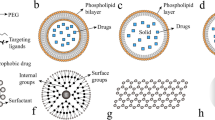
Abstract
Childhood cancer is the leading cause of mortality in children between 1 and 14 years of age. Malignancy accounts for 18 % of overall childhood mortality. Therapeutic advances in the field of pediatric oncology have helped to increase survival. Nanotechnology is the modification of materials at a nanoscale and can be used to deliver therapeutic agents. Examples of nanotechnology applications are organic self-assembled amphiphilic polymers, non-organic nanocarriers such as nanotubes and quantum dots. Each of these has their own utility in different settings. Application of nanotechnology in medicine has been extensively studied. Examples of pediatric tumors that received special attention are: neuroblastoma, retinoblastoma, central nervous system tumors and musculoskeletal tumors. This review will summarize the application of nanomedicine as an innovative management strategy in pediatric oncology.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cancer Stats CRU (2014) Childhood cancer mortality statistics. Cancer Research UK. http://www.cancerresearchuk.org/cancer-info/cancerstats/childhoodcancer/mortality/childhood-cancer-mortality-statistics. Accessed 29 Sept 2014
Pritchard-Jones K, Pieters R, Reaman GH, Hjorth L, Downie P, Calaminus G, Naafs-Wilstra MC, Steliarova-Foucher E (2013) Sustaining innovation and improvement in the treatment of childhood cancer: lessons from high-income countries. Lancet Oncol 14(3):e95–e103. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70010-X
Moreno L, Marshall LV, Pearson AD (2013) At the frontier of progress for paediatric oncology: the neuroblastoma paradigm. Br Med Bull 108:173–188. doi:10.1093/bmb/ldt033
Ries LAG SM, Gurney JG, Linet M, Tamra T, Young JL, Bunin GR (eds) (1999) Cancer incidence and survival among children and adolescents: United States SEER Program 1975–1995. National Cancer Institute, SEER Program, Bethesda, MD
Statistics CCSsACoC (2014) Canadian cancer statistics 2014. Canadian Cancer Society, Toronto
Childhood Cancer Canada Foundation (2011) Are survival rates improving for childhood cancers? http://childhoodcancer.ca/education/survival-rates. Accessed 29 Sept 2014
Sumer B, Gao J (2008) Theranostic nanomedicine for cancer. Nanomedicine 3(2):137–140. doi:10.2217/17435889.3.2.137
Gao J, Chen X, Cheng Z (2010) Near-infrared quantum dots as optical probes for tumor imaging. Curr Top Med Chem 10(12):1147–1157
Klumpp C, Kostarelos K, Prato M, Bianco A (2006) Functionalized carbon nanotubes as emerging nanovectors for the delivery of therapeutics. Biochim Biophys Acta 1758(3):404–412. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2005.10.008
Rastogi V, Yadav P, Bhattacharya SS, Mishra AK, Verma N, Verma A, Pandit JK (2014) Carbon nanotubes: an emerging drug carrier for targeting cancer cells. J Drug Deliv 2014:670815. doi:10.1155/2014/670815
Kalele S, Gosavi SW, Urban J, Kulkarni SK (2006) Nanoshell particles: synthesis, properties and applications. Curr Sci 91(8):1038–1052
Mueller S, Matthay KK (2009) Neuroblastoma: biology and staging. Curr Oncol Rep 11(6):431–438
Gao RN, Levy IG, Woods WG, Coombs BA, Gaudette LA, Hill GB (1997) Incidence and mortality of neuroblastoma in Canada compared with other childhood cancers. Cancer Causes Control CCC 8(5):745–754
Gurney JG, Ross JA, Wall DA, Bleyer WA, Severson RK, Robison LL (1997) Infant cancer in the US: histology-specific incidence and trends, 1973 to 1992. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 19(5):428–432
Spix C, Pastore G, Sankila R, Stiller CA, Steliarova-Foucher E (2006) Neuroblastoma incidence and survival in European children (1978–1997): report from the Automated Childhood Cancer Information System project. Eur J Cancer 42(13):2081–2091. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2006.05.008
Heck JE, Ritz B, Hung RJ, Hashibe M, Boffetta P (2009) The epidemiology of neuroblastoma: a review. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol 23(2):125–143. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3016.2008.00983.x
