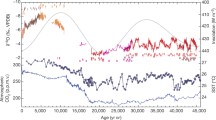
Abstract
Intense Asian summer monsoon rainfall responds to high boreal summer insolation and environmental feedbacks in the early and middle Holocene. However, it is unclear what role of the Asian summer monsoon strength might have played for the heterogeneous wetness pattern in northern China. Here, we report two wet periods in the early and middle Holocene by paleosol, lacustrine, and peat stratigraphies in the southeast Mu Us Desert, and that early-Holocene wetness records are common and seen in valleys and missing from valley walls while mid-Holocene wetness records are found everywhere in the region. The preliminary analysis of the stable carbon isotopic composition (δ13C) of soil carbonate and organic carbon from a riverine dune–paleosol sequence in a river valley reveals that wet springs/falls with dry summers frequently prevailed in the early Holocene, while wet summers with dry springs/falls became predominant in the middle Holocene. Strong-wind and low-temperature springs and falls on valley walls and uplands cause eolian sedimentation faster than soil formation but weak-wind and warmer-soil temperature in valleys facilitate vegetation metabolism and thus soil formation. Warm summer rainfall with no strong northwesterly wind causes paleosol, lacustrine and peat formation either in valleys or on uplands. The early-Holocene heterogeneous and middle-Holocene uniform wetness records are indeed controlled by seasonal hydroclimate conditions but not a single factor of summer monsoon rainfall strength in the southeast Mu Us Desert.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
An ZS, Porter SC, Kutzbach JE, Wu XH, Wang SM, Liu XD, Li X, Zhou WJ (2000) Asynchronous Holocene optimum of the East Asian monsoon. Quatern Sci Rev 19:743–762
An ZS, Colman SM, Zhou WJ, Li XQ, Brown ET, Jull AJ, Cai YJ, Huang YS, Lu X, Chang H, Song YG, Sun YB, Xu H, Liu WG, Jin ZD, Liu X, Cheng P, Liu Y, Ai L, Li X, Liu X, Yan L, Shi ZG, Wang X, Wu F, Qiang X, Dong J, Lu F, Xu X (2012) Interplay between the Westerlies and Asian monsoon recorded in Lake Qinghai sediments since 32 ka. Sci Rep 2:619–619. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep00619
Ashley GM, Deocampo DM, Kahmann-Robinson J, Steven GD (2013) Groundwater-fed wetland sediments and paleosols: It’s all about water table. In: New frontiers in paleopedology and terrestrial paleoclimatology: paleosols and soil surface analog systems SEPM, vol 104. Special Publication, pp 47–61. https://doi.org/10.2110/sepmsp.104.03
Blaauw M, Christen JA (2011) Flexible paleoclimate age-depth models using an autoregressive gamma process. Bayesian anal 6:457–474
Cai YJ, Tan LC, Cheng H, An ZS, Edwards RL, Kelly MJ, Kong X, Wang XY (2010) The variation of summer monsoon precipitation in central China since the last deglaciation. Earth Planet Sci Lett 291:21–31
Carlson AE, Legrande AN, Oppo DW, Came RE, Schmidt GA, Anslow FS, Licciardi JM, Obbink EA (2008) Rapid early Holocene deglaciation of the Laurentide ice sheet. Nat Geosci 1:620–624
Cerling TE (1984) The stable isotopic composition of modern soil carbonate and its relationship to climate. Earth Planet Sci Lett 71:229–240
Cerling TE, Solomon DK, Quade J, Bowman JR (1991) On the isotopic composition of carbon in soil carbon dioxide. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 55:3403–3405
Cerling TE, Wynn JG, Andanje SA (2011) Woody cover and hominin environments in the past 6 million years. Nature 476:51–56
Chen FH, Yu ZC, Yang ML, Ito E, Wang SM, Madsen DB, Huang XZ, Zhao Y, Sato T, Birks HJB, Boomer I, Chen JH, An CB, Wünnemann B (2008) Holocene moisture evolution in arid central Asia and its out-of-phase relationship with Asian monsoon history. Quatern Sci Rev 27:351–364
