Abstract
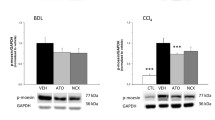
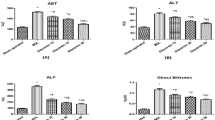
Inhibitors of 3-hydroxy-3methylglutarly coenzyme A, reductase, namely statins, exert pleiotropic actions beyond lipid-lowering effects. In ex vivo and in vitro studies, statins have antioxidative and antiinflammatory effects. Herein, we sought to determine whether treatment with fluvastatin (FV) would be beneficial in a rat model of common bile duct ligation (BDL)-induced liver injury. Female rats were subjected to a sham (n = 10) or BDL (n = 20). Obstructive jaundice was induced in rats by the ligation and division of the common bile duct. Three days after operation, rats subjected to CBDL were randomized to receive treatment with either FV (10 mg/kg) or saline every day over a 10 days experimental period. High levels of alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, and gamma glutamyltransferase decreased significantly (P < 0.05) in animals treated with FV with compared to saline-administrated BDL animals. Compared with sham-operated rats, CBDL rats showed significantly higher levels of total nitrite and nitrate, malondihaldehyde, tumor necrosis factor alpha, myeloperoxidase, and lower concentrations of glutathione, superoxide dismutase, and catalase in the liver tissue (P < 0.001). All of these changes were significantly attenuated (P < 0.05) by treatment with FV after CBDL. CBDL was associated with increased apoptosis and nuclear factor kappa beta expression in saline-treated rats. Treatment with FV also decreased these parameters. These data support the view that FV ameliorates hepatic inflammation, lipid peroxidation, and tissue injury in rats subjected to CDBL. FV warrants further evaluation as an adjunctive treatment to ameliorate liver injury from extrahepatic biliary obstruction.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Greig JD, Krukowski ZH, Matheson NA (1988) Surgical morbidity and mortality in one hundred and twenty-nine patients with obstructive jaundice. Br J Surg 75:216–219
Tracy T Jr, Fox ES (1996) Molecular and cellular control points in pediatric liver injury and repair. Semin Pediatr Surg 5:175–181
Greim H, Trulzsch D, Roboz J, Dressler K, Czygan P, Hutterer F, Schaffner F, Popper H (1972) Mechanism of cholestasis.5. Bile acids in normal rat livers and in those after bile duct ligation. Gastroenterology 63:837–845
Miyoshi H, Rust C, Roberts PJ, Burgart LJ, Gores GJ (1999) Hepatocyte apoptosis after bile duct ligation in the mouse involves Fas. Gastroenterology 117:669–677
Tsai LY, Lee KT, Tsai S, Lee SC, Yu HS (1993) Changes of lipid peroxides levels in blood and liver tissue of patients with obstructive jaundice. Clin Chim Acta 215:41–50
Liu TZ, Lee KT, Chern CL, Cheng JT, Stern A, Tsai LY (2001) Free radical triggered hepatic injury of experimental obstructive jaundice of rats involves overproduction of proinflammatory cytokines and enhanced activation of nuclear factor kappaβ. Ann Clin Lab Sci 31:383–390
Richter L, Hesselbarth N, Eitner K, Schubert K, Bosseckert H, Krell H (1996) Increased biliary secretion of cysteinyl-leukotrienes in human bile duct obstruction. J Hepatol 25:725–732
Cukubova MV (1998) Intracellular adhesion molecula-1 (ICAM-1) expression in the liver of patients with extrahepatic cholestasis. Acta Histochem 100:59–74
Takaoka M, Kubota Y, Tsuji K, Yamamoto S, Ogura M, Yanagitani K, Shimatani M, Shibatani N, Inoue K (2001) Human neutrophil functions in obstructive jaundice. Hepatogastroenterology 48:71–75
Lechner AJ, Velasquez A, Knudsen KR, Johanns CA, Tracy TF Jr, Matuschak GM (1998) Cholestatic liver injury increases circulating TNF-alpha and IL-6 and mortality after Escherichia coli endotoxemia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 157:1550–1558
