Abstract
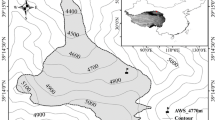
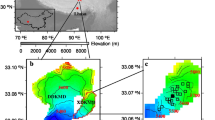
Despite projections of extreme reduction in glacier volume in the Qilian Mountains by the end of the century, comprehensive studies of regional glacier-wide mass and energy balance characteristics remain lacking. This study undertook a comparative analysis of the surface energy and mass balance characteristics of Laohugou glacier No. 12 (LHG glacier) in the Shule River Basin (western Qilian Mountains) and Bailanghe glacier No. 21 (BLH glacier) in the Heihe River Basin (middle Qilian Mountains) based on in situ measurements from September 2020 to August 2021. During the cold season (September–April), precipitation was greater on the BLH glacier than on the LHG glacier. This resulted in a more positive mass balance on the BLH glacier during the cold season, and less melting in May–June owing to the higher incoming shortwave radiation. During the ablation season (May–August), snowfall was greater on the LHG glacier owing to its higher elevation, while melting was also greater owing to the anomalously low cloud fraction during summer 2021. The annual mass balance was notably more negative on the LHG glacier than on the BLH glacier at the same elevation below 5000 m, whereas the annual glacier-wide mass balance was just slightly more negative on the LHG glacier than on the BLH glacier because most of the area in the LHG glacier is at higher elevation. The equilibrium line altitude varied between 4900 and 5100 on the glaciers of Qilian Mountains during recent two decades, which signified that only 5.8–25.5% of the total glacier area is within the accumulation zone in the Heihe River Basin; thus, further global warming will place the regional glaciers in a very vulnerable position.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available via linking to www.ncdc.ac/portal/ or chenjizu@lzb.ac.cn.
References
Azam MF, Wagnon P, Vincent C, Ramanathan AL, Favier V, Mandal A, Pottakkal JG (2014) Processes governing the mass balance of Chhota Shigri Glacier (western Himalaya, India) assessed by point-scale surface energy balance measurements. Cryosphere 8(6):2195–2217. https://doi.org/10.5194/tc-8-2195-2014
Brun F, Berthier E, Wagnon P, Kaab A, Treichler D (2017) A spatially resolved estimate of High Mountain Asia glacier mass balances, 2000–2016. Nat Geosci 10(9):668–673. https://doi.org/10.1038/NGEO2999
Brun F, Wagnon P, Berthier E et al (2019) Heterogeneous influence of glacier morphology on the mass balance variability in high Mountain Asia. J Geophys Res Earth Surf 124(6):1331–1345. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018jf004838
Chen JZ, Kang SC, Qin X et al (2017) The mass-balance characteristics and sensitivities to climate variables of Laohugou Glacier No. 12, western Qilian Mountains, China. Sci Cold Arid Reg 9(6):0543–0553. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1226.2017.000543
Chen JZ, Qin X, Kang SC et al (2018a) Effects of clouds on surface melting of Laohugou glacier No. 12, western Qilian Mountains. China J Glaciol. https://doi.org/10.1017/jog.2017.82
Chen RS, Han CT, Liu J et al (2018b) Maximum precipitation altitude on the northern flank of the Qilian Mountains, northwest China. Hydrol Res 49(5):1696–1710. https://doi.org/10.2166/nh.2018.121
Chen JZ, Qin X, Kang SC et al (2019) Potential Effect of Black Carbon on Glacier Mass Balance during the Past 55 Years of Laohugou Glacier No. 12, Western Qilian Mountains. J Earth Sci 31(2):410–418. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-019-1238-5
Chen JZ, Du WT, Kang SC et al (2021) Eight-year analysis of radiative properties of clouds and its impact on melting on the Laohugou Glacier No. 12, western Qilian Mountains. Atmos Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2020.105410
Conway JP, Cullen NJ, Spronken-Smith RA, Fitzsimons SJ (2015) All-sky radiation over a glacier surface in the Southern Alps of New Zealand: characterizing cloud effects on incoming shortwave, longwave and net radiation. Int J Climatol 35(5):699–713. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.4014
Denby B, Snellen H (2002) A comparison of surface renewal theory with the observed roughness length for temperature on a melting glacier surface. Bound-Layer Meteorol 103(3):459–468
Ding YJ, Zhao QD, Wu JK et al (2021) The future changes of Chinese cryospheric hydrology and their impacts on water security in arid areas. J Glaciol Geocryol 42(1):23–32. https://doi.org/10.7522/j.issn.1000-0240.2020.0003. (in Chinese)
