Abstract
Purpose
Pulmonary hypoplasia (PH), characterized by alveolar immaturity, remains the main cause of neonatal mortality and long-term morbidity in infants with congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH). Lipid-containing interstitial fibroblasts (LIFs) are critically important for normal alveolar development. Thymocyte antigen 1 (Thy-1) is a highly expressed cell-surface protein in this specific subset of lung fibroblasts, which plays a key role in fetal alveolarization by coordinating the differentiation and lipid homeostasis of alveolar LIFs. Thy-1 increases the lipid content of LIFs by upregulation of adipocyte differentiation-related protein (ADRP), a lipogenic molecular marker characterizing pulmonary LIFs. Thy-1 −/− mice further show impaired alveolar development with reduced proliferation of pulmonary LIFs, resulting in a PH-similar phenotype. We hypothesized that pulmonary Thy-1 signaling is disrupted in experimentally induced CDH, which may has an adverse effect on the lipid content of alveolar LIFs.
Methods
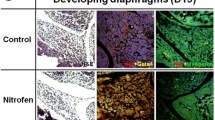
Timed-pregnant Sprague–Dawley rats were treated with either 100 mg nitrofen or vehicle on embryonic day 9.5 (E9.5). Fetuses were killed on E21.5, and lungs were divided into controls (n = 14) and CDH-associated PH (n = 14). Pulmonary gene expression levels of Thy-1 and ADRP were assessed by quantitative real-time PCR. ADRP immunohistochemistry and oil-red-O staining were used to localize alveolar LIF expression and lipid droplets. Immunofluorescence double staining for Thy-1 and oil-red-O was performed to evaluate Thy-1 expression and lipid content in alveolar LIFs.
Results
Radial alveolar count was significantly reduced in CDH-associated PH with significant downregulation of pulmonary Thy-1 and ADRP mRNA expression compared to controls. ADRP immunoreactivity and lipid droplets were markedly diminished in alveolar interstitial cells, which coincided with decreased alveolar LIF expression in CDH-associated PH compared to controls. Confocal laser scanning microscopy confirmed markedly decreased Thy-1 expression and lipid content in alveolar LIFs of CDH-associated PH compared to controls.
Conclusion
Our study provides strong evidence that disruption of pulmonary Thy-1 signaling results in reduced lipid droplets in alveolar LIFs and may thus contribute to PH in the nitrofen-induced CDH model. Treatment modalities aimed at increasing lipid content in alveolar LIFs may therefore have a therapeutic potential in attenuating CDH-associated PH.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Langham MR Jr, Kays DW, Ledbetter DJ et al (1996) Congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Epidemiology and outcome. Clin Perinatol 23(4):671–688
Stege G, Fenton A, Jaffray B (2003) Nihilism in the 1990s: the true mortality of congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Pediatrics 112(3 Pt 1):532–535
Keijzer R, Puri P (2010) Congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Semin Pediatr Surg 19(3):180–185
Garriboli M, Duess JW, Ruttenstock E et al (2012) Trends in the treatment and outcome of congenital diaphragmatic hernia over the last decade. Pediatr Surg Int 28(12):1177–1181
van den Hout L, Schaible T, Cohen-Overbeek TE et al (2011) Actual outcome in infants with congenital diaphragmatic hernia: the role of a standardized postnatal treatment protocol. Fetal Diagn Ther 29(1):55–63
Madderom MJ, Toussaint L, van der Cammen-van Zijp MH et al (2013) Congenital diaphragmatic hernia with (out) ECMO: impaired development at 8 years. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 98(4):F316–F322
Rocha G, Azevedo I, Pinto JC et al (2012) Follow-up of the survivors of congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Early Hum Dev 88(4):255–258
Tovar JA (2012) Congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Orphanet J Rare Dis 7:1
Mortell A, Montedonico S, Puri P (2006) Animal models in pediatric surgery. Pediatr Surg Int 22(2):111–128
van Loenhout RB, Tibboel D, Post M et al (2009) Congenital diaphragmatic hernia: comparison of animal models and relevance to the human situation. Neonatology 96(3):137–149
Noble BR, Babiuk RP, Clugston RD et al (2007) Mechanisms of action of the congenital diaphragmatic hernia-inducing teratogen nitrofen. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 293(4):L1079–L1087
Beurskens N, Klaassens M, Rottier R et al (2007) Linking animal models to human congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol 79(8):565–572
McGowan SE, Torday JS (1997) The pulmonary lipofibroblast (lipid interstitial cell) and its contributions to alveolar development. Annu Rev Physiol 59:43–62
Torday JS, Torres E, Rehan VK (2003) The role of fibroblast transdifferentiation in lung epithelial cell proliferation, differentiation, and repair in vitro. Pediatr Pathol Mol Med 22(3):189–207
Torday J, Hua J, Slavin R (1995) Metabolism and fate of neutral lipids of fetal lung fibroblast origin. Biochim Biophys Acta 1254(2):198–206
Tordet C, Marin L, Dameron F (1981) Pulmonary di-and-triacylglycerols during the perinatal development of the rat. Experientia 37(4):333–334
Varisco BM, Ambalavanan N, Whitsett JA et al (2012) Thy-1 signals through PPARgamma to promote lipofibroblast differentiation in the developing lung. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 46(6):765–772
Brasaemle DL, Barber T, Wolins NE et al (1997) Adipose differentiation-related protein is an ubiquitously expressed lipid storage droplet-associated protein. J Lipid Res 38(11):2249–2263
Schultz CJ, Torres E, Londos C et al (2002) Role of adipocyte differentiation-related protein in surfactant phospholipid synthesis by type II cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 283(2):L288–L296
Nicola T, Hagood JS, James ML et al (2009) Loss of Thy-1 inhibits alveolar development in the newborn mouse lung. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 296(5):L738–L750
Randell SH, Mercer RR, Young SL (1989) Postnatal growth of pulmonary acini and alveoli in normal and oxygen-exposed rats studied by serial section reconstructions. Am J Anat 186(1):55–68
Brandsma AE, ten Have-Opbroek AA, Vulto IM et al (1994) Alveolar epithelial composition and architecture of the late fetal pulmonary acinus: an immunocytochemical and morphometric study in a rat model of pulmonary hypoplasia and congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Exp Lung Res 20(6):491–515
Roth-Kleiner M, Post M (2003) Genetic control of lung development. Biol Neonate 84(1):83–88
Kaplan NB, Grant MM, Brody JS (1985) The lipid interstitial cell of the pulmonary alveolus: age and species differences. Am Rev Respir Dis 132(6):1307–1312
Rehan VK, Sugano S, Wang Y et al (2006) Evidence for the presence of lipofibroblasts in human lung. Exp Lung Res 32(8):379–393
Torday J, Rehan V (2011) Neutral lipid trafficking regulates alveolar type II cell surfactant phospholipid and surfactant protein expression. Exp Lung Res 37(6):376–386
Londos C, Brasaemle DL, Schultz CJ et al (1999) Perilipins, ADRP, and other proteins that associate with intracellular neutral lipid droplets in animal cells. Semin Cell Dev Biol 10(1):51–58
Magra AL, Mertz PS, Torday JS et al (2006) Role of adipose differentiation-related protein in lung surfactant production: a reassessment. J Lipid Res 47(11):2367–2373
Doi T, Lukosiute A, Ruttenstock E et al (2010) Disturbance of parathyroid hormone-related protein signaling in the nitrofen-induced hypoplastic lung. Pediatr Surg Int 26(1):45–50
Gosemann JH, Doi T, Kutasy B et al (2012) Alterations of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 gene expression in the nitrofen-induced hypoplastic lung. J Pediatr Surg 47(5):847–851
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Children’s Research Centre and the Children’s Medical and Research Foundation.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Friedmacher, F., Hofmann, A.D., Takahashi, H. et al. Disruption of THY-1 signaling in alveolar lipofibroblasts in experimentally induced congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Pediatr Surg Int 30, 129–135 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-013-3444-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-013-3444-z