Gatta G, Capocaccia R, Coleman MP, Ries LA, Berrino F (2002) Childhood cancer survival in Europe and the United States. Cancer 95(8):1767–1772. doi:10.1002/cncr.10833
Carlin S, Mairs RJ, McCluskey AG, Tweddle DA, Sprigg A, Estlin C, Board J, George RE, Ellershaw C, Pearson AD, Lunec J, Montaldo PG, Ponzoni M, van Eck-Smit BL, Hoefnagel CA, van den Brug MD, Tytgat GA, Caron HN (2003) Development of a real-time polymerase chain reaction assay for prediction of the uptake of meta-[(131)I]iodobenzylguanidine by neuroblastoma tumors. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res 9(9):3338–3344
Yu AL, Gilman AL, Ozkaynak MF, London WB, Kreissman SG, Chen HX, Smith M, Anderson B, Villablanca JG, Matthay KK, Shimada H, Grupp SA, Seeger R, Reynolds CP, Buxton A, Reisfeld RA, Gillies SD, Cohn SL, Maris JM, Sondel PM, Children’s Oncology G (2010) Anti-GD2 antibody with GM-CSF, interleukin-2, and isotretinoin for neuroblastoma. N Engl J Med 363(14):1324–1334. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0911123
Janoueix-Lerosey I, Lequin D, Brugieres L, Ribeiro A, de Pontual L, Combaret V, Raynal V, Puisieux A, Schleiermacher G, Pierron G, Valteau-Couanet D, Frebourg T, Michon J, Lyonnet S, Amiel J, Delattre O (2008) Somatic and germline activating mutations of the ALK kinase receptor in neuroblastoma. Nature 455(7215):967–970. doi:10.1038/nature07398
Mosse YP, Laudenslager M, Longo L, Cole KA, Wood A, Attiyeh EF, Laquaglia MJ, Sennett R, Lynch JE, Perri P, Laureys G, Speleman F, Kim C, Hou C, Hakonarson H, Torkamani A, Schork NJ, Brodeur GM, Tonini GP, Rappaport E, Devoto M, Maris JM (2008) Identification of ALK as a major familial neuroblastoma predisposition gene. Nature 455(7215):930–935. doi:10.1038/nature07261
Modak S, Cheung NK (2007) Disialoganglioside directed immunotherapy of neuroblastoma. Cancer Invest 25(1):67–77. doi:10.1080/07357900601130763
Navid F, Santana VM, Barfield RC (2010) Anti-GD2 antibody therapy for GD2-expressing tumors. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 10(2):200–209
Park SJ, Woo SJ, Park KH (2014) Incidence of retinoblastoma and survival rate of retinoblastoma patients in Korea using the Korean National Cancer Registry database (1993–2010). Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 55(5):2816–2821. doi:10.1167/iovs.14-14078
Wong JR, Tucker MA, Kleinerman RA, Devesa SS (2014) Retinoblastoma incidence patterns in the US Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results program. JAMA Ophthalmol 132(4):478–483. doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2013.8001
Chintagumpala M, Chevez-Barrios P, Paysse EA, Plon SE, Hurwitz R (2007) Retinoblastoma: review of current management. Oncologist 12(10):1237–1246. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.12-10-1237
Kang SJ, Durairaj C, Kompella UB, O’Brien JM, Grossniklaus HE (2009) Subconjunctival nanoparticle carboplatin in the treatment of murine retinoblastoma. Arch Ophthalmol 127(8):1043–1047. doi:10.1001/archophthalmol.2009.185
Ahmed F, Ali MJ, Kondapi AK (2014) Carboplatin loaded protein nanoparticles exhibit improve anti-proliferative activity in retinoblastoma cells. Int J Biol Macromol 70:572–582. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.07.041
Dougherty TJ (1986) Photosensitization of malignant tumors. Semin Surg Oncol 2(1):24–37
Stephan H, Boeloeni R, Eggert A, Bornfeld N, Schueler A (2008) Photodynamic therapy in retinoblastoma: effects of verteporfin on retinoblastoma cell lines. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 49(7):3158–3163. doi:10.1167/iovs.07-1016
Thorne RN, Pearson AD, Nicoll JA, Coakham HB, Oakhill A, Mott MG, Foreman NK (1994) Decline in incidence of medulloblastoma in children. Cancer 74(12):3240–3244
Frange P, Alapetite C, Gaboriaud G, Bours D, Zucker JM, Zerah M, Brisse H, Chevignard M, Mosseri V, Bouffet E, Doz F (2009) From childhood to adulthood: long-term outcome of medulloblastoma patients. The Institut Curie experience (1980–2000). J Neurooncol 95(2):271–279. doi:10.1007/s11060-009-9927-z