Du W, Kang S, Qin X et al (2016a) Atmospheric insight to climatic signals of δ18O in a Laohugou ice core in the northeastern Tibetan Plateau during 1960–2006. Sci Cold Arid Regions 8(5):367377. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1226.2016a.00367
Du WT, Qin X, Kang SC, Cui XQ, Sun WJ (2016b) Variations in annual accumulation recorded in a Laohugou ice core from the northeastern Tibetan Plateau and their relationship with atmospheric circulation. Environ Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5601-x
Du W, Kang S, Qin X et al (2020) Can summer monsoon moisture invade the Jade Pass in Northwestern China? Clim Dyn 55(11–12):3101–3115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-020-05423-y
Essery R, Morin S, Lejeune Y, Ménard CB (2013) A comparison of 1701 snow models using observations from an alpine site. Adv Water Resour 55:131–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2012.07.013
Foken T (2008) Micrometeorology. Springer, Berlin. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-74666-9
Fugger S, Fyffe CL, Fatichi S et al (2022) Understanding monsoon controls on the energy and mass balance of glaciers in the Central and Eastern Himalaya. Cryosphere 16(5):1631–1652. https://doi.org/10.5194/tc-16-1631-2022
Gao X, Zhang SQ, Ye BS, Gao HK (2011) Recent changes of glacier runoff in the Hexi Inland river basin. Advances Water Sci 22(3):344–350. https://doi.org/10.14042/j.cnki.32.1309.2011.03.019. (in Chinese)
Gardelle J, Berthier E, Arnaud Y (2012) Slight mass gain of Karakoram glaciers in the early twenty-first century. Nat Geosci 5(5):322–325. https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo1450
Guo WQ, Liu SY, Xu JL et al (2015) The second Chinese glacier inventory: data, methods and results. J Glaciol 61(226):357–372. https://doi.org/10.3189/2015JoG14J209
Hantel M, Ehrendorfer M, Haslinger A (2000) Climate sensitivity of snow cover duration in Austria. Int J Climatol 20:615–640
Hugonnet R, McNabb R, Berthier E et al (2021) Accelerated global glacier mass loss in the early twenty-first century. Nature 592(7856):726–731. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03436-z
Huintjes E, Neckel N, Hochschild V, Schneider C (2015) Surface energy and mass balance at Purogangri ice cap, central Tibetan Plateau, 2001–2011. J Glaciol 61(230):1048–1060. https://doi.org/10.3189/2015JoG15J056
Immerzeel WW, Lutz AF, Andrade M et al (2020) Importance and vulnerability of the world’s water towers. Nature 577(7790):364–369. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1822-y
Jia W-x, Ma X-g, Xu X-t et al (2018) Composition of stable isotope in precipitation and its influences by different vapor sources in the eastern Qilian Mountains. J Mt Sci 15(10):2207–2217. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-018-4844-2
Jiang X, Wang NL, He JQ, Wu X, Song G (2010) A distributed surface energy and mass balance model and its application to a mountain glacier in China. Chin Sci Bull 55(20):2079–2087. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-010-3068-9
Jin ZZ, Zhao QD, Qin X et al (2021) Quantifying the impact of landscape changes on hydrological variables in the alpine and cold region using hydrological model and remote sensing data. Hydrol Process. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.14392
Kraaijenbrink PDA, Bierkens MFP, Lutz AF, Immerzeel WW (2017) Impact of a global temperature rise of 1.5 degrees Celsius on Asia’s glaciers. Nature 549(7671):257–260. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature23878
Li J, Liu SY, Zhang Y, Shuangguan DH (2011) Surface energy balance of Keqicar Glacier, Tianshan Mountains, China, during ablation period. Sci Cold Arid Reg 3(3):0197–0205. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1226.2011.00197
Li Z, Gao Y, Wang Y et al (2015) Can monsoon moisture arrive in the Qilian Mountains in summer? Quatern Int 358:113–125
Li SH, Yao TD, Yang W, Yu W, Zhu M (2018) Glacier energy and mass balance in the inland Tibetan Plateau: seasonal and interannual variability in relation to atmospheric changes. J Geophys Res Atmos 123:6390–9409. https://doi.org/10.1029/2017JD028120
Li SH, Yao TD, Yu WS, Yang W, Zhu ML (2019) Energy and mass balance characteristics of the Guliya ice cap in the West Kunlun Mountains, Tibetan Plateau. Cold Reg Sci Technol 159:71–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coldregions.2018.12.001
