Abstract
Aim
To evaluate the effects of repeated injections of onabotulinumtoxinA in children with neurogenic bladders refractory to conventional treatment.
Patients and methods
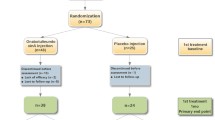
A total of 26 children with neurogenic bladder were prospectively studied. Some patients received up to four repeat injections. Patients were reinjected if they showed improvement in voiding diary, score of urinary incontinence and/or urodynamic studies; otherwise, augmentation cystoplasty was indicated.
Results
Of the 26 patients, 12 were reinjected a second time, 6 patients were reinjected a third time and 2 patients received a repeat injection for the fourth time. Six months after the first, second and third injection, the urinary incontinence score 0 (dry) was 50, 77 and 75 %, respectively. After each injection, the mean bladder capacity in voiding diary and the mean maximum cystometric capacity increased. The mean detrusor pressure at the end of filling decreased. Only compliance after the first injection improved significantly. Detrusor overactivity (n: 4), improved during 3 months and reappeared in three children after the first injection, but at greater cystometric volumes. In the fourth case, it reappeared 11 months after the third injection. Five patients underwent cystoplasty.
Conclusion
After treatment with onabotulinumtoxinA, urinary continence achieved was 50–77 %. There were favorable changes in urodynamic variables, but they were insufficient. Detrusor overactivity was attenuated, but did not disappear completely.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Game’ X, Grima F, Chartier-Kastler E, Ruffion A (2007) Troubles vesico-sphincteriens et sexuels des spinabidida et myelomeningoceles. ProgUrol 17:352e7
McGuire EJ, Woodside JR, Borden TA, Weiss RM (1981) Prognostic value of urodynamic testing in myelodysplastic patients. J Urol 126(2):205–209
Abrams P, Larsson G, Chapple C, Wein AJ (1999) Factors involved in the success of antimuscarinic treatment. BJU Int 83(Suppl. 2):42–47
Hernandez RD, Hurwitz RS, Foote JE, Zimmern PE, Leach GE (1994) Non-surgical management of threatened upper urinary tracts and incontinence in children with myelomeningocele. J Urol 152:1582–1585
Dykstra DD, Sidi AA (1990) Treatment of detrusor-sphincter dyssynergia with botulinum A toxin: a double-blind study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 71:24–26
Stohrer M, Schuch B, Kramer G, Schmidt D, Gaul D, Hauri D (1999) Botulinum A toxin in the treatment of detrusor hyperreflexia in spinal cord injury. A new alternative to medical and surgical procedures? Neurourolurodyn 18:401–402
Schulte-Baukloh H, Michael T, Schobert J, Stolze T, Knispel HH (2002) Efficacy of botulinum-A toxin in children with detrusor hyperreflexia due to myelomeningocele: preliminary results. Urology 59:325–327 discussion: 327–328
Pascali M et al (2011) Effects of Botulinum toxin type A in the bladder wall of children with neurogenic bladder dysfunction: a comparison of histological features before and after injections. J Urol 185:2552–2557
Lowes R. Botox Approved to Treat Overactive Bladder. FDA Approvals, January 2013
Schurch B, Stöhrer M, Kramer G, Schmid DM, Gaul G, Hauri D (2000) Botulinum-A toxin for treating detrusor hyperreflexia in spinal cord injured patients: a new alternative to anticholinergic drugs? Preliminary results. J Urol 164:692–697
Dolly O (2003) Synaptic transmission: inhibition of neurotransmitter release by botulinum toxins. Headache 43(Suppl 1):S16–S24
Welch MJ, Purkiss JR, Foster KA (2000) Sensitivity of embryonic rat dorsal root ganglia neurons to Clostridium botulinum neurotoxins. Toxicon 38:245–258
Apostolidis A, Dasgupta P, Fowler CJ (2006) Proposed mechanism for the efficacy of injected botulinum toxin in the treatment of human detrusor overactivity. Eur Urol 49:644–650
Schulte-Baukloh H, Michael T, Schobert J, Stolze T, Knispel HH (2002) Efficacy of botulinum-a toxin in children with detrusor hyperreflexia due to myelomeningocele: preliminary results. Urology 59:325–328
Riccabona M, Koen M, Schindler M, Goedele B, Pycha A, Lusuardi L et al (2004) Botulinum-A toxin injection into the detrusor: a safe alternative in the treatment of children with myelomeningocele with detrusor hyperreflexia. J Urol 171:845–848
Gamé X, Mouracade P, Chartier-Kastler E, Viehweger E, Moog R et al (2009) Botulinum toxin-A (Botox) intradetrusor injection in children with neurogenic detrusor overactivity/neurogenic overactive bladder: a systematic literature review. J Pediatr Urol 5:156–164
Apostolidis A, Dasgupta P, Denys P, Elneir S, Fowler C et al (2009) Recommendations on the use of botulinum toxin in the treatment of lower urinary tract disorder and pelvic floor dysfunctions: a European Consensus Report. Eur Urol 55:100–120
Deshpande A, Sampang R, Smith G (2010) Study of Botulinum toxin A in neurogenic bladder due to spina bifida in children. ANZ J Surg 80:250–253
Sager C, Burek C, Duran V et al (2011) Toxina botulínica-A en el tratamiento de niños con vejiga neurogénica. Cir Pediatr 24:38–43
Grosse J, Kramer G, Stohrer M (2005) Success of repeated detrusor injections of botulinum A Toxin in patients with severe neurogenic detrusor overactivity and incontinence. Eur Urol 47:653–659
Kajbafzadeh AM, Nikfarjam L, Mahboudi A et al (2010) Antibody formation following botulinum toxin type A (Dysport) injection in children with intractable bladder hyperreflexia. J Urol. doi:10.1016/J.urology.2010.03.023
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Nurse Carmen Machado for her invaluable work.
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sager, C., Burek, C., Bortagaray, J. et al. Repeated injections of intradetrusor onabotulinumtoxinA as adjunctive treatment of children with neurogenic bladder. Pediatr Surg Int 30, 79–85 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-013-3365-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-013-3365-x