Chen FH, Chen JH, Huang W, Chen S, Huang XZ, Jin LY, Jia J, Zhang XJ, An CB, Zhang J (2019a) Westerlies Asia and monsoonal Asia: Spatiotemporal differences in climate change and possible mechanisms on decadal to sub-orbital timescales. Earth Sci Rev 192:337–354
Chen JH, Liu JB, Zhang XJ, Chen SQ, Huang W, Chen J, Zhang SR, Zhou AF, Chen FH (2019b) Unstable Little Ice Age climate revealed by high-resolution proxy records from northwestern China. Clim Dyn 53:1517–1526. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-019-04685-5
Cheng H, Zhang HW, Zhao JY, Li HY, Ning YF, Kathayat G (2019) Chinese stalagmite paleoclimate researches: a review and perspective. Sci China Earth Sci 62:1–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-019-9478-3
Chen FH, Xu QH, Chen JH, Birks J, Liu JB, Zhang SR, Jin LY, An CB, Telford R, Cao XY, Wang ZL, Zhang XJ, Selvaraj K, Lv HY, Li YC, Zheng Z, Wang HP, Zhou AF, Dong GH, Zhang JW, Huang XZ, Bloemendal J, Rao ZG (2015) East Asian summer monsoon precipitation variability since the last deglaciation. Sci Rep 5:11186. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep11186
Chen WN, Gao SY, Shao YB, Zhang H (1990) The pollen combination and climate change in Mu Us Desert during the Holocene. Collect Essays Chin Hist Geogr 1:39–54 ((In Chinese))
Chiang J, Fung IY, Wu C-H, Cai YJ, Edman JP, Liu Y, Day JA, Bhattacharya T, Mondal Y, Labrousse CA (2015) Role of seasonal transitions and westerly jets in East Asian paleoclimate. Quatern Sci Rev 108:111–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2014.11.009
Cui JX, Sun ZY, Burr GS, Shao J, Chang H (2019) The great cultural divergence and environmental background of Northern Shaanxi and its adjacent regions during the late Neolithic. Archaeol Res Asia 20:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ara.2019.100164
Gao SY, Chen WN, Jin HL, Dong GR, Li BS, Yang GS, Liu LY, Guan YZ, Sun Z, Jin J (1993) A peliminary study of the desert envolution in the northwestern limit of monsoonal China. Sci China Ser B 23:202–208 ((In Chinese))
Goldsmith Y, Broecker WS, Xu H, Polissar PJ, Demenocal PB, Porat N, Lan JH, Cheng P, Zhou WJ, An ZS (2017) Northward extent of East Asian monsoon covaries with intensity on orbital and millennial timescales. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114:1817–1821
Han R, Su ZZ, Li X, Liu M, Ma Y (2019) Holocene climate change revealed by grain size and magnetic susceptibility in the Eastern Mu Us Sandy Land. J Desert Res 39:105–114 ((In Chinese))
He Z, Zhou J, Lai ZP, Yang LH, Liang J, Long H, Ou X (2010) Quartz OSL dating of sand dunes of Late Pleistocene in the Mu Us Desert in northern China. Quatern Geochronol 5:102–106
Herzschuh U, Cao XY, Laepple T, Dallmeyer A, Telford R, Ni J, Chen FH, Kong ZC, Liu GX, Liu K-B, Liu XQ, Stebich M, Tang LY, Tian F, Wang YB, Wischnewski J, Xu QH, Shun Yan S, Yang ZJ, Yu G, Zhang Y, Zhao Y, Zheng Z (2019) Position and orientation of the westerly jet determined Holocene rainfall patterns in China. Nat Commun 1:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09866-8
Hong YT, Hong B, Lin Q, Shibatab Y, Hirotab M, Zhua YX, Lengc XT, Wanga Y, Wanga H, Yia L (2005) Inverse phase oscillations between the East Asian and Indian Ocean summer monsoons during the last 12000 years and paleo-El Nio. Earth Planet Sci Lett 231:337–346
Hou JZ, Dandrea WJ, Wang M, He Y, Liang J (2017) Influence of the Indian monsoon and the subtropical jet on climate change on the Tibetan Plateau since the late Pleistocene. Quatern Sci Rev 163:84–94
Huang D, Zhu J, Zhang Y, Wang J, Kuang X (2015) The impact of the East Asian subtropical jet and polar front jet on the frequency of spring persistent rainfall over Southern China in 1997–2011. J Clim 28:6054–6066