Liberopoulos EN, Daskalopoulou SS, Mikhailidis DP, Wierzbicki AS, Elisaf MS (2005) A review of the lipid-related effects of fluvastatin. Curr Med Res Opin 21:231–244
Imaeda A, Kaneko T, Aoki T, Kondo Y, Nakamura N, Nagase H, Yoshikawa T (2002) Antioxidative effects of fluvastatin and its metabolites against DNA damage in streptozotocin-treated mice. Food Chem Toxicol 40:1415–1422
Franzoni F, Quinones-Galvan A, Regoli F, Ferrannini E, Galetta F (2003) A comparative study of the in vitro antioxidant activity of statins. Int J Cardiol 90:317–321
Palinski W, Tsimikas S (2002) Immunomodulatory effects of statins: mechanisms and potential impact on arteriosclerosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:1673–1681
Kusama T, Mukai M, Iwasaki T, Tatsuta M, Matsumoto Y, Akedo H, Inoue M, Nakamura H (2002) 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme a reductase inhibitors reduce human pancreatic cancer cell invasion and metastasis. Gastroenterology 122:308–317
Cortas NK, Wakid NW (1990) Determination of inorganic nitrate in serum and urine by a kinetic cadmium-reduction method. Clin Chem 36:1440–1443
Uchiyama M, Mihara M (1978) Determination of malonaldehyde precursor in tissues by tiobarbituric acid test. Anal Biochem 34:271–278
Lowry O, Rosenbraugh N, Farr L, Rondall R (1951) Protein measurement with the folin–phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 183:265–275
Paglia DE, Valentine WN (1967) Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. J Lab Clin Med 70:158–170
Aebi H (1974) Catalase. In: Bergmeyer Hu (ed) Methods of enzymatic analysis. Academic, New York, pp 673–677
Sun Y, Oberley L, Li Y (1988) A simple method for clinical assay of superoxide dismutase. Clin Chem 34:497–500
Bradley PP, Priebat DA, Christensen RD (1982) Measurement of cutaneous inflammation: estimation of neutrophil content with an enzyme marker. J Invest Dermatol 78:206–209
Rivera CA, Bradford BU, Hunt KJ, Adachi Y, Schurum LW, Koop DR, Burchardt ER et al (2001) Thurman RG. Attenuation of CCl (4)-induced hepatic fibrosis by GdCl(3) treatment or dietary glycine. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 281:G200–G207
Singh S, Shackleton G, Ah-Sing E, Chakraborty J, Bailey ME (1992) Antioxidant defenses in the bile duct-ligated rat. Gastroenterology 103:1625–1629
Krahenbuhl S, Talos C, Lauterburg BH, Reichen J (1995) Reduced antioxidative capacity in liver mitochondria from bile duct ligated rats. Hepatology 22:607–612
Parola M, Leonarduzzi G, Robino G, Albano E, Poli G, Dianzani MU (1996) On the role of lipid peroxidation in the pathogenesis of liver damage induced by long-standing cholestasis. Free Radic Biol Med 20:351–35
Alptekin N, Mehmetcik G, Uysal M, Aykac-toker G (1997) Evidence for oxidative stress in the hepatic mitochondria of bile duct ligated rats. Pharmacol Res 36:243–247
Tsai LY, Lee KT, Liu TZ (1998) Evidence for accelerated generation of hydroxyl radicals in experimental obstructive jaundice of rats. Free Radic Biol Med 24:732–737
Dain JG, Fu E, Gorski J, Nicoletti J, Scallen TJ (1993) Biotransformation of fluvastatin sodium in humans. Drug Metab Dispos 21:567–572
Hussein O, Schlezinger S, Rosenblat M, Keidar S, Aviram M (1997) Reduced susceptibility of low density lipoprotein (LDL) to lipid peroxidation after fluvastatin therapy is associated with the hypocholesterolemic effect of the drug and its binding to the LDL. Atherosclerosis 128:11–18
Nakamura T, Nishi H, Kokusenya Y, Hirota K, Miura Y (2000) Mechanism of antioxidative activity of fluvastatin-determination of the active position. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 48:235–237
Imaeda A, Tanigawa T, Aoki T, Kondo Y, Nakamura N, Yoshikawa T (2001) Antioxidative effects of fluvastatin and its metabolites against oxidative DNA damage in mammalian cultured cells. Free Radic Res 35:789–801
