Abstract
Purpose
Down syndrome (DS) is the most frequent chromosomal abnormality associated with Hirschsprung’s disease (HD). It has often been suggested that this association results in poorer outcomes with regard to postoperative complications, continence and mortality. On the other hand, the results after surgical treatment of HD in patients with DS are reportedly similar to those in cases with HD alone. The objective of this study was to determine the incidence of DS in cohorts with HD, and to compare pre-/postoperative complications, functional outcome and mortality between cohorts with and without coexisting DS.
Methods
A systematic literature-based search for relevant cohorts was conducted using multiple online databases. The number of DS cases in HD cohorts was recorded and data on pre-/postoperative complications, functional outcome and mortality were extracted. Pooled odds ratios with 95 % confidence intervals were calculated using meta-analysis methodology.
Results
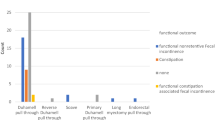
Sixty-one articles met defined inclusion criteria, comprising data from 16,497 patients with HD. The overall incidence of DS among them was 7.32 %. Vice versa, the incidence of HD in 29,418 patients with DS was 2.62 %. There were no significant differences regarding the male-to-female ratio between cohorts with and without coexisting DS (4:1 vs. 3:1 respectively; P = 0.5376). The rate of additional comorbidities was significantly higher in HD associated with DS (P < 0.0001). Recto-sigmoid HD was in both cohorts the most common type of HD (P = 0.8231). Long-segment HD was significantly more frequent in HD with coexisting DS (P = 0.0267), while total colonic aganglionosis occurred significantly more often in HD without DS (P = 0.0003). There were no significant differences in preoperative constipation/obstruction (P = 0.5967), but the rate of preoperative enterocolitis was significantly higher in HD associated with DS (P = 0.0486). Postoperative complications such as recurrent enterocolitis (P = 0.0112) and soiling (P = 0.0002) were significantly more frequent in HD with coexisting DS. Although not statistically significant, fecal incontinence (P = 0.1014) and persistent constipation (P = 0.1670) occurred more often after surgical treatment of HD with DS. The mortality rate was significantly higher in HD associated with DS (P < 0.0001).
Conclusions
The association of HD with DS is well-recognized with an incidence of 7.32 %. A large number of patients with DS continue to have persistent bowel dysfunction after surgical treatment of HD. Our data provide strong evidence that the coexistence of HD and DS is associated with higher rates of pre-/postoperative enterocolitis, poorer functional outcomes and increased mortality.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amiel J, Sproat-Emison E, Garcia-Barcelo M et al (2008) Hirschsprung disease, associated syndromes and genetics: a review. J Med Genet 45(1):1–14
Moore SW, Zaahl MG (2012) Intronic RET gene variants in Down syndrome-associated Hirschsprung disease in an African population. J Pediatr Surg 47(2):299–302
Arnold S, Pelet A, Amiel J et al (2009) Interaction between a chromosome 10 RET enhancer and chromosome 21 in the Down syndrome–Hirschsprung disease association. Hum Mutat 30(5):771–775
Borbolla Vacher L, Garcia Palacio A, Martinez Garcia W (1956) Hirschsprung’s disease in a 38 day old mongoloid boy. Rev Cuba Pediatr 28(8):473–484