Jia FF, Lu RJ, Gao SY, Li J, Liu XK (2015) Holocene aeolian activities in the southeastern Mu Us Desert, China. Aeol Res 19:267–274
Jia FF, Lu RJ, Liu XK, Zhao C, Lv Z, Gao SY (2018) Palaeoenvironmental implications of a Holocene sequence of lacustrine-peat sediments from the desert-loess transitional zone in Northern China. J Asian Earth Sci 156:167–173
Jin HL, Dong GR, Su ZZ, Sun L (2001) Reconstruction of the spatial patterns of desert/loess boundary belt in North China during the Holocene. Chin Sci Bull 46:969–974
Kang SG, Du JH, Wang N, Dong JB, Wang D, Wang XL, Qiang XK, Song YG (2020) Early Holocene weakening and mid- to late Holocene strengthening of the East Asian winter monsoon. Geology. https://doi.org/10.1130/G47621.1
Kong WW, Swenson LM, Chiang J (2017) Seasonal transitions and the westerly jet in the Holocene East Asian Summer Monsoon. J Clim 30:3343–3365
Kutzbach JE (1981) Monsoon climate of the early Holocene: climate experiment with the earth’s orbital parameters for 9000 years ago. Science 214:59–61
Kutzbach JE, Street-Perrott FA (1985) Milankovitch forcing of fluctuations in the level of tropical lakes from 18 to 0 kyr BP. Nature 317:130–134
Li BS, Zhang DD, Jin HL, Wu Z, Yan MC, Sun W, Zhu YZ, Sun DH (2000) Paleo-monsoon activities of Mu Us Desert, China since 150 ka BP—a study of the stratigraphic sequences of the Milanggouwan Section, Salawusu River area. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 162:1–16
Li S-H, Sun JM, Li B (2012) Holocene environmental changes in central Inner Mongolia revealed by luminescence dating of sediments from the Sala Us River valley. The Holocene 22:397–404
Li Y, Wang N, Zhou XH, Zhang CQ, Wang Y (2014) Synchronous or asynchronous Holocene Indian and East Asian summer monsoon evolution: a synthesis on Holocene Asian summer monsoon simulations, records and modern monsoon indices. Glob Planet Change116:30–40
Liu K, Lai ZP (2012) Chronology of Holocene sediments from the archaeological Salawusu site in the Mu Us Desert in China and its palaeoenvironmental implications. J Asian Earth Sci 45:247–255
Liu B, Jin HL, Sun LY, Sun Z, Niu QH, Xie SB, Li GH (2014) Holocene moisture change revealed by the Rb/Sr ratio of aeolian deposits in the southeastern Mu Us Desert, China. Aeol Res 13:109–119
Liu XK, Lu RJ, Du J, Lyu ZQ, Wang L, Gao SY, Wu Y (2018) Evolution of peatlands in the Mu Us Desert, Northern China, since the last deglaciation. J Geophys Res 123:252–261
Liu XK, Lu RJ, Jia FF, Chen L, Li TF, Ma YZ, Wu YQ (2018b) Holocene water-level changes inferred from a section of fluvio-lacustrine sediments in the southeastern Mu Us Desert, China. Quatern Int 469:58–67
Liu XX, Sun YB, Vandenberghe J, Cheng P, Zhang Xu, Gowan E, Lohmann G, An ZS (2020) Centennial- to millennial-scale monsoon changes since the last deglaciation linked to solar activities and North Atlantic cooling. Climate of The Past 16:315–324
Liu XY, Zhan T, Zhou X, Wu HB, Li Q, Zhao C, Qiao YS, Jiang SW, Tu LY, Ma YF, Zhang J, Jiang X, Lou BJ, Zhang XL, Zhou X (2019) Late onset of the Holocene rainfall maximum in northeastern China inferred from a pollen record from the sediments of Tianchi Crater Lake. Quatern Res 92:1–13
Lu HY, Miao XD, Zhou YL, Mason JA, Swinehart JB, Zhang JF, Zhou LP, Yi SW (2005) Late Quaternary aeolian activity in the Mu Us and Otindag dune fields (north China) and lagged response to insolation forcing. Geophys Res Lett 32:1–4
Lu HY, Yi SW, Liu ZY, Mason JA, Jiang DB, Cheng J, Stevens T, Xu ZW, Zhang EL, Jin LY, Zhang ZH, Guo ZT, Wang Y, Otto-Bliesner B (2013) Variation of East Asian monsoon precipitation during the past 21 k.y. and potential CO2 forcing. Geology 41:1023–1026
Ma J, Yue LP, Yang LR, Sun L, Xu R (2011) OSL dating of Holocene sequence and palaeoclimate change record in southeastern margin of Mu Us desert, north China. Quatern Sci 31:120–129 ((In Chinese))
