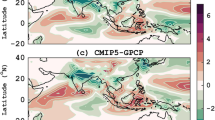
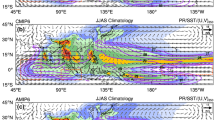
Abstract
As a new generation of global climate models, monsoon simulation in Coupled Model Intercomparison Project (CMIP) Phase 6 models is of great concern to climate modeling community. Using 21 CMIP3 models, 28 CMIP5 models and 38 CMIP6 models, we show evidence that the long-standing dry biases in South Asia (SA) are resulted from less rainfall with both less frequency and intensity in a shortened monsoon season. By evaluating several key metrics, we identify that the monsoon rainfall simulation in CMIP6 models has improved in both of the multimodel ensemble mean (MME) and individual models, consistent with the improvements in monsoon annual cycle and rainfall characteristics. Further analyses and sensitivity experiments show that the cold SST biases all year round over the northern Indian Ocean (NIO) are important sources for the persistent dry biases in the CMIPs’ models. The cooling effect of SST biases on the tropospheric temperature becomes increasingly prominent since the boreal spring, weakening the baroclinity of monsoon circulation via the thermal wind relationship and eventually resulting in insufficient monsoon rainfall. Comparison across the three generation CMIP models also confirms that the improvement of SA summer rainfall simulation in CMIP6 MME benefits from the reduction of NIO SST biases. This study highlights the importance of improving SST simulation in reducing the monsoon rainfall biases.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All datasets can be accessed publicly. APHRODITE dataset http://aphrodite.st.hirosaki-u.ac.jp/products.html; GPCP dataset https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/products/global-precipitation-climatology-project; HadISST dataset https://www.metoffice.gov.uk/hadobs/hadisst; ERA5 reanalysis https://www.ecmwf.int/en/forecasts/datasets/reanalysis-datasets/era5; CMIP3 dataset https://esgf-node.llnl.gov/search/cmip3/; CMIP5 dataset https://esgf-node.llnl.gov/search/cmip5/; CMIP6 dataset https://esgf-node.llnl.gov/search/cmip6/.
References
Acosta RP, Huber M (2017) The neglected Indo-Gangetic Plains low-level jet and its importance for moisture transport and precipitation during the peak summer monsoon. Geophys Res Lett 44:8601–8610. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017GL074440
Annamalai H, Taguchi B, McCreary JP et al (2017) Systematic errors in South Asian monsoon simulation: importance of equatorial Indian Ocean processes. J Clim 30:8159–8178. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-16-0573.1
Annamalai H, Boos WR, Martin G et al (2021) Grand challenges in asian summer monsoon modeling - representation of processes and sources of model error. In: The Multiscale Global Monsoon System. 367–386
Bollasina M, Nigam S (2009) Indian Ocean SST, evaporation, and precipitation during the South Asian summer monsoon in IPCC-AR4 coupled simulations. Clim Dyn 33:1017–1032. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00382-008-0477-4/FIGURES/10
Boos WR, Hurley JV (2013) Thermodynamic bias in the multimodel mean boreal summer monsoon. J Clim 26:2279–2287. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-12-00493.1
Chen X, Zhou T (2015) Distinct effects of global mean warming and regional sea surface warming pattern on projected uncertainty in the South Asian summer monsoon. Geophys Res Lett 42:9433–9439. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015GL066384
Choudhury BA, Rajesh PV, Zahan Y, Goswami BN (2021) Evolution of the Indian summer monsoon rainfall simulations from CMIP3 to CMIP6 models. Clim Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-021-06023-0
Dai A, Li H, Sun Y et al (2013) The relative roles of upper and lower tropospheric thermal contrasts and tropical influences in driving Asian summer monsoons. J Geophys Res Atmos 118:7024–7045. https://doi.org/10.1002/jgrd.50565
Dong T, Dong W (2021) Evaluation of extreme precipitation over Asia in CMIP6 models. Clim Dyn 57:1751–1769. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-021-05773-1
Eyring V, Bony S, Meehl GA et al (2016) Overview of the coupled model intercomparison project phase 6 (CMIP6) experimental design and organization. Geosci Model Dev 9:1937–1958. https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-9-1937-2016
Geen R, Bordoni S, Battisti DS, Hui K (2020) Monsoons, ITCZs, and the concept of the global monsoon. Rev Geophys 58:1–45. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020RG000700