Giordana MT, Cavalla P, Dutto A, Borsotti L, Chio A, Schiffer D (1997) Is medulloblastoma the same tumor in children and adults? J Neurooncol 35(2):169–176
Korshunov A, Remke M, Werft W, Benner A, Ryzhova M, Witt H, Sturm D, Wittmann A, Schottler A, Felsberg J, Reifenberger G, Rutkowski S, Scheurlen W, Kulozik AE, von Deimling A, Lichter P, Pfister SM (2010) Adult and pediatric medulloblastomas are genetically distinct and require different algorithms for molecular risk stratification. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 28(18):3054–3060. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.25.7121
Yakut H, Tabar E, Zenginerler Z, Demirci N, Ertugral F (2013) Measurement of (222)Rn concentration in drinking water in Sakarya, Turkey. Radiat Prot Dosimetry 157(3):397–406. doi:10.1093/rpd/nct157
Corcoran RB, Scott MP (2006) Oxysterols stimulate Sonic hedgehog signal transduction and proliferation of medulloblastoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(22):8408–8413. doi:10.1073/pnas.0602852103
Dubey AK, Dubey S, Handu SS, Qazi MA (2013) Vismodegib: the first drug approved for advanced and metastatic basal cell carcinoma. J Postgrad Med 59(1):48–50
Meiss F, Zeiser R (2014) Vismodegib. Recent Results Cancer Res Fortschritte der Krebsforschung Progres dans les recherches sur le cancer 201:405–417. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-54490-3_25
Gajjar A, Stewart CF, Ellison DW, Kaste S, Kun LE, Packer RJ, Goldman S, Chintagumpala M, Wallace D, Takebe N, Boyett JM, Gilbertson RJ, Curran T (2013) Phase I study of vismodegib in children with recurrent or refractory medulloblastoma: a pediatric brain tumor consortium study. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res 19(22):6305–6312. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-1425
Zhi F, Wang S, Wang R, Xia X, Yang Y (2013) From small to big: microRNAs as new players in medulloblastomas. Tumour Biol J Int Soc Oncodevelopmental Biol Med 34(1):9–15. doi:10.1007/s13277-012-0579-9
Pang JC, Kwok WK, Chen Z, Ng HK (2009) Oncogenic role of microRNAs in brain tumors. Acta Neuropathol 117(6):599–611. doi:10.1007/s00401-009-0525-0
Vidal DO, Marques MM, Lopes LF, Reis RM (2013) The role of microRNAs in medulloblastoma. Pediatr Hematol Oncol 30(5):367–378. doi:10.3109/08880018.2013.783890
Jin Y, Xiong A, Zhang Z, Li S, Huang H, Yu TT, Cao X, Cheng SY (2014) MicroRNA-31 suppresses medulloblastoma cell growth by inhibiting DNA replication through minichromosome maintenance 2. Oncotarget 5(13):4821–4833
Arndt CA, Rose PS, Folpe AL, Laack NN (2012) Common musculoskeletal tumors of childhood and adolescence. Mayo Clin Proc 87(5):475–487. doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2012.01.015
Maksimenko A, Polard V, Villemeur M, Elhamess H, Couvreur P, Bertrand JR, Aboubakar M, Gottikh M, Malvy C (2005) In vivo potentialities of EWS-Fli-1 targeted antisense oligonucleotides-nanospheres complexes. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1058:52–61. doi:10.1196/annals.1359.010
Scherzinger-Laude K, Schonherr C, Lewrick F, Suss R, Francese G, Rossler J (2013) Treatment of neuroblastoma and rhabdomyosarcoma using RGD-modified liposomal formulations of patupilone (EPO906). Int J Nanomedicine 8:2197–2211. doi:10.2147/IJN.S44025
Dhule SS, Penfornis P, Frazier T, Walker R, Feldman J, Tan G, He J, Alb A, John V, Pochampally R (2012) Curcumin-loaded gamma-cyclodextrin liposomal nanoparticles as delivery vehicles for osteosarcoma. Nanomedicine 8(4):440–451. doi:10.1016/j.nano.2011.07.011
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aleassa, E.M., Xing, M. & Keijzer, R. Nanomedicine as an innovative therapeutic strategy for pediatric cancer. Pediatr Surg Int 31, 611–616 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-015-3683-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-015-3683-2