Clarke SA, Van der Avoirt A (1999) Imperforate anus, Hirschsprung’s disease, and trisomy 21: a rare combination. J Pediatr Surg 34(12):1874
DuBois JJ, Cheng J, Pokorny WJ (1995) Inflammatory pseudocyst associated with trisomy 21 and Hirschsprung’s disease. Mil Med 160(9):477–479
Flageole H, Fecteau A, Laberge JM et al (1996) Hirschsprung’s disease, imperforate anus, and Down’s syndrome: a case report. J Pediatr Surg 31(6):759–760
Leung AK, Mui CY, Lau JT (1986) Hirschsprung’s disease and mongolism. J Natl Med Assoc 78(5):443–446
Wolf HG, Zweymüller E (1962) Mongolismus und aganglionäres megacolon. Wiener Klin Wochenschr 74(12):219–223
Zarnitsky C, Lhuintre JP, Joly JP et al (1988) Association d’une malaide de hirschsprung, d’un diverticule de Meckel et d’une lethiase vesiculaire chez une jeune mongolienne. Ann Gastroenterol Hepatol 24:21–22
Quinn FM, Surana R, Puri P (1994) The influence of trisomy 21 on outcome in children with Hirschsprung’s disease. J Pediatr Surg 29(6):781–783
Russell MB, Russell CA, Niebuhr E (1994) An epidemiological study of Hirschsprung’s disease and additional anomalies. Acta Paediatr 83(1):68–71
Suita S, Taguchi T, Ieiri S et al (2005) Hirschsprung’s disease in Japan: analysis of 3852 patients based on a nationwide survey in 30 years. J Pediatr Surg 40(1):197–201
Wilcox DT, Bruce J, Bowen J et al (1997) One-stage neonatal pull-through to treat Hirschsprung’s disease. J Pediatr Surg 32(2):243–245
Caniano DA, Teitelbaum DH, Qualman SJ (1990) Management of Hirschsprung’s disease in children with trisomy 21. Am J Surg 159(4):402–404
Moore SW, Johnson AG (1998) Hirschsprung’s disease: genetic and functional associations of Down’s and Waardenburg syndromes. Semin Pediatr Surg 7(3):156–161
Rescorla FJ, Morrison AM, Engles D et al (1992) Hirschsprung’s disease. Evaluation of mortality and long-term function in 260 cases. Arch Surg 127(8):934–941
Catto-Smith AG, Trajanovska M, Taylor RG (2006) Long-term continence in patients with Hirschsprung’s disease and Down syndrome. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 21(4):748–753
Sherman JO, Snyder ME, Weitzman JJ et al (1989) A 40-year multinational retrospective study of 880 Swenson procedures. J Pediatr Surg 24(8):833–838
Hackam DJ, Reblock K, Barksdale EM et al (2003) The influence of Down’s syndrome on the management and outcome of children with Hirschsprung’s disease. J Pediatr Surg 38(6):946–949
Ieiri S, Higashi M, Teshiba R et al (2009) Clinical features of Hirschsprung’s disease associated with Down syndrome: a 30-year retrospective nationwide survey in Japan. J Pediatr Surg 44(12):2347–2351
Menezes M, Puri P (2005) Long-term clinical outcome in patients with Hirschsprung’s disease and associated Down’s syndrome. J Pediatr Surg 40(5):810–812
Morabito A, Lall A, Gull S et al (2006) The impact of Down’s syndrome on the immediate and long-term outcomes of children with Hirschsprung’s disease. Pediatr Surg Int 22(2):179–181
Teitelbaum DH, Qualman SJ, Caniano DA (1988) Hirschsprung’s disease. Identification of risk factors for enterocolitis. Ann Surg 207(3):240–244
Travassos D, van Herwaarden-Lindeboom M, van der Zee DC (2011) Hirschsprung’s disease in children with Down syndrome: a comparative study. Eur J Pediatr Surg 21(4):220–223
Moore SW (2008) Down syndrome and the enteric nervous system. Pediatr Surg Int 24(8):873–883
Madsen CM (1964) Hirschsprung’s disease. Munksgaard, Copenhagen, p 245
Cleves MA, Hobbs CA, Cleves PA et al (2007) Congenital defects among liveborn infants with Down syndrome. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol 79(9):657–663