Gent PR, Danabasoglu G, Donner LJ et al (2011) The community climate system model version 4. J Clim 24:4973–4991. https://doi.org/10.1175/2011JCLI4083.1
Gusain A, Ghosh S, Karmakar S (2020) Added value of CMIP6 over CMIP5 models in simulating Indian summer monsoon rainfall. Atmos Res 232:104680. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2019.104680
Ha KJ, Moon S, Timmermann A, Kim D (2020) Future changes of summer monsoon characteristics and evaporative demand over Asia in CMIP6 simulations. Geophys Res Lett 47:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020GL087492
Hanf FS, Annamalai H (2020) Systematic errors in South Asian monsoon precipitation: process-based diagnostics and sensitivity to entrainment in NCAR models. J Clim 33:2817–2840. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-18-0495.1
He L, Zhou T, Li L et al (2022) Simulation of South Asian summer monsoon using the FGOALS-g3 climate system model: climatology and interannual variability. Chin J Atmos Sci. https://doi.org/10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2105.21042 (in Chinese)
Hersbach H, Bell B, Berrisford P et al (2020) The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q J R Meteorol Soc 146:1999–2049. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.3803
Huang X, Zhou T, Wu B, Chen X (2019) South Asian summer monsoon simulated by two versions of FGOALS climate system model: model biases and mechanims. Chin J Atmos Sci 43:437–455. https://doi.org/10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.1805.18131 (in Chinese)
Huang X, Zhou T, Dai A et al (2020) South Asian summer monsoon projections constrained by the interdecadal Pacific oscillation. Sci Adv. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aay6546
Huang X, Zhou T, Turner A et al (2020) The recent decline and recovery of Indian summer monsoon rainfall: relative roles of external forcing and internal variability. J Clim 33:5035–5060. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-19-0833.1
Jin Q, Wang C (2017) A revival of Indian summer monsoon rainfall since 2002. Nat Clim Chang 7:587–594. https://doi.org/10.1038/NCLIMATE3348
Johnson SJ, Levine RC, Turner AG et al (2016) The resolution sensitivity of the South Asian monsoon and Indo-Pacific in a global 0.35° AGCM. Clim Dyn 46:807–831. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-015-2614-1
Levine RC, Turner AG (2012) Dependence of Indian monsoon rainfall on moisture fluxes across the Arabian Sea and the impact of coupled model sea surface temperature biases. Clim Dyn 38:2167–2190. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00382-011-1096-Z/FIGURES/15
Levine RC, Turner AG, Marathayil D, Martin GM (2013) The role of northern Arabian Sea surface temperature biases in CMIP5 model simulations and future projections of Indian summer monsoon rainfall. Clim Dyn 41:155–172. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00382-012-1656-X/FIGURES/11
Li G, Xie SP, He C, Chen Z (2017) Western Pacific emergent constraint lowers projected increase in Indian summer monsoon rainfall. Nat Clim Chang 7:708–712. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate3387
Liu Z, Bollasina MA, Wilcox LJ et al (2021) Contrasting the role of regional and remote circulation in driving Asian monsoon biases in MetUM GA71. J Geophys Res Atmos. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020JD034342
Mahendra N, Chowdary JS, Darshana P et al (2021) Interdecadal modulation of interannual ENSO-Indian summer monsoon rainfall teleconnections in observations and CMIP6 models: regional patterns. Int J Climatol 41:2528–2552. https://doi.org/10.1002/JOC.6973
Marathayil D, Turner AG, Shaffrey LC, Levine RC (2013) Systematic winter sea-surface temperature biases in the northern Arabian Sea in HiGEM and the CMIP3 models. Environ Res Lett 8:014028. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/8/1/014028
Meehl GA, Covey C, Delworth T et al (2007) THE WCRP CMIP3 multimodel dataset: a new Era in climate change research. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 88:1383–1394. https://doi.org/10.3375/0885-8608-41.4.237
Mitra A (2021) A comparative study on the skill of CMIP6 models to preserve daily spatial patterns of monsoon rainfall over India. Front Clim 3:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fclim.2021.654763