Liu SY, Sun W, Shen W, Li G (2003) Glacier changes since the Little Ice Agemaximumin the westernQilian Shan, northwest China, and consequences of glacier runoff for water supply. J Glaciol 49(164):117–124
Liu YS, Qin X, Chen JZ et al (2018) Variations of Laohugou Glacier No 12 in the western Qilian Mountains, China, from 1957 to 2015. J MT Sci 15(1):25–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-017-4492-y
Mölg T, Cullen NJ, Hardy DR et al (2009) Quantifying climate change in the tropical midtroposphere over East Africa from Glacier Shrinkage on Kilimanjaro. J Clim 22(15):4162–4181. https://doi.org/10.1175/2009jcli2954.1
Mölg T, Maussion F, Yang W, Scherer D (2012) The footprint of Asian monsoon dynamics in the mass and energy balance of a Tibetan glacier. Cryosphere 6(4):3243–3286. https://doi.org/10.5194/tcd-6-3243-2012
Mölg T, Maussion F, Scherer D (2014) Mid-latitude westerlies as a driver of glacier variability in monsoonal High Asia. Nat Clim Chang 4(1):68–73. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate2055
Munro DS (1989) Surface roughness and bulk heat transfer on a glacier: comparison with eddy correlation. J Glaciol 35:343–348. https://doi.org/10.3189/S0022143000009266
Oerlemans J (1991) The mass balance of Greenland Ice sheet: sensitivity to climate change as revealed by energy-balance modeling. Holocene 1(1):40–48
Oerlemans J, Knap WH (1998) A 1 year record of global radiation and albedo in the ablation zone of Morteratschgletscher. Switzerland J Glaciol 44(147):231–238. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0022143000002574
Sakai A, Fujita F, Duan KQ, Pu JC, Nakawo M, Yao TD (2006) Five decades of shrinkage of July 1st glacier, Qilian Shan, China. J Glaciol 52(176):11–16
Sauter T, Arndt A, Schneider C (2020) COSIPY v1.3—an open-source coupled snowpack and ice surface energy and mass balance model. Geosci Model Dev 13(11):5645–5662. https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-13-5645-2020
Scherler D, Bookhagen B, Strecker MR (2011) Spatially variable response of Himalayan glaciers to climate change affected by debris cover. Nat Geosci 4(3):156–159. https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo1068
Stull RB (1988) An introduction to boundary layer meteorology. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-009-3027-8
Sun WJ, Qin X, Ren JW et al (2012) The Surface Energy Budget in the Accumulation Zone of the Laohugou Glacier No. 12 in the Western Qilian Mountains, China, in Summer 2009. Arct Antarct Alp Res 44(3):296–305. https://doi.org/10.1657/1938-4246-44.3.296
Sun WJ, Qin X, Du WT et al (2014) Ablation modeling and surface energy budget in the ablation zone of Laohugou glacier No. 12, western Qilian mountains. China. Ann Glaciol 55(66):111–120. https://doi.org/10.3189/2014AoG66A902
Sun WJ, Qin X, Wang Y et al (2017) The response of surface mass and energy balance of a continental glacier to climate variability, western Qilian Mountains, China. Clim Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-017-3823-6
Sun ML, Liu SY, Yao X, Guo X, Xu J (2018) Glacier changes in the Qilian Mountains in the past half-century: based on the revised First and Second Chinese Glacier Inventory. J Geogr Sci 28(2):206–220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-018-1468-y
Thayyen RJ, Geragan JT (2010) Role of glaciers in watershed hydrology: a preliminary study of a “Himalayan catchment.” Cryosphere 4:115–128. https://doi.org/10.5194/tc-4-115-2010
Tian H, Yang T, Liu Q (2014) Climate change and glacier area shrinkage in the Qilian mountains, China, from 1956 to 2010. Ann Glaciol 55(66):187–197. https://doi.org/10.3189/2014AoG66A045
Vionnet V, Brun E, Morin S et al (2012) The detailed snowpack scheme Crocus and its implementation in SURFEX v7.2. Geosci Model Dev 5:773–791. https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-5-773-2012
Wang NL, He JQ, Pu JC, Jiang X, Jing Z (2010) Variations in equilibrium line altitude of the Qiyi Glacier, Qilian Mountains, over the past 50 years. Chinese Sci Bull 55(33):3810–3817. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-010-4167-3
Wang S, Yao TD, Tian LD, Pu JC (2017) Glacier mass variation and its effect on surface runoff in the Beida River catchment during 1957–2013. J Glaciol 63(239):523–534. https://doi.org/10.1017/jog.2017.13
Wu F, Zhan J, Wang Z, Zhang Q (2015) Streamflow variation due to glacier melting and climate change in upstream Heihe River Basin, Northwest China. Phys Chem Earth Parts a/b/c 79–82:11–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2014.08.002