Fabia J, Drolette M (1970) Malformations and leukemia in children with Down’s syndrome. Pediatrics 45(1):60–70
Rintala RJ, Pakarinen MP (2012) Long-term outcomes of Hirschsprung’s disease. Semin Pediatr Surg 21(4):336–343
Nair MP, Schwartz SA (1984) Association of decreased T-cell-mediated natural cytotoxicity and interferon production in Down’s syndrome. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 33(3):412–424
Wilson-Storey D, Scobie WG, Raeburn JA (1988) Defective white blood cell function in Hirschsprung’s disease: a possible predisposing factor to enterocolitis. J R Coll Surg Edinb 33(4):185–188
Yin H, Boyd T, Pacheco MC et al (2012) Rectal biopsy in children with Down syndrome and chronic constipation: Hirschsprung disease vs non-Hirschsprung disease. Pediatr Dev Pathol 15(2):87–95
Hays DM, Norris WJ (1956) Congenital aganglionic megacolon. Calif Med 84(6):403–406
Althoff W (1962) On the genetics of Hirschsprung’s disease. Z Mensch Vererb Konstitutionsl 36:314–340
Eek S, Knutrud O (1962) Megacolon congenitum Hirschsprung: a follow-up study of 63 patients. J Oslo City Hosp 12:245
Bodian M, Carter CO (1963) A family study of Hirschsprung’s disease. Ann Hum Genet 26(3):261–277
Emanuel B, Padorr MP, Swenson O (1965) Mongolism associated with Hirschsprung’s disease. J Pediatr 66:437–439
Graivier L, Sieber WK (1966) Hirschsprung’s disease and mongolism. Surgery 60(2):458–461
Hofmann S, Rehbein F (1966) Hirschsprungsche Krankheit im Neugeborenenalter. Z Kinderchir 3(2):1966
Gordon H, Torrington M, Louw JH et al (1966) A genetical study of Hirschsprung’s disease: congenital intestinal aganglionosis. S Afr Med J 40(30):720–721
Passarge E (1967) The genetics of Hirschsprung’s disease. Evidence for heterogeneous etiology and a study of sixty-three families. N Engl J Med 276(3):138–143
Fraser GC, Wilkinson AW (1967) Neonatal Hirschsprung’s disease. Br Med J 3(5556):7–10
Kilcoyne RF, Taybi H (1970) Conditions associated with congenital megacolon. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med 108(3):615–620
Knox GE, ten Bensel RW (1972) Gastrointestinal malformations in Down’s syndrome. Minn Med 55(6):542–544
Tobon F, Schuster MM (1974) Megacolon: special diagnostic and therapeutic features. Johns Hopkins Med J 135(2):91–105
Goldberg EL (1984) An epidemiological study of Hirschsprung’s disease. Int J Epidemiol 13(4):479–485
Spouge D, Baird PA (1985) Hirschsprung disease in a large birth cohort. Teratology 32(2):171–177
Garver KL, Law JC, Garver B (1985) Hirschsprung disease: a genetic study. Clin Genet 28(6):503–508
Polley TZJ, Coran AG (1986) Hirschsprung’s disease in the newborn. Pediatr Surg Int 1(2):80–83
Badner JA, Sieber WK, Garver KL et al (1990) A genetic study of Hirschsprung disease. Am J Hum Genet 46(3):568–580
Molander ML (1990) Hirschsprung’s disease in mentally retarded patients: a bad prognostic combination. Pediatr Surg Int 5(5):339–340
Cass D (1990) Aganglionosis: associated anomalies. J Paediatr Child Health 26(6):351–354
Ryan ET, Ecker JL, Christakis NA et al (1992) Hirschsprung’s disease: associated abnormalities and demography. J Pediatr Surg 27(1):76–81
Russell MB, Russell CA, Fenger K et al (1994) Familial occurrence of Hirschsprung’s disease. Clin Genet 45(5):231–235
Halevy H, Mares A, Cohen Z et al (1994) Hirschsprung’s disease in the Negev. Harefuah 127(5–6):148–154
Rajab A, Freeman NV, Patton MA (1997) Hirschsprung’s disease in Oman. J Pediatr Surg 32(5):724–727
