Abstract
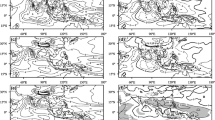
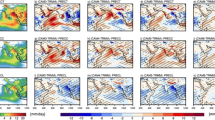
Model simulations are highly sensitive to the formulation of the atmospheric mixing process or entrainment in the deep convective parameterizations used in their atmospheric component. In this paper, we have implemented stochastic entrainment in the deep convection scheme of NCAR CAM5 and analyzed the improvements in model simulation, focusing on the South Asian Summer Monsoon (SASM), as compared to the deterministic entrainment formulation in the default version of the model. Simulations using stochastic entrainment (StochCAM5) outperformed default model simulations (DefCAM5), as inferred from multiple metrics associated with the SASM. StochCAM5 significantly alleviated some of the longstanding SASM biases seen in DefCAM5, such as precipitation pattern and magnitude over the Arabian Sea and western Equatorial Indian ocean, early monsoon withdrawal, and the overestimation in the frequency of light precipitation and the underestimation in the frequency of large-to-extreme precipitation. Related SASM dynamical and thermodynamical features, such as Somali Jet, low-level westerly winds, and meridional tropospheric temperature gradient (MTTG), are improved in StochCAM5. Further, the simulation of monsoon intra-seasonal oscillation (MISO), Madden Julian Oscillation (MJO), and equatorial Kelvin waves are improved in StochCAM5. Many essential climate variables, such as shortwave and longwave cloud forcing, cloud cover, relative and specific humidity, and precipitable water, show significant improvement in StochCAM5.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The observed data used in this study is publicly available and the model simulated data can be obtained from the corresponding author.
Code Availability
The climate model used for simulations are freely available at https://www.cesm.ucar.edu/ and the code used for figure generation is available with corresponding author and can be obtained on request.
References
Abhik S, Halder M, Mukhopadhyay P et al (2013) A possible new mechanism for northward propagation of boreal summer intraseasonal oscillations based on TRMM and MERRA reanalysis. Clim Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-012-1425-x
Abhilash S, Sahai AK, Borah N et al (2014) Prediction and monitoring of monsoon intraseasonal oscillations over Indian monsoon region in an ensemble prediction system using CFSv2. Clim Dyn 42:2801–2815. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-013-2045-9
Adler RF, Huffman GJ, Chang A et al (2003) The version-2 global precipitation climatology project (GPCP) monthly precipitation analysis (1979-present). J Hydrometeorol. https://doi.org/10.1175/1525-7541(2003)004%3c1147:TVGPCP%3e2.0.CO;2
Anand A, Mishra SK, Sahany S et al (2018) Indian Summer Monsoon Simulations: Usefulness of Increasing Horizontal Resolution, Manual Tuning, and Semi-Automatic Tuning in Reducing Present-Day Model Biases. Sci Rep 8:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-21865-1
Arnold NP, Kuang Z, Tziperman E (2013) Enhanced MJO-like variability at high SST. J Clim 26:988–1001. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-12-00272.1
Ashfaq M, Shi Y, Tung WW et al (2009) Suppression of south Asian summer monsoon precipitation in the 21st century. Geophys Res Lett 36:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008GL036500
Bechtold P, Köhler M, Jung T et al (2008) Advances in simulating atmospheric variability with the ECMWF model: From synoptic to decadal time-scales. QJRMS. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.289
Benedict JJ, Randall DA (2009) Structure of the Madden–Julian Oscillation in the Superparameterized CAM. J Atmos Sci. https://doi.org/10.1175/2009jas3030.1
Benedict JJ, Randall DA (2011) Impacts of idealized air-Sea coupling on Madden-Julian oscillation structure in the superparameterized CAM. J Atmos Sci. https://doi.org/10.1175/JAS-D-11-04.1
Berner J, Shutts GJ, Leutbecher M, Palmer TN (2009) A spectral stochastic kinetic energy backscatter scheme and its impact on flow-dependent predictability in the ECMWF ensemble prediction system. J Atmos Sci. https://doi.org/10.1175/2008JAS2677.1