Mason JA, Lu HY, Zhou YL, Miao XD, Swinehart JB, Liu ZY, Goble RJ, Yi SW (2009) Dune mobility and aridity at the desert margin of northern China at a time of peak monsoon strength. Geology 37:947–950
Ming GD, Zhou WJ, Wang H, Cheng P, Shu PX, Xian F, Fu YC (2020) Moisture variations in Lacustrine–eolian sequence from the Hunshandake sandy land associated with the East Asian Summer Monsoon changes since the late Pleistocene. Quatern Sci Rev 233:106210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2020.106210
Porter SC, Zhou WJ (2006) Synchronism of Holocene East Asian monsoon variations and North Atlantic drift-ice tracers. Quatern Res 65:443–449
Quade J, Cerling TE, Bowman JR (1989) Systematic variations in the carbon and oxygen isotopic composition of pedogenic carbonate along elevation transects in the southern Great Basin, United States. Geol Soc Am Bull 101:464–475
Ran M, Feng ZD (2013) Holocene moisture variations across China and driving mechanisms: a synthesis of climatic records. Quatern Int 313/314:179–193
Stebich M, Rehfeld K, Schlutz F, Tarasov P, Liu JQ, Mingram J (2015) Holocene vegetation and climate dynamics of NE China based on the pollen record from Sihailongwan Maar Lake. Quatern Sci Rev 124:275–289
Shu PX, Li BS, Niu DF, Wang FN, Wen XH, Si YJ, Chen Q (2016) Holocene climate change recorded by the grain-size from the DGS1 Segment in the Southeast of Mu Us Desert, North China. Sci Geograph Sin 36:448–457 ((In Chinese))
Sun J, Li S-H, Han P, Chen Y (2006) Holocene environmental changes in the central Inner Mongolia, based on single-aliquot-quartz optical dating and multi-proxy study of dune sands. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 233:51–62
Wang H, Follmer LR (1998) Proxy of monsoon seasonality in carbon isotopes from paleosols of the southern Chinese Loess Plateau. Geology 26:987–990
Wang H, Ambrose SH, Fouke BW (2004) Evidence of long-term seasonal climate forcing in rhizolith isotopes during the last glaciation. Geophys Res Lett 31:L13203
Wang YJ, Cheng H, Edwards RL, He Y, Kong X, An ZS, Wu J, Kelly MJ, Dykoski CA, Li X (2005) The Holocene Asian monsoon: links to solar changes and North Atlantic climate. Science 308:854–857
Wang W, Feng ZD (2013) Holocene moisture evolution across the Mongolian Plateau and its surrounding areas: a synthesis of climatic records. Earth Sci Rev 122:38–57
Wen XH, Li BS, Zheng YM, Yang QJ, Niu DF, Shu PX (2016) Early Holocene multi-centennial moisture change reconstructed from lithology, grain-size and chemical composition data in the eastern Mu Us desert and potential driving forces. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 459:440–452
Wen RL, Xiao JL, Fan JW, Zhang S, Yamagata H (2017) Pollen evidence for a mid-Holocene East Asian summer monsoon maximum in northern China. Quatern Sci Rev 176:29–35
Wu J, Lu HY, Yi SW, Xu ZW, Gu Y, Liang C, Cui M, Sun X (2019) Establishing a high-resolution luminescence chronology for the Zhenbeitai sand-loess section at Yulin, North-Central China. Quat Geochronol 49:78–84
Wu YS (2013) Analysis on climatic feature and its change in recent fifty-five years in Shenmu county. Shaanxi Meteorol 2:20–23. (In Chinese)
Wynn JG, Bird MI (2008) Environmental controls on the stable carbon isotopic composition of soil organic carbon: implications for modelling the distribution of C3 and C4 plants, Australia. Tellus B Chem Phys Meteorol 60:604–621
Xiao JL, Xu QH, Nakamura T, Yang X, Liang W, Inouchi Y (2004) Holocene vegetation variation in the Daihai Lake region of north-central China: a direct indication of the Asian monsoon climatic history. Quatern Sci Rev 23:1669–1679
