Abstract
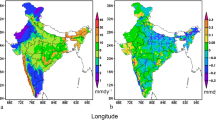
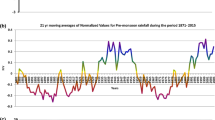
This study presents the contrasting trends of rainfall in the northern and southern Western Ghats (WG) and examines possible reasons for the phenomenon. The WG is one of the important mountain ranges that run parallel to the west coast of India. The mountain chain lies almost perpendicular to the low level jet stream (LLJ) and hence, receives about three times the average rainfall in India. The onset of southwest monsoon also occurs at this region, and thus WG plays a key role in regulating Indian climate through regional climate modulations. Therefore, detecting changes in the rainfall in WG is necessary to identify changes in regional climate. Here, we examine the features of rainfall received and reasons for the observed rainfall patterns in the northern and southern WG. In general, the rainfall peaks are observed in low elevated areas with high inter-annual variability. We find an increase (decrease) southwest monsoon rainfall of about 1.6 mm day−1 decade−1 in certain pockets of the northern (southern) WG. However, an average trend of + 0.3 (− 0.39) mm day−1 decade−1 is estimated in the northern (southern) WG for the 1931–2015 period. Our analyses reveal that this contrasting trend in rainfall (i.e. positive in the north and negative in the south WG) is due to the northward movement of LLJ; from 10°N to 15°N. This shift in LLJ is triggered by an abnormal increase in the surface temperature of the northern Arabian Sea and tropospheric temperature of the north India in the recent decades. The warming helped the LLJ core to move northwards and that weakened (strengthened) the westerly winds over the southern (northern) WG to significantly change the pattern of southwest monsoon rainfall. Henceforth, this study cautions the changes in the rainfall pattern over WG, which can have significant long-term implications for regional climate change.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Findlater J (1969) A major low level current near the Indian Ocean during northern summer. Q J R Meteorol Soc 95:362–380
Gadgil S, Gadgil S (2006) The Indian monsoon, GDP and agriculture. Econ Polit Wkly 25:4887–4895
Ghosh S, Luniya V, Gupta A (2009) Trend analysis of Indian summer monsoon rainfall at different spatial scales. Atmos Sci Lett 10:285–290
Goswami BN, Venugopal V, Sengupta D, Madhusoodanan MS, Xavier PK (2006) Increasing trend of extreme rain events over India in a warming environment. Science 314:1442–1445
Goswami BN, Kripalani RH, Borgaonkar HP, Preethi B (2015) Multi-decadal variability in Indian summer monsoon rainfall using proxy data. Climate change: multidecadal and beyond, p 327
Grossman RL, Durran DR (1984) Interaction of low-level flow with the western Ghat Mountains and offshore convection in the summer monsoon. Mon Weather Rev 112:652–672
Guhathakurta P, Rajeevan M (2008) Trends in rainfall pattern over India. Int J Climatol 28:1453–1469
Gunnell Y (1997) Relief and climate in South Asia: the influence of the Western Ghats on the current climate pattern of peninsular India. Int J Climatol 17:1169–1182
Gunnell Y, Bourgeon G (1997) Soils and climatic geomorphology on the Karnataka Plateau, peninsular India. Catena 29:239–262
Hamza V, Babu CA (2007) Recent changes in the rainfall trend and associated characteristics with good and bad monsoon years. Vayu Mandal 33:105–110
Joseph PV, Sijikumar S (2004) Intraseasonal variability of the low-level jet stream of the Asian summer monsoon. J Clim 17:1449–1458
Joseph PV, Simon A (2005) Weakening trend of the southwest monsoon current through peninsular India from 1950 to the present. Curr Sci 89:687–694
Ju J, Slingo J (1995) The Asian summer monsoon and ENSO. Q J R Meteorol Soc 121:1133–1168
Kalnay E, Kanamitsu M, Kistler R, Collins W, Deaven D, Gandin L, Iredell M, Saha S, White G, Woollen J, Zhu Y (1996) The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 77:437–471
Koteswaram P (1958) Easterly jet stream in the tropics. Tellus 10:43–57
Krishnakumar KN, Rao GP, Gopakumar CS (2009) Rainfall trends in twentieth century over Kerala, India. Atmos Environ 43:1940–1944
Krishnan R, Sabin TP, Ayantika DC, Kitoh A, Sugi M, Murakami H, Turner AG, Slingo JM, Rajendran K (2012) Will the South Asian monsoon overturning circulation stabilize any further? Clim Dyn 40:187–211
Mooley DA, Parthasarathy B (1984) Fluctuation in all India summer monsoon rainfall during 1871–1978. Clim Change 6:287–301
Mooley DA, Parthasarathy B, Sontakke NA, Munot AA (1981) Annual rain-water over India, its variability and impact on the economy. J Climatol 1:167–186
Nair PJ, Chakraborty A, Varikoden H, Francis PA, Kuttippurath J (2018) The local and global climate forcings induced inhomogeneity of Indian rainfall. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-24021-x
Pai DS, Sridhar L, Rajeevan M, Sreejith OP, Satbhai NS, Mukhopadhyay B (2014) Development of a new high spatial resolution (0.25 × 0.25) long period (1901–2010) daily gridded rainfall data set over India and its comparison with existing data sets over the region. Mausam 65:1–18
Pant GB, Parthasarathy SB (1981) Some aspects of an association between the southern oscillation and Indian summer monsoon. Arch Meteorol Geophys B 29:245–252