Boos WR, Kuang Z (2010) Dominant control of the South Asian monsoon by orographic insulation versus plateau heating. Nature. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08707
Bretherton CS, Park S (2009) A new moist turbulence parameterization in the community atmosphere model. J Clim. https://doi.org/10.1175/2008JCLI2556.1
Bright DR, Mullen SL (2002) Short-range ensemble forecasts of precipitation during the Southwest monsoon. Weather Forecast. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0434(2002)017%3c1080:SREFOP%3e2.0.CO;2
Buizza R, Milleer M, Palmer TN (2007) Stochastic representation of model uncertainties in the ECMWF ensemble prediction system. QJRMS. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.49712556006
Bush SJ, Turner AG, Woolnough SJ et al (2015) The effect of increased convective entrainment on Asian monsoon biases in the MetUM general circulation model. QJRMS. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.2371
Dash SK et al (2017) Climate modeling in India: present status and the way forward. BAMS. https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-D-16-0322.1
Dee DP, Uppala SM, Simmons AJ et al (2011) The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. QJRMS 137:553–597. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.828
DeMott CA, Stan C, Randall DA et al (2011) The Asian monsoon in the superparameterized CCSM and its relationship to tropical wave activity. J Clim. https://doi.org/10.1175/2011JCLI4202.1
DeMott CA, Stan C, Randall DA (2013) Northward propagation mechanisms of the boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation in the ERA-interim and SP-CCSM. J Clim. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-12-00191.1
Deng Q, Khouider B, Majda AJ (2015) The MJO in a coarse-resolution GCM with a stochastic multicloud parameterization. J Atmos Sci. https://doi.org/10.1175/JAS-D-14-0120.1
Dorrestijn J, Crommelin DT, Siebesma AP, Jonker HJJ (2013) Stochastic parameterization of shallow cumulus convection estimated from high-resolution model data. Theor Comput Fluid Dyn 27:133–148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00162-012-0281-y
Drbohlav HK-L, Wang B (2005) Mechanism of the northward propagating Intraseasonal oscillations: insight from a zonally symmetric model. J Clim 18:952–972
Findlater J (1969) A major low-level air current near the Indian Ocean during the northern summer. QJRMS. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.49709540409
Gadgil S (2018) The monsoon system: Land–sea breeze or the ITCZ? J Earth Syst Sci 127:1–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-017-0916-x
Gettelman A, Liu X, Ghan SJ et al (2010) Global simulations of ice nucleation and ice supersaturation with an improved cloud scheme in the Community Atmosphere Model. J Geophys Res Atmos 115:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009JD013797
Goswami BN, Chakravorty S (2017) Dynamics of the Indian Summer Monsoon Climate. Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Climate Science. https://doi.org/10.1093/acrefore/9780190228620.013.613
Goswami BN, Xavier PK (2005) ENSO control on the South Asian monsoon through the length of the rainy season. Geophys Res Lett 32:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005GL023216
Goswami BB, Krishna RPM, Mukhopadhyay P et al (2015) Simulation of the Indian Summer Monsoon in the superparameterized climate forecast system version 2: preliminary results. J Clim. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-14-00607.1
Goswami BB, Khouider B, Phani R et al (2017a) Improving synoptic and intraseasonal variability in CFSv2 via stochastic representation of organized convection. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016GL071542
Goswami BB, Khouider B, Phani R et al (2017b) Improved tropical modes of variability in the NCEP Climate Forecast System (Version 2) via a stochastic multicloud model. J Atmos Sci. https://doi.org/10.1175/JAS-D-17-0113.1
Goswami BN, Wheeler M, Gottschalck JC, Waliser DE (2011) Intra-seasonal variability and forecasting: a review of recent research. The global monsoon system: research and forecast WMO, pp 389–407