Xu ZW, Lu HY, Yi SW, Vandenberghe J, Mason JA, Zhou YL, Wang X (2015) Climate-driven changes to dune activity during the Last Glacial Maximum and deglaciation in the Mu Us dune field, north-central China. Earth Planet Sci Lett 427:149–159
Xu ZW, Stevens T, Yi SW, Mason JA, Lu HY (2018a) Seesaw pattern in dust accumulation on the Chinese Loess Plateau forced by late glacial shifts in the East Asian monsoon. Geology 46:871–874
Xu B, Wang L, Gu ZY, Hao QZ, Wang HZ, Chu GQ, Jiang DB, Liu Q, Qin XG (2018b) Decoupling of climatic drying and Asian dust export during the Holocene. J Geophys Res Atmos 123:915–928. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JD027483
Xu DK, Lv HY, Chu GQ, Liu L, Shen CM, Li FJ, Wang C, Wu NQ (2019a) Synchronous 500-year oscillations of monsoon climate and human activity in Northeast Asia. Nat Commun 10:1–10
Xu H, Zhou KE, Lan JH, Zhang GL, Zhou XY (2019b) Arid Central Asia saw mid-Holocene drought. Geology 47:255–258
Xu ZW, Mason JA, Xu C, Yi SW, Bathiany S, Yizhaq H, Zhou YL, Cheng J, Holmgren M, Lu HY (2020) Critical transitions in Chinese dunes during the past 12,000 years. Sci Adv 6(9):eaay8020
Yang XP, Liang P, Zhang D, Li HW, Rioual P, Wang X, Xu B, Ma Z, Liu Q, Ren XZ (2019) Holocene aeolian stratigraphic sequences in the eastern portion of the desert belt (sand seas and sandy lands) in northern China and their palaeoenvironmental implications. Sci China Earth Sci 62:1302–1315
Yang XL, Yang H, Wang BY, Huang L-J, Shen C-C, Edwards RL, Cheng H (2019b) Early-Holocene monsoon instability and climatic optimum recorded by Chinese stalagmites. Holocene 29:1059–1067
Zhang XJ, Jin LY, Lu HY, Park W, Schneider B, Latif M (2018) East–west contrast of Northeast Asian summer precipitation during the Holocene. Glob Planet Change 170:190–200
Zhang HW, Brahim A, Li HY, Zhao JY, Kathayat G, Tian Y, Baker J, Wang J, Zhang F, Ning YF, Edwards LR, Cheng H (2019) The Asian summer monsoon: teleconnections and forcing mechanisms—a review from Chinese speleothem δ18O records. Quaternary 26:1–38
Zhao Y, Yu ZC, Chen FH (2009) Spatial and temporal patterns of Holocene vegetation and climate changes in arid and semi-arid China. Quatern Int 194:6–18
Zhao H, Sheng Y, Li B, Fan Y (2016) Holocene environment changes around the Sara Us River, northern China, revealed by optical dating of lacustrine–aeolian sediments. J Asian Earth Sci 120:184–191
Zhou WJ, Donahue DJ, Porter SC, Jull T, Li XQ, Stuiver M, An ZS, Matsumoto E, Dong GR (1996) Variability of monsoon climate in East Asia at the end of the last glaciation. Quatern Res 46:219–229
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Profs. An, Zhisheng; Liu, Xiaodong; Shi, Zhengguo and Yan, Hong for constructive suggestions and comments. We would like to thank Dr. Huot Sebastien, Dr. Shari Eilene Effert-Fanta and Morgan Kay Bailey for their help in the experiments. We thank Drs. Lu, Ruijie; Xu, Zhiwei; Liu, Bing and Liu, Xiaokang who provided helpful information. We also thank two anonymous reviewers and the editor for providing helpful suggestions and reviews. This study was financially supported by the international partnership program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. 132B61KYSB20170005); the Strategic Priority Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. XDB 40000000); the National Basic Research Program of China (Grant No. 2013CB955903); and State Key Laboratory of Loess and Quaternary Geology (SKLLQG1853). This study was also inspired by the NSFC Grant No. 42072206 and No. 42030512.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shu, P., Wang, H., Zhou, W. et al. Seasonal rainfall patterns in stable carbon isotopes in the Mu Us Desert, northern China during the early and middle Holocene. Clim Dyn 56, 799–812 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-020-05504-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-020-05504-y