Xiao Z, Duan A, Wang Z (2019) Atmospheric heat sinks over the western Tibetan Plateau associated with snow depth in late spring. Int J Climatol 39(13):5170–5180. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.6133
Yan Y, You Q, Wu F et al (2020) Surface mean temperature from the observational stations and multiple reanalyses over the Tibetan Plateau. Clim Dyn 55(9–10):2405–2419. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-020-05386-0
Yang ZL (1988) Glacier water resources of Qilian Mountains. J Glaciol Geocryol 10(1):36–46 (in Chinese)
Yang W, Guo X, Yao T, Yang K, Zhao L, Li S, Zhu M (2011) Summertime surface energy budget and ablation modeling in the ablation zone of a maritime Tibetan glacier. J Geophys Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010jd015183
Yang W, Guo X, Yao T et al (2016) Recent accelerating mass loss of southeast Tibetan glaciers and the relationship with changes in macroscale atmospheric circulations. Clim Dyn 47(3–4):805–815. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-015-2872-y
Yao TD, Thompson L, Yang W et al (2012) Different glacier status with atmospheric circulations in Tibetan Plateau and surroundings. Nat Clim Change 2(9):663–667. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate1580
You Q, Cai Z, Pepin N et al (2021) Warming amplification over the Arctic Pole and Third Pole: Trends, mechanisms and consequences. Earth Sci Rev 217:103625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2021.103625
Zhang Q, Zhang J, Sun G et al (2007) Research on water-vapor distribution in the air over Qilian Mountains. Acta Meteor Sin 22(1):107–118
Zhang GS, Kang SC, Fujita K et al (2013) Energy and mass balance of Zhadang glacier surface, central Tibetan Plateau. J Glaciol 59(213):137–148. https://doi.org/10.3189/2013JoG12J152
Zhang H, Li ZQ, Zhou P (2020) Mass balance reconstruction for Shiyi Glacier in the Qilian Mountains, Northeastern Tibetan Plateau, and its climatic drivers. Clim Dyn 56(3–4):969–984. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-020-05514-w
Zhu ML, Yao TD, Yang W, Maussion F, Huintjes E, Li S (2015) Energy- and mass-balance comparison between Zhadang and Parlung No. 4 glaciers on the Tibetan Plateau. J Glaciol 61(227):595–607. https://doi.org/10.3189/2015JoG14J206
Zhu M, Yao T, Yang W et al (2017) Evaluation of parameterizations of incoming longwave radiation in the high-Mountain Region of the Tibetan Plateau. J Appl Meteorol Climatol 56(4):833–848. https://doi.org/10.1175/jamc-d-16-0189.1
Zhu ML, Yao TD, Yang W, Xu B, Wu G, Wang X (2018) Differences in mass balance behavior for three glaciers from different climatic regions on the Tibetan Plateau. Clim Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-017-3817-4
Zhu ML, Yao TD, Xie Y, Xu BQ, Yang W, Yang S (2020) Mass balance of Muji Glacier, northeastern Pamir, and its controlling climate factors. J Hydrol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125447
Zhu ML, Yang W, Yao TD, Tian LD, Thompson L, Zhao H (2021) The Influence of Key Climate Variables on Mass Balance of Naimona’nyi Glacier on a North-Facing Slope in the Western Himalayas. J Geophys Res Atmos. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020jd033956
Zhu M, Yao T, Thompson LG et al (2022) What induces the spatiotemporal variability of glacier mass balance across the Qilian Mountains. Clim Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-022-06283-4
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U22A20564, 41971073, 42101139), the State Key Laboratory of Cryospheric Science (SKLCS-ZZ-2022), and national key research and development project (2022YFF0711704). We thank James Buxton MSc, from Liwen Bianji (Edanz) (www.liwenbianji.cn/), for editing the English text of a draft of this manuscript.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation and data collection were performed by XQ, WS and YL. Conceptualization and review were performed by WD and SK. Data analysis and software were performed by LL and JH. The first draft of the manuscript was written by JC and WD. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Du, W., Kang, S. et al. Comparison of energy and mass balance characteristics between two glaciers in adjacent basins in the Qilian Mountains. Clim Dyn 61, 1535–1550 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-022-06641-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-022-06641-2