Pant GB, Rupakumar K, Parthasarathy B, Borgaonkar HP (1988) Long term variability of the Indian summer monsoon related parameters. Adv Atmos Sci 5:469–481
Parthasarathy B (1984) Inter-annual and long term variability of Indian summer monsoon rainfall. Proc Indian Acad Sci (Earth Planet Sci) 93:371–385
Parthasarathy B, Sontakke NA, Munot AA, Kothawale DR (1990) Vagaries of Indian monsoon rainfall and its relationships with regional/global circulations. Mausam 41:301–308
Parthasarthy B, Munot AA, Kothawale DR (1994) All-India monthly and seasonal rainfall series: 1871–1993. Theor Appl Climatol 49:217–224
Preethi B, Mujumdar M, Kripalani RH, Prabhu A, Krishnan R (2017) Recent trends and teleconnections among South and East Asian summer monsoons in a warming environment. Clim Dyn 48:2489–2505
Rajeevan M, Bhate J (2009) A high resolution daily gridded rainfall dataset (1971–2005) for mesoscale meteorological studies. Curr Sci 96:558–562
Rajeevan M, Bhate J, Kale JD, Lal B (2006) High resolution daily gridded rainfall data for the Indian region: analysis of break and active monsoon spells. Curr Sci 91:296–306
Rajendran K, Kitoh A (2008) Indian summer monsoon in future climate projection by a super high-resolution global model. Curr Sci 95:1560–1569
Rajendran K, Kitoh A, Srinivasan J, Mizuta R, Krishnan R (2012) Monsoon circulation interaction with Western Ghats orography under changing climate. Theor Appl Climatol 110:555–571
Ramage CS (1966) The summer atmospheric circulation over the Arabian Sea. J Atmos Sci 23:144–150
Rao YP (1976) Southwest monsoon; meteorological monograph, synoptic meteorology, No 1/1976, India Meteorological Department
Rayner NA, Parker DE, Horton EB, Folland CK, Alexander LV, Rowell DP, Kent EC, Kaplan A (2003) Global analyses of sea surface temperature, sea ice, and night marine air temperature since the late nineteenth century. J Geophys Res 108:D14
Revadekar JV, Varikoden H, Murumkar PK, Ahmed SA (2016) On the relationship between sea surface temperatures, circulation parameters and temperatures over west coast of India. Sci Total Environ 551:175–185
Revadekar JV, Varikoden H, Murumkar PK, Ahmed SA (2018) Latitudinal variation in summer monsoon rainfall over Western Ghat of India and its association with global sea surface temperatures. Sci Total Environ 613:88–97
Roxy M, TanimotoY (2007) Role of SST over the Indian ocean in influencing intraseasonal variability of the Indian summer monsoon. J Meteorol Soc Jpn 85:349–358
Roxy MK et al (2015) Drying of Indian subcontinent by rapid Indian Ocean warming and a weakening land-sea thermal gradient. Nat Commun 6:7423. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms8423
Rupakumar K, Pant GB, Parthasarathy B, Sontakke NA (1992) Spatial and Subseasonal patterns of the long term trends of Indian summer monsoon rainfall. Int J Climatol 12:257–268
Rupakumar K, Ashrit RG, Pant GB (2002) Indian summer monsoon: past, present and future. Sci Cult 68:217–224
Rupakumar K, Kumar KK, Prasanna V, Kamala K, Deshpande NR, Patwardhan SK, Pant GB (2003) Future climate scenarios, Chapter-3 in book climate change and india: vulnerability assessment and adaption edited by Shukla, PR, Sharma, SK, Ravindranath, NH, Garg, A, Bhattcharya, S, Universities Press (India) Ltd, pp 69–125
Sandeep S, Ajayamohan RS (2015) Poleward shift in Indian summer monsoon low level jetstream under global warming. Cli Dyn 45:337–351
Sathyamoorthy V, Pal PK, Joshi PC (2004) Influence of the upper-tropospheric wind shear upon cloud radiative forcing in the Asian monsoon region. J Clim 17:2725–2735
Shepard DA (1968) Two-dimensional interpolation function for irregularly spaced data. In: Proceedings of 1968 ACM national conference, pp 517–524
Soman MR, Krishnakumar K, Singh N (1988) Decreasing trend in the rainfall of Kerala. Curr Sci 57:7–12
Swapna P, Krishnan R, Wallace JM (2014) Indian Ocean and monsoon coupled interactions in a warming environment. Cli Dyn 42:2439–2454
Tripti M, Lambs L, Gurumurthy GP, Moussa I, Balakrishna K, Chadaga MD (2016) Water circulation and governing factors in humid tropical river basins in the central Western Ghats, Karnataka, India. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 30:175–190
Varikoden H, Kumar KK, Babu CA (2013) Long term trends of seasonal and monthly rainfall in different intensity ranges over Indian subcontinent. Mausam 64:481–488
Vialard J, Jayakumar A, Gnanaseelan C, Lengaigne M, Sengupta D, Goswami BN (2012) Processes of 30–90 days sea surface temperature variability in the northern Indian Ocean during boreal summer. Cli Dyn 38:1901–1916
Webster PJ, Fasullo J (2003) Monsoon: dynamical theory. Encycl Atmos Sci 3:1370–1391
Webster PJ, Yang S (1992) Monsoon and ENSO: selectively interactive systems. Q J R Meteorol Soc 118:877–926
Xie SP, Saji NH, Wang Y (2006) Role of narrow mountains in large scale organization of Asian monsoon convection. J Clim 19:3420–3442
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Director, Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM) for providing the necessary facilities and to the Executive Director, Centre for Climate Change Research, IITM for encouragement. We also thank India Meteorological Department (IMD) for the rainfall data, NCEP-NCAR reanalysis and HadISST data products. JK is funded by the Department of Science Technology, Climate Change Programme (SPLICE). CAