Abstract
Purpose
To assess the impact of urgent surgery on neonates and the value of an orally administered probiotic preparation of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis LKM512 (LKM) using fecal DNA sequencing to analyze intestinal microbiota.
Methods
Subjects for this study were 13 neonates born at our institution. Surgical cases required surgery within 3 days of birth. Groups studied were surgical cases administered LKM (n = 4; LKM+), surgical cases not administered have surgery and were not administered LKM (n = 2; CS), and normal healthy neonates (n = 3; CN). Stool specimens (20 mg) were collected five times (after birth, and on days 3, 7, 10, and 14 after surgery in surgical cases, and after birth, and on days 4, 8, 11, and 15 of life in controls).
Results
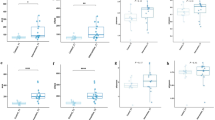
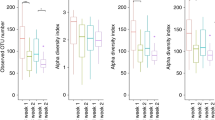
Clinical data were similar for LKM+ and LKM−. Enterobacteriaceae, Streptococcaceae, Staphylococcaceae and Bifidobacteriaceae were identified in the descending order of abundance in CS stool. Streptococcaceae, Staphylococcaceae, Enterococcaceae and Bifidobacteriaceae were identified in the descending order of abundance in LKM+ stool. Bifidobacteriaceae, Enterobacteriaceae, Staphylococcaceae and Streptococcaceae were identified in the descending order of abundance in LKM− stool. Unexpectedly, Bifidobacteriaceae was significantly more abundant in LKM− than LKM+ (p < 0.05).
Conclusion
Surgical stress appears to affect intestinal microbiota considerably. Probiotic administration in neonates requires clarification.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Martin R, Nauta AJ, Ben Amor K, Knippels LM, Knol J, Garssen J (2010) Early life: gut microbiota and immune development in infancy. Benef Microbes 1(4):367–382
Johnson CL, Versalovic J (2012) The human microbiome and its potential importance to pediatrics. Pediatrics 129(5):950–960
Drell T, Lutsar I, Stsepetova J, Parm U, Metsvaht T, Ilmoja ML, Simm J, Sepp E (2014) The development of gut microbiota in critically ill extremely low birth weight infants assessed with 16S rRNA gene based sequencing. Gut Microbes 5(3):304–312
Magne F, Abely M, Boyer F, Morville P, Pochart P, Suau A (2006) Low species diversity and high interindividual variability in faeces of preterm infants as revealed by sequences of 16S rRNA genes and PCR-temporal temperature gradient gel electrophoresis profiles. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 57(1):128–138
Mitsuoka T, Kaneuchi C (1977) Ecology of the bifidobacteria. Am J Clin Nutr 30(11):1799–1810
Bergmann KR, Liu SX, Tian R, Kushnir A, Turner JR, Li HL, Chou PM, Weber CR, De Plaen IG (2013) Bifidobacteria stabilize claudins at tight junctions and prevent intestinal barrier dysfunction in mouse necrotizing enterocolitis. Am J Pathol 182(5):1595–1606
Kanamori Y, Iwanaka T, Sugiyama M, Komura M, Takahashi T, Yuki N, Morotomi M, Tanaka R (2010) Early use of probiotics is important therapy in infants with severe congenital anomaly. Pediatr Int 52(3):362–367
Matsumoto M, Ishige A, Yazawa Y, Kondo M, Muramatsu K, Watanabe K (2012) Promotion of intestinal peristalsis by Bifidobacterium spp. capable of hydrolysing sennosides in mice. PLoS One 7(2):e31700
Arboleya S, Sanchez B, Milani C, Duranti S, Solis G, de los Reyes-Gavilan CG, Fernandez N, Ventura M, Margolles A, Gueimonde M (2015) Intestinal microbiota development in preterm neonates and effect of perinatal antibiotics. J Pediatr 166(3):538–544
Matsumoto M, Aranami A, Ishige A, Watanabe K, Benno Y (2007) LKM512 yogurt consumption improves the intestinal environment and induces the T-helper type 1 cytokine in adult patients with intractable atopic dermatitis. Clin Exp Allergy: J Br Soc Allergy Clin Immunol 37(3):358–370
Matsumoto M, Ohishi H, Benno Y (2001) Impact of LKM512 yogurt on improvement of intestinal environment of the elderly. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 31(3):181–186
Ichikawa S, Ishihara M, Okazaki T, Warabi K, Kato Y, Hori S, Lane GJ, Hiramatsu K, Inada E, Kobayashi H, Yamataka A (2007) Prospective study of antibiotic protocols for managing surgical site infections in children. J Pediatr Surg 42(6):1002–1007 (discussion 1007)
Neefs JM, Van de Peer Y, De Rijk P, Chapelle S, De Wachter R (1993) Compilation of small ribosomal subunit RNA structures. Nucleic Acids Res 21(13):3025–3049
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Pena AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Turnbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7(5):335–336
Edgar RC (2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26(19):2460–2461
Caporaso JG, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, DeSantis TZ, Andersen GL, Knight R (2010) PyNAST: a flexible tool for aligning sequences to a template alignment. Bioinformatics 26(2):266–267
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2007) Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(16):5261–5267
Lau CS, Chamberlain RS (2015) Probiotic administration can prevent necrotizing enterocolitis in preterm infants: a meta-analysis. J Pediatr Surg. doi:10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2015.05.008
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
H. Murakami and Y. Shimomura contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murakami, H., Shimomura, Y., Matsumoto, M. et al. Intestinal microbiota in neonates requiring urgent surgery: assessing the role of probiotics using fecal DNA sequencing. Pediatr Surg Int 32, 37–43 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-015-3810-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-015-3810-0