Abstract
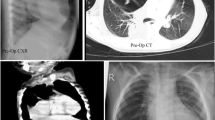
Eight children with Morgagni hernia were operated between January 2000 and May 2005. Medical records of the patients were evaluated retrospectively. Ages of the patients were between 3.5 months and 9 years. The diaphragmatic defect was on the right in all patients except one. One patient had bilateral diapragmatic hernia. All of the patients were operated by abdominal approach. All patients had hernial sacs. During operation sac of hernia was everted to peritoneal space without removal and the defect was closed by using nonabsorbable material. There was no intraoperative complication. The patients were discharged on the sixth day in uneventful condition. There was no complication or recurrence during follow up. Excision of sac of hernia is recommended in majority. Most of the published studies favour the removal of hernial sac. In our practise, in the treatment of Morgagni hernia we did not remove the hernia sac during the last 5 years.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stolar CJH, Dillon PW (1998) Congenital diaphragmatic hernia and eventration. In: O’Neill JA, Rowe MI, Grosfeld JL, Fonkalsrud EW, Coran A (eds) Pediatric surgery. Mosby, St. Louis, pp 819–837
De Vogelaere K (2003) Laparoscopic repair of Morgagni diaphragmatic hernia. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 13:401–403
Harris GJ, Soper RT, Kimura KK (1993) Foramen of Morgagni hernia in identical twins: is this an inheritable defect?. J Pediatr Surg 28:177–178
Soylu H, Koltuksuz U, Kutlu NO, Sarihan H et al (2000) Morgagni hernia: an unexpected cause of respiratory complaints and a chest mass. Pediatr Pulmonol 30:429–433
Arca MJ, Barnhart DC, Lelli JL, Greenfeld J et al (2003) Early experience with minimal invasive repair of congenital diaphragmatic hernias: results and lessons learned. J Pediatr Surg 38:1563–1568
Azzie G, Maoate K, Beasley S, Retief W, Bensoussan A (2003) A simple technique of laparoscopic full thickness anterior abdominal wall repair of retrosternal (Morgagni) hernias. J Pediatr Surg 38:768–770
Okutan H, Uçan ES, Silistreli E et al (2000) Erişkin Morgagni hernisinde transtorasik yaklaşım. Toraks Derg 1:79–81
Machmouchi M, Jaber N, Naamani J (1999) Morgagni hernia in children: Nine cases and a review of the literature. Annals of Saudi Medicine. Accessed December 23rd 2005. http://www.kfshrc.edu.sa/annals/201/99-080.htm
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akbiyik, F., Tiryaki, T.H., Şenel, E. et al. Is hernial sac removal necessary? Retrospective evaluation of eight patients with Morgagni hernia in 5 years. Pediatr Surg Int 22, 825–827 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-006-1750-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-006-1750-4