Sarioğlu A, Tanyel FC, Büyükpamukçu N et al (1997) Hirschsprung-associated congenital anomalies. Eur J Pediatr Surg 7(6):331–337
Torfs CP, Christianson RE (1998) Anomalies in Down syndrome individuals in a large population-based registry. Am J Med Genet 77(5):431–438
Das K, Alladi A, Kini U et al (2001) Hirschsprung’s disease, associated rare congenital anomalies. Indian J Pediatr 68(9):835–837
Singh SJ, Croaker GD, Manglick P et al (2003) Hirschsprung’s disease: the Australian paediatric surveillance unit’s experience. Pediatr Surg Int 19(4):247–250
Carter CO (1958) A life-table for Mongols with the cause of death. J Ment Defic Res 2(2):64–74
Hanhart E (1960) 800 Fälle von Mongoloidismus in konstitutioneller Betrachtung. Arch Julius Klaus-Stiftg 35(1–2):1–312
Rowe RD, Uchida IA (1961) Cardiac malformation in mongolism: a prospective study of 184 mongoloid children. Am J Med 31:726–735
de Wolff E (1964) Clinical study of 134 Mongoloids. Ann Paediatr 202(Suppl):1–47
Buchin PJ, Levy JS, Schullinger JN (1986) Down’s syndrome and the gastrointestinal tract. J Clin Gastroenterol 8(2):111–114
Khoury MJ, Erickson JD (1992) Can maternal risk factors influence the presence of major birth defects in infants with Down syndrome? Am J Med Genet 43(6):1016–1022
Källén B, Mastroiacovo P, Robert E (1996) Major congenital malformations in Down syndrome. Am J Med Genet 65(2):160–166
Hayes C, Johnson Z, Thornton L et al (1997) Ten-year survival of Down syndrome births. Int J Epidemiol 26(4):822–829
Aquino A, Domini M, Rossi C et al (1998) Correlation between Down’s syndrome and malformations of pediatric surgical interest. J Pediatr Surg 33(9):1380–1382
Spahis JK, Wilson GN (1999) Down syndrome: perinatal complications and counseling experiences in 216 patients. Am J Med Genet 89(2):96–99
Frid C, Drott P, Lundell B et al (1999) Mortality in Down’s syndrome in relation to congenital malformations. J Intellect Disabil Res 43(Pt 3):234–241
Kava MP, Tullu MS, Muranjan MN et al (2004) Down syndrome: clinical profile from India. Arch Med Res 35(1):31–35
Abbag FI (2006) Congenital heart diseases and other major anomalies in patients with Down syndrome. Saudi Med J 27(2):219–222
Azman BZ, Ankathil R, Siti Mariam I et al (2007) Cytogenetic and clinical profile of Down syndrome in Northeast Malaysia. Singap Med J 48(6):550–554
Yam WK, Tse PW, Yu CM et al (2008) Medical issues among children and teenagers with Down syndrome in Hong Kong. Downs Syndr Res Pract 12(2):138–140
Freeman SB, Torfs CP, Romitti PA et al (2009) Congenital gastrointestinal defects in Down syndrome: a report from the Atlanta and National down syndrome projects. Clin Genet 75(2):180–184
Karaman A (2011) Medical problems in children with Down syndrome in the Erzurum area of Turkey. Genet Couns 21(4):385–395
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the medical staff librarians at Our Lady’s Children’s Hospital, Crumlin for their outstanding support in the literature search process for this manuscript: Suzanne Feeney, MA, DLIS; Jane Doyle, BA, Dip.LIS; and Caitríona Lee, B.Sc., H.Dip., MLIS.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Friedmacher, F., Puri, P. Hirschsprung’s disease associated with Down syndrome: a meta-analysis of incidence, functional outcomes and mortality. Pediatr Surg Int 29, 937–946 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-013-3361-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-013-3361-1