Moon S, Ha KJ (2020) Future changes in monsoon duration and precipitation using CMIP6. npj Clim Atmos Sci. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41612-020-00151-w
Rajendran K, Surendran S, Varghese SJ, Sathyanath A (2021) Simulation of Indian summer monsoon rainfall, interannual variability and teleconnections: evaluation of CMIP6 models. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg
Rayner NA, Parker DE, Horton EB et al (2003) Global analyses of sea surface temperature, sea ice, and night marine air temperature since the late nineteenth century. J Geophys Res Atmos. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002jd002670
Sandeep S, Ajayamohan RS (2014) Origin of cold bias over the Arabian Sea in climate models. Sci Rep 4:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep06403
Sperber KR, Annamalai H, Kang IS et al (2013) The Asian summer monsoon: an intercomparison of CMIP5 vs. CMIP3 simulations of the late 20th century. Clim Dyn 41:2711–2744. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-012-1607-6
Taylor KE (2001) Summarizing multiple aspects of model performance in a single diagram. J Geophys Res 106:7183–7192
Taylor KE, Stouffer RJ, Meehl GA (2012) An overview of CMIP5 and the experiment design. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 93:485–498. https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-D-11-00094.1
Turner AG, Annamalai H (2012) Climate change and the South Asian summer monsoon. Nat Clim Chang 2:587–595. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate1495
Wang B, Ding Q (2008) Global monsoon: dominant mode of annual variation in the tropics. Dyn Atmos Ocean 44:165–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.DYNATMOCE.2007.05.002
Wang B, Ho L (2002) Rainy season of the Asian-Pacific summer monsson. J Clim 15:386–398. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(2002)0152.0.CO;2
Wang Z, Li G, Yang S (2018) Origin of Indian summer monsoon rainfall biases in CMIP5 multimodel ensemble. Clim Dyn 51:755–768. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-017-3953-x
Wang C, Zou L, Zhou T, Wu B (2019) SST Bias over the Northwest Pacific in Oceanic data assimilation experiments with the interdecadal climate prediction system IAP DecPreS and its impacts on the Asian summer monsoon simulation. Chin J Atmos Sci 43:498–510. https://doi.org/10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.1809.18133
Wang B, Biasutti M, Byrne MP et al (2021) Monsoons climate change assessment. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 102:E1–E19. https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-D-19-0335.1
Webster PJ, Yang S (1992) Monsoon and enso: selectively interactive systems. Q J R Meteorol Soc 118:877–926. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.49711850705
Webster PJ, Magaña VO, Palmer TN et al (1998) Monsoons: processes, predictability, and the prospects for prediction. J Geophys Res Ocean 103:14451–14510. https://doi.org/10.1029/97JC02719
Wu G, Liu Y, He B et al (2012) Thermal controls on the Asian summer monsoon. Sci Rep 2:404. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep00404
Xavier PK, Marzin C, Goswami BN (2007) An objective definition of the Indian summer monsoon season and a new perspective on the ENSO – monsoon relationship. 764:749–764. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj
Xie SP, Xu H, Saji NH et al (2006) Role of narrow mountains in large-scale organization of Asian Monsoon convection. J Clim 19:3420–3429. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI3777.1
Yatagai A, Kamiguchi K, Arakawa O et al (2012) Aphrodite constructing a long-term daily gridded precipitation dataset for Asia based on a dense network of rain gauges. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 93:1401–1415. https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-D-11-00122.1
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the World Climate Research Program’s Working Group on Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 3, 5 and 6, and we thank all the modelling groups that producing the simulation used in this study.
Funding
This work is supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2020YFA0608901).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
He, L., Zhou, T. & Chen, X. South Asian summer rainfall from CMIP3 to CMIP6 models: biases and improvements. Clim Dyn 61, 1049–1061 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-022-06542-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-022-06542-4