Grabowski WW, Smolarkiewicz PK (1999) CRCP: A cloud resolving convection parameterization for modeling the tropical convecting atmosphere. Phys D Nonlinear Phenom. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-2789(99)00104-9
Held IM, Zhao M, Wyman B (2007) Dynamic radiative-convective equilibria using GCM column physics. J Atmos Sci. https://doi.org/10.1175/JAS3825.11
Huffman GJ, Adler RF, Bolvin DT et al (2007) The TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA): quasi-global, multiyear, combined-sensor precipitation estimates at fine scales. J Hydrometeorol. https://doi.org/10.1175/JHM560.1
Iacono MJ, Delamere JS, Mlawer EJ et al (2008) Radiative forcing by long-lived greenhouse gases: calculations with the AER radiative transfer models. J Geophys Res Atmos. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008JD009944
Jain S, Salunke P, Mishra SK, Sahany S (2019) Performance of CMIP5 models in the simulation of Indian summer monsoon. Theor Appl Climatol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-018-2674-3
Jiang X, Li T, Wang B (2004) Structures and mechanisms of the northward propagating boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation. J Clim 17:1022–1039. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(2004)017%3c1022:SAMOTN%3e2.0.CO;2
Jiang X, Waliser DE, Li JL, Woods C (2011) Vertical cloud structures of the boreal summer intraseasonal variability based on CloudSat observations and ERA-interim reanalysis. Clim Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-010-0853-8
Jones TR, Randall DA (2011) Quantifying the limits of convective parameterizations. J Geophys Res Atmos. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010JD014913
Jones TR, Randall DA, Branson MD (2019a) Multiple-instance superparameterization. 1: concept, and predictability of precipitation. JAMES 11:3497–3520. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019ms001610
Jones TR, Randall DA, Branson MD (2019) Multiple-instance superparameterization: 2. the effects of stochastic convection on the simulated climate. JAMES 11:3521–3544. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019MS001611
Joseph S, Sahai AK, Goswami BN (2009) Eastward propagating MJO during boreal summer and Indian monsoon droughts. Clim Dyn 32:1139–1153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-008-0412-8
Joseph S, Sahai AK, Goswami BN, Terray P, Masson S, Luo JJ (2012) Possible role of warm SST bias in the simulation of boreal summer monsoon in SINTEX-F2 coupled model. Clim Dyn 38:1561–1576. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-011-1264-1
Joshi MM, Webb MJ, Maycock AC, Collins M (2010) Stratospheric water vapour and high climate sensitivity in a version of the HadSM3 climate model. Atmos Chem Phys. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-10-7161-2010
Khairoutdinov MF, Randall DA (2001) A cloud resolving model as a cloud parameterization in the NCAR community climate system model: preliminary results. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2001GL013552
Khouider B, Majda AJ (2006) A simple multicloud parameterization for convectively coupled tropical waves. Part I: linear analysis. J Atmos Sci 63(4):1308–1323
Khouider B, Biello J, Majda AJ (2010) A stochastic multicloud model for tropical convection. Commun Math Sci. https://doi.org/10.4310/cms.2010.v8.n1.a10
Knight CG, Knight SHE, Massey N et al (2007) Association of parameter, software, and hardware variation with large-scale behavior across 57,000 climate models. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0608144104
Kooperman GJ, Pritchard MS, O’Brien TA, Timmermans BW (2018) Rainfall from resolved rather than parameterized processes better represents the present-day and climate change response of moderate rates in the community atmosphere model. JAMES 10:971–988. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017MS001188
Koteswaram P (1958) The easterly jet stream in the tropics. Tellus. https://doi.org/10.3402/tellusa.v10i1.9220
Krishnamurthy V, Stan C, Randall DA et al (2014) Simulation of the South Asian monsoon in a coupled model with an embedded cloud-resolving model. J Clim. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-13-00257.1
