Abstract.
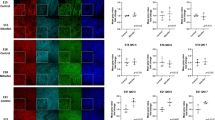
The surrounding extracellular matrix of airway wall tissues changes in response to mechanical stresses and hypoxia. The presence of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) and its inhibitor, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1), is correlated with collagen degradation and tissue repair in lung disorders. The aim of this study was to evaluate the expression of MMP-9 and TIMP-1 in the lung of fetal rats with nitrofen-induced congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH). Administering 100 mg of nitrofen dissolved in 1 ml olive oil to pregnant Wistar rats on day 9 of gestation induced left-sided CDH in fetal rats. In control animals, the same dose of olive oil was given without nitrofen. Cesarean section was performed on day 21 of gestation. The fetuses were divided into two groups: normal controls (n = 10) and nitrofen-induced left-sided CDH (n = 10). Immunoreactivity of the staining for MMP-9 and TIMP-1 in the lung tissues was semiquantitatively analyzed using the staining scores. The relative amount of MMP-9 or TIMP-1 divided by the amount of β-actin for each lung sample was measured by using the real-time reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction. The immunoreactivity of MMP-9 was significantly increased in the CDH group (n = 5) compared with the control group (n = 5) (p = 0.031). On the other hand, the immunoreactivity of TIMP-1 in the two groups was not significantly different (n = 0.134). The relative amount of MMP-9 (or TIMP-1) in the CDH group (n = 5) does not differ significantly from that in the control group (n = 5) (p = 0.059, 0.596, respectively), but the relative amount of MMP-9 is higher in the CDH group, although it is not significantly higher. On the other hand, the ratios of MMP-9 to TIMP-1 were significantly higher in the CDH group (p = 0.028). In conclusion, fetal rats with nitrofen-induced CDH, a model of respiratory disorders, manifested the excess of MMP-9 activity due to the absence of TIMP-1 that would suggest a trend toward disruption of the extracellular matrix in the CDH lung tissues.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamson IY, King GM, Bowden DH (1998) Collagen breakdown during acute lung injury. Thorax 43: 562–568
Albin RJ, Senior RM, Welgus HG, et al (1987) Human alveolar macrophages secrete an inhibitor of metalloproteinase elastase. Am Rev Respir Dis 135: 1281–1285
Campbell EJ, Cury JD, Shapiro SD, et al (1991) Neutral proteinases of human mononuclear phagocytes. Cellular differentiation markedly alters cell phenotype for serine proteinases, metalloproteinases, and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases. J Immunol 146: 1286–1293
Fukuda Y, Ishizaki M, Okada Y, et al (2000) Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 in fetal rabbit lung. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 279: L555–561
Hayashi T, Stetler-Stevenson WG, Fleming MV, et al (1996) Immunohistochemical study of metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitors in the lungs of patients with diffuse alveolar damage and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Pathol 149: 1241–1256
Kluth D, Kangah R, Reich P, et al (1990) Nitrofen-induced diaphragmatic hernias in rats: an animal model. J Pediatr Surg 25: 850–854
Leeper-Woodford SK, Detmer K (1999) Acute hypoxia increases alveolar macrophage tumor necrosis factor activity and alters NF-kappaB expression. Am J Physiol 276: L909–916
Mautino G, Henriquet C, Jaffuel D, et al (1999) Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 levels in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from asthmatic subjects. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 160: 324–330
Minoo P, Penn R, deLemos DM, et al (1993) Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 mRNA is specifically induced in lung tissue after birth. Pediatr Res 34: 729–734
Ohno I, Ohtani H, Nitta Y, et al (1997) Eosinophils as a source of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in asthmatic airway inflammation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 16: 212–219
Ohshiro K, Miyazaki E, Taira Y, et al (1998) Upregulated tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene expression in the hypoplastic lung in patients with congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Pediatr Surg Int 14: 21–24
Pardo A, Selman M, Ramirez R, et al (1992) Production of collagenase and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases by fibroblasts derived from normal and fibrotic human lungs. Chest 102: 1085–1089
Ricou B, Nicod L, Lacraz S, et al (1996) Matrix metalloproteinases and TIMP in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 154: 346–352
Saren P, Welgus HG, Kovanen PT (1996) TNF-alpha and IL-1-beta selectively induce expression of 92-kDa gelatinase by human macrophages. J Immunol 157: 4159–4165
Schock BC, Sweet DG, Ennis M, et al (2001) Oxidative stress and increased type-IV collagenase levels in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from newborn babies. Pediatr Res 50: 29–33
Schwingshackl A, Duszyk M, Brown N, et al (1999) Human eosinophils release matrix metalloproteinase-9 on stimulation with TNF-alpha. J Allergy Clin Immunol 104: 983–989
Shehata SM, Mooi WJ, Okazaki T, et al (1999) Enhanced expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in lungs of newborn infants with congenital diaphragmatic hernia and pulmonary hypertension. Thorax 54: 427–431
Shochat SJ, Naeye RL, Ford WD, et al (1979) Congenital diaphragmatic hernia. New concept in management. Ann Surg 190: 332–341
Swartz MA, Tschumperlin DJ, Kamm RD, et al (2001) Mechanical stress is communicated between different cell types to elicit matrix remodeling. Proc Natl Acad Sci 98: 6180–6185
Takabatake N, Nakamura H, Abe S, et al (2000) The relationship between chronic hypoxemia and activation of the tumor necrosis factor-alpha system in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 161: 1179–1184
Vignola AM, Chanez P, Chiappara G, et al (1996) Release of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) and fibronectin by alveolar macrophages in airway diseases. Clin Exp Immunol 106: 114–119
Vignola AM, Riccobono L, Mirabella A, et al (1998) Sputum metalloproteinase-9/tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 ratio correlates with airflow obstruction in asthma and chronic bronchitis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 158: 1945–1950
Wahl SM, Allen JB, Weeks BS, et al (1993) Transforming growth factor beta enhances integrin expression and type IV collagenase secretion in human monocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci 90: 4577–4581
Yamataka T, Puri P (1997) Active collagen synthesis by pulmonary arteries in pulmonary hypertension complicated by congenital diaphragmatic hernia. J Pediatr Surg 32: 682–687
Yao PM, Delclaux C, d'Ortho MP, et al (1998) Cell-matrix interactions modulate 92-kD gelatinase expression by human bronchial epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 18: 813–822
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tatekawa, Y., Kanehiro, H., Hisanaga, M. et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1: expression in the lung of fetal rats with nitrofen-induced diaphragmatic hernia. Ped Surgery Int 19, 25–28 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-002-0890-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-002-0890-4