(10):2673–2678. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI26251
Tamm I, Wang Y, Sausville E, Scudiero DA, Vigna N, Oltersdorf T, Reed JC (1998) IAP-family protein survivin inhibits caspase activity and apoptosis induced by Fas (CD95), Bax, caspases, and anticancer drugs. Cancer Res 58(23):5315–5320
Sun XM, Bratton SB, Butterworth M, MacFarlane M, Cohen GM (2002) Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL inhibit CD95-mediated apoptosis by preventing mitochondrial release of Smac/DIABLO and subsequent inactivation of X-linked inhibitor-of-apoptosis protein. J Biol Chem 277(13):11345–11351. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109893200
Delhalle S, Deregowski V, Benoit V, Merville MP, Bours V (2002) NF-kappaB-dependent MnSOD expression protects adenocarcinoma cells from TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 21(24):3917–3924. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1205489
Guttridge DC, Albanese C, Reuther JY, Pestell RG, Baldwin AS Jr (1999) NF-kappaB controls cell growth and differentiation through transcriptional regulation of cyclin D1. Mol Cell Biol 19(8):5785–5799
Hinz M, Krappmann D, Eichten A, Heder A, Scheidereit C, Strauss M (1999) NF-kappaB function in growth control: regulation of cyclin D1 expression and G0/G1-to-S-phase transition. Mol Cell Biol 19(4):2690–2698
Bobrovnikova-Marjon EV, Marjon PL, Barbash O, Vander Jagt DL, Abcouwer SF (2004) Expression of angiogenic factors vascular endothelial growth factor and interleukin-8/CXCL8 is highly responsive to ambient glutamine availability: role of nuclear factor-kappaB and activating protein-1. Cancer Res 64(14):4858–4869. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0682
Martin D, Galisteo R, Gutkind JS (2009) CXCL8/IL8 stimulates vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression and the autocrine activation of VEGFR2 in endothelial cells by activating NFkappaB through the CBM (Carma3/Bcl10/Malt1) complex. J Biol Chem 284(10):6038–6042. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.C800207200
Kumar S, Rajkumar SV (2005) Thalidomide and dexamethasone: therapy for multiple myeloma. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 5(5):759–766. https://doi.org/10.1586/14737140.5.5.759
Chintagumpala M, Blaney SM, Bomgaars LR, Aleksic A, Kuttesch JF, Klenke RA, Berg SL (2004) Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of thalidomide with carboplatin in children with cancer. J Clin Oncol 22(21):4394–4400. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2004.04.565
Lopez-Aguilar E, Sepulveda-Vildosola AC, Betanzos-Cabrera Y, Rocha-Moreno YG, Gascon-Lastiri G, Rivera-Marquez H, Wanzke-del-Angel V, Cerecedo-Diaz F, de la Cruz-Yanez H (2008) Phase II study of metronomic chemotherapy with thalidomide, carboplatin-vincristine-fluvastatin in the treatment of brain stem tumors in children. Arch Med Res 39(7):655–662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arcmed.2008.05.008
Yang CS, Kim C, Antaya RJ (2015) Review of thalidomide use in the pediatric population. J Am Acad Dermatol 72(4):703–711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2015.01.002
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Mimi Zeiger, MA, University of California, San Francisco, for editorial assistance, Rei Kudo, MD, PhD, for conceptional advice, and Takashi Horiuchi, MD and Hiroshi Sugano, MD for technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hiramatsu, T., Yoshizawa, J., Miyaguni, K. et al. Thalidomide potentiates etoposide-induced apoptosis in murine neuroblastoma through suppression of NF-κB activation. Pediatr Surg Int 34, 443–450 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-018-4234-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-018-4234-4