Kummerow C, Barnes W, Kozu T et al (1998) The tropical rainfall measuring mission (TRMM) sensor package. J Atmos Ocean Technol. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0426(1998)015%3c0809:TTRMMT%3e2.0.CO;2
Langan R, Archibald R, Plumlee M et al (2014) Stochastic parameterization to represent variability and extremes in climate modeling. Proc Comput Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2014.05.103
Li C, Yanai M (1996) The onset and interannual variability of the asian summer monsoon in relation to land-sea thermal contrast. J Clim 9:358–375
Li Y et al (2018) The Indian summer monsoon intraseasonal oscillations in CFSv2 Forecasts: biases and importance of improving air-sea interaction processes. J Clim 31(14):5351–5370. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-17-0623.1
Lin SJ (2004) A “vertically Lagrangian” finite-volume dynamical core for global models. Mon Weather Rev. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(2004)132%3c2293:AVLFDC%3e2.0.CO;2
Lin JWB, Neelin JD (2003) Toward stochastic deep convective parameterization in general circulation models. Geophys Res Lett 30:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002GL016203
Liu X et al (2007) Inclusion of ice microphysics in the NCAR community atmospheric model version 3 (CAM3. J Clim 20(18):4526–4547. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI4264.1
Loeb NG et al (2009) Toward optimal closure of the earth’s top-of-atmosphere radiation budget. J Clim 22(3):748–766
Madden RA, Julian PR (1971) Detection of a 40–50 day oscillation in the zonal wind in the tropical Pacific. J Atmos Sci 28:702–708
Mishra SK, Anand A, Fasullo J, Bhagat S (2018) Importance of the resolution of surface topography in Indian monsoon simulation. J Clim 31:4879–4898. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-17-0324.1
Mlawer EJ et al (1997) Radiative transfer for inhomogeneous atmospheres: RRTM, a validated correlated-k model for the longwave. J Geophys Res 102(14):16663–16682
Moncrieff MW, Waliser DE, Miller MJ et al (2012) Multiscale convective organization and the YOTC virtual global field campaign. BAMS. https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-D-11-00233.1
Morrison H, Gettelman A (2008) A new two-moment bulk stratiform cloud microphysics scheme in the community atmosphere model, version 3 (CAM3). Part I: description and numerical tests. J Clim. https://doi.org/10.1175/2008JCLI2105.1
Neale RB, Richter JH, Jochum M (2008) The impact of convection on ENSO: from a delayed oscillator to a series of events. J Clim. https://doi.org/10.1175/2008JCLI2244.1
Neggers RAJ, Siebesma AP, Jonker HJJ (2002) A multiparcel model for shallow cumulus convection. J Atmos Sci 59:1655–1668. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0469(2002)059%3c1655:AMMFSC%3e2.0.CO;2
Nie J, Kuang Z (2012) Responses of shallow cumulus convection to large-scale temperature and moisture perturbations: a comparison of large-eddy simulations and a convective parameterization based on stochastically entraining parcels. J Atmos Sci. https://doi.org/10.1175/JAS-D-11-0279.1
Oueslati B, Bellon G (2013) Convective entrainment and large-scale organization of tropical precipitation: sensitivity of the CNRM-CM5 hierarchy of models. J Clim. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-12-00314.1
Palmer TN (2001) A nonlinear dynamical perspective model error: a proposal for non-local stochastic-dynamic parametrization in weather and climate prediction models. QJRMS. https://doi.org/10.1256/smsqj.57201
Park S, Bretherton CS (2009) The University of Washington shallow convection and moist turbulence schemes and their impact on climate simulations with the community atmosphere model. J Clim. https://doi.org/10.1175/2008JCLI2557.1
Pathak R, Sahany S, Mishra SK, Dash SK (2019) Precipitation Biases in CMIP5 Models over the South Asian Region. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-45907-4
Plant RS, Craig GC (2008) A stochastic parameterization for deep convection based on equilibrium statistics. J Atmos Sci 65:87–105. https://doi.org/10.1175/2007JAS2263.1
Pritchard MS, Moncrieff MW, Somerville RCJ (2011) Orogenic propagating precipitation systems over the united states in a global climate model with embedded explicit convection. J Atmos Sci. https://doi.org/10.1175/2011JAS3699.1
Pritchard MS, Bretherton CS, DeMott CA (2014) Restricting 32–128 km horizontal scales hardly affects the MJO in the Superparameterized Community Atmosphere Model vol 3.0 but the number of cloud-resolving grid columns constrains vertical mixing. JAMES 6:723–739. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014MS000340
Qian Y, Yan H, Hou Z et al (2015) Parametric sensitivity analysis of precipitation at global and local scales in the Community Atmosphere Model CAM5. JAMES. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014MS000354
Randel DL et al (1996) A new global water vapor dataset. BAMS 77(6):1233–1246
Raymond DJ, Blyth AM (1986) A stochastic mixing model for non-precipitating cumulus clouds. J Atmos Sci 43:2708–2718
Richter JH, Rasch P (2008) Effects of convective momentum transport on the atmospheric circulation in the community atmosphere model, Version 3. J Clim 21(7):1487–1499. https://doi.org/10.1175/2007JCLI1789.1
Rio C, Hourdin F, Couvreux F, and Jam A (2010) Resolved versus parametrized boundary-layer plumes. Part II: Continuous formulations of mixing rates for mass-flux schemes. Bound-Layer Meteor 135:469–483
Romps DM, Kuang Z (2010) Do undiluted convective plumes exist in the upper tropical troposphere? J Atmos Sci 67:468–484. https://doi.org/10.1175/2009JAS3184.1
Sabeerali CT, Rao SA, George G et al (2014) Modulation of monsoon intraseasonal oscillations in the recent warming period. J Geophys Res. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013JD021261
Salunke P, Jain S, Mishra SK (2019) Performance of the CMIP5 models in the simulation of the Himalaya-Tibetan Plateau monsoon. Theor Appl Climatol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-018-2644-9
Sathiyamoorthy V (2005) Large scale reduction in the size of the Tropical Easterly Jet. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005GL022956
Sharmila S, Pillai PA, Joseph S, Roxy M, Krishna RPM, Chattopadhyay R, Abhilash S, Sahai AK, Goswami BN (2013) Role of ocean–atmosphere interaction on northward propagation of Indian summer monsoon intra-seasonal oscillations (MISO). Clim Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-013-1854-1
Sherwood SC, Bony S, Dufresne JL (2014) Spread in model climate sensitivity traced to atmospheric convective mixing. Nature. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12829
Shutts G (2005) A kinetic energy backscatter algorithm for use in ensemble prediction systems. QJRMS. https://doi.org/10.1256/qj.04.106
Siebesma AP, Bretherton CS, Brown A et al (2003) A large eddy simulation intercomparison study of shallow cumulus convection. J Atmos Sci. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0469(2003)60%3c1201:ALESIS%3e2.0.CO;2
Sperber KR, Annamalai H, Kang IS et al (2013) The Asian summer monsoon: an intercomparison of CMIP5 vs CMIP3 simulations of the late 20th century. Clim Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-012-1607-6
Sreekala PP, Bhaskara Rao SV, Arunachalam MS, Harikiran C (2014) A study on the decreasing trend in tropical easterly jet stream (TEJ) and its impact on Indian summer monsoon rainfall. Theor Appl Climatol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-013-1049-z
Stan C, Khairoutdinov M, Demott CA et al (2010) An ocean-atmosphere climate simulation with an embedded cloud resolving model. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009GL040822
Suhas E, Neena JM, Goswami BN (2012) An Indian monsoon intraseasonal oscillations (MISO) index for real time monitoring and forecast verification. Clim Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-012-1462-5
Sušelj K, Teixeira J, Matheou G (2012) EDMF and shallow cumulus boundary layer: an updraft pdf multiple mass flux scheme. J Atmos Sci 69:1513–1533
Sušelj K, Teixeira J, Chung D (2013) A unified model for moist convective boundary layers based on a stochastic eddy-diffusivity/mass-flux parameterization. J Atmos Sci 70:1929–1953. https://doi.org/10.1175/JAS-D-12-0106.1
Sušelj K, Hogan TF, Teixeira J (2014) Implementation of a stochastic eddy-diffusivity/mass-flux parameterization into the Navy Global environmental model. Weather Forecast. https://doi.org/10.1175/WAF-D-14-00043.1
Waliser DE et al (2012) The “year” of tropical convection (May 2008–April 2010): climate variability and weather highlights. BAMS 93:1189–1218. https://doi.org/10.1175/2011BAMS3095.1
Wang Y, Zhang GJ (2016) Global climate impacts of stochastic deep convection parameterization in the NCAR CAM5. JAMES. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016MS000756
Wang Y, Zhang GJ, Craig GC (2016) Stochastic convective parameterization improving the simulation of tropical precipitation variability in the NCAR CAM5. Geophys Res Lett 43:6612–6619. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016GL069818
Wang Y, Zhang GJ, He YJ (2017) Simulation of precipitation extremes using a stochastic convective parameterization in the NCAR CAM5 under different resolutions. J Geophys Res Atmos 122:12875–12891. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JD026901
Wang Y, Zhang GJ, Jiang Y (2018) Linking stochasticity of convection to large-scale vertical velocity to improve Indian Summer Monsoon simulation in the NCAR CAM5. J Clim. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-17-0785.1
Webster PJ, Magaña VO, Palmer TN et al (1998) Monsoons: processes, predictability, and the prospects for prediction. J Geophys Res Ocean. https://doi.org/10.1029/97jc02719
Wheeler M, Kiladis GN (1999) Convectively coupled equatorial waves: analysis of clouds and temperature in the wavenumber-frequency domain. J Atmos Sci. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0469(1999)056%3c0374:CCEWAO%3e2.0.CO;2
Xavier PK, Marzin C, Goswami BN (2007) An objective definition of the Indian summer monsoon season and a new perspective on the ENSO–monsoon relationship. QJRMS 133:496
Yang B, Qian Y, Lin G et al (2013) Uncertainty quantification and parameter tuning in the cam5 zhang-mcfarlane convection scheme and impact of improved convection on the global circulation and climate. J Geophys Res Atmos 118:395–415. https://doi.org/10.1029/2012JD018213
Young A et al (2018) (2018) The International Satellite Cloud Climatology Project H-Series climate data record product. Earth Syst Sci Data 10:583–593. https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-10-583-2018
Zhang GJ, McFarlane NA (1995) Sensitivity of climate simulations to the parameterization of cumulus convection in the canadian climate centre general circulation model. Atmos - Ocean. https://doi.org/10.1080/07055900.1995.9649539
Zhang GJ, Mu M (2005) Effects of modifications to the Zhang-McFarlane convection parameterization on the simulation of the tropical precipitation in the National Center for Atmospheric Research Community Climate Model, version 3. J Geophys Res 110:D09109. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004JD005617
Zhang GJ, Song X (2009) Interaction of deep and shallow convection is key to Madden-Julian Oscillation simulation. Geophys Res Lett 36:L09708. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009GL037340
Zhou L, Murtugudde R (2014) Impact of northward-propagating intraseasonal variability on the onset of Indian summer monsoon. J Clim. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-13-00214.1
Acknowledgements
Authors are greatly thankful to the Indian Ministry of Human Resource Development for providing the Ph.D. fellowship to RP. Authors are also thankful to the supercomputing facility (http://supercomputing.iitd.ac.in/), DST CoE in Climate Modeling (RP03350), and DST FIST project of CAS at IIT Delhi for providing partial support in the form of computing resources. The NCAR Community Atmosphere Model version-5 (CAM5) used for the model simulations, the NCAR-NCL6.4.0 used for data analysis, and the Grammarly software used for correcting the grammar and punctuation type errors in the manuscript writing are also acknowledged. Finally, we want to express our gratitude to the five anonymous reviewers for their suggestions, which helped to improve the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pathak, R., Sahany, S. & Mishra, S.K. Impact of Stochastic Entrainment in the NCAR CAM Deep Convection Parameterization on the Simulation of South Asian Summer Monsoon. Clim Dyn 57, 3365–3384 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-021-05870-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-021-05870-1