Imaeda A, Kaneko T, Aoki T, Kondo Y, Nakamura N, Nagase H, Yoshikawa T (2002) Antioxidative effects of fluvastatin and its metabolites against DNA damage in streptozotocin-treated mice. Food Chem Toxicol 40:1415–1422
Imaeda A, Kaneko T, Aoki T, Kondo Y, Nagase H (2002) The DNA damage and the effect of antioxidants in streptozotocin-treated mice. Food Chem Toxicol 40:979–987
Aldana PR, Goerke ME, Carr SC, Tracy TF Jr (1994) The expression of regenerative growth factors in chronic liver injury. J Surg Res 57:711–717
Koeppel TA, Trauner M, Baas JC, Thies JC, Schlosser SF, Post S, Gebhard MM, Herfarth C, Boyer JL, Otto GE (1997) Extrahepatic biliary obstruction impairs microvascular perfusion and increases leukocyte adhesion in rat liver. Hepatology 26:1085–1091
Saito JM, Maher JJ (2000) Bile duct ligation in rats induced biliary expression of cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant. Gastroenterology 118:1157–1168
Guan JZ, Murakami H, Yamato K, Tanabe J, Matsui J, Tamasawa N, Suda T (2004) Effects of fluvastatin in type 2 diabetic patients with hyperlipidemia: reduction in cholesterol oxidation products and VCAM-1. J Atheroscler Thromb 11:56–61
Fischetti F, Carretta R, Borotto G, Durigutto P, Bulla R, Meroni PL, Tedesco F (2004) Fluvastatin treatment inhibits leucocyte adhesion and extravasation in models of complement-mediated acute inflammation. Clin Exp Immunol 135:186–193
Madej A, Kalina Z, Okopie B (1997) The release of tumor necrosis factor-alpha by cultured macrophages from hyperlipidemic patients treated with fluvastatin. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 52 (Supp):76 (abstract)
Hillyard DZ, Cameron AJ, McIntyre AH, Hadden MH, Marshall HE, Johnston N, Jardine AG (2002) Inhibition of proliferation and signalling mechanisms in human lymphocytes by fluvastatin. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 29:673–678
Inoue I, Goto S, Mizotani K, Awata T, Mastunaga T, Kawai S, Nakajima T, Hokari S, Komoda T, Katayama S (2000) Lipophilic HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor has an anti-inflammatory effect: reduction of MRNA levels for interleukin-1beta, interleukin-6, cyclooxygenase-2, and p22phox by regulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha) in primary endothelial cells Life Sci 67:863–876
Hillyard DZ, Jardine AG, McDonald KJ, Cameron AJM (2004) Fluvastatin inhibits raft dependent Fcgamma signaling in human monocytes. Atherosclerosis 172:219–228
Wang HR, Li JJ, Huang CX, Jiang H (2005) Fluvastatin inhibits the expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and activation of nuclear factor-kappaB in human endothelial cells stimulated by C-reactive protein. Clin Chim Acta 353:53–60
Azuma RW, Suzuki J, Ogawa M, Futamatsu H, Koga N, Onai Y, Kosuge H, Isobe M (2004) HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor attenuates experimental autoimmune myocarditis through inhibition of T cell activation. Cardiovasc Res 64:412–420
Corsini A, Mazzotti M, Raiteri M, Soma MR, Gabbiani G, Fumagalli R, Paoletti R (1993) Relationship between mevalonate pathway and arterial myocyte proliferation: in vitro studies with inhibitors of HMG-CoA reductase. Atherosclerosis 101:117–125
Ogata Y, Takahashi M, Takeuchi K, Ueno S, Mano H, Ookawara S, Kobayashi E, Ikeda U, Shimada K (2002) Fluvastatin induces apoptosis in rat neonatal cardiac myocytes: a possible mechanism of statin-attenuated cardiac hypertrophy. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 40:907–915
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Demirbilek, S., Tas, E., Gurunluoglu, K. et al. Fluvastatin reduced liver injury in rat model of extrahepatic cholestasis. Pediatr Surg Int 23, 155–162 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-006-1829-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-006-1829-y