Abstract
Background
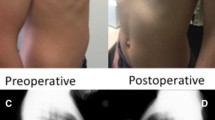
This report presents early results of surgical experience of minimal invasive extrathoracic presternal compression using a metal bar for correction of the pectus carinatum.
Methods
From February 2008 to February 2012, 15 patients with combined pectus carinatum and pectus excavatum underwent minimal invasive extrathoracic presternal compression using a metal bar for correction of pectus carinatum and Nuss operation for pectus excavatum. After 2 years, bar removal was done in all patients. In this paper, we focused on pectus carinatum repair. The effects and complications of the minimally invasive extrathoracic presternal compression using a metal bar for correction of pectus carinatum were reviewed.
Results
The median age was 15.7 years. The mean operation time for pectus carinatum with pectus excavatum was 122 min. The median length of hospitalization was 6 days. The Haller pectus index of pectus carinatum was 2.93 ± 0.36 pre-operatively and this was increased to 3.33 ± 0.61 post-operatively. There were no special complications. The degree of satisfaction of pectus carinatum correction was 3.75 ± 0.46 (range 1–4).
Conclusion
Our results were favorable in spite of the small number of cases and short follow-up, and our modified technique of pectus carinatum was easy and simple. However, long-term follow-up is needed to accurately evaluate the effects of this surgery in many cases.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ravitch MM (1960) The operative correction of pectus carinatum (pigeon breast). Ann Surg 151:705–714
Abramson H (2005) A minimally invasive technique to repair pectus carinatum. Preliminary report. Arch Bronconeumol 41:349–351
Abramson H, D’Agostino J, Wuscovi S (2009) A 5-year experience with a minimally invasive technique for pectus carinatum repair. J Pediatr Surg 44:118–123
Park HJ, Lee SY, Lee CS, Youm W, Lee KR (2004) The Nuss procedure for pectus excavatum: evolution of techniques and early results on 322 patients. Ann Thorac Surg 77:289–295
Ravitch MM (1952) Unusual sternal deformity with cardiac symptoms–operative correction. J Thorac Surg 23:138–144
Haje SA, Bowen JR (1992) Preliminary results of orthotic treatment of pectus deformities in children and adolescents. J Pediatr Orthop 12:795–800
Lee SY, Lee SJ, Jeon CW, Lee CS, Lee KR (2008) Effect of the compressive brace in pectus carinatum. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 34:146–149
Kálmán A (2009) Initial results with minimally invasive repair of pectus carinatum. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 138:434–438
Hock A (2009) Minimal access treatment of pectus carinatum: a preliminary report. Pediatr Surg Int 25:337–342
Kim S, Idowu O (2009) Minimally invasive thoracoscopic repair of unilateral pectus carinatum. J Pediatr Surg 44:471–474
Pérez D, Cano JR, Quevedo S, López L (2011) New minimally invasive technique for correction of pectus carinatum. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 39:271–273
Yüksel M, Bostanci K, Evman S (2011) Minimally invasive repair of pectus carinatum using a newly designed bar and stabilizer: a single-institution experience. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 40:339–342
Nuss D, Kelly RE, Croitoru DP, Katz ME (1988) A 10-year review of a minimally invasive technique for the correction of pectus excavatum. J Ped Surg 33:545–552
Nuss D (2005) Recent experiences with minimally invasive pectus excavatum repair “Nuss procedure”. Jpn J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 53(7):338–344
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, S.Y., Song, I.H. & Lee, S.J. Minimal invasive extrathoracic presternal compression using a metal bar for correction of pectus carinatum. Pediatr Surg Int 30, 25–30 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-013-3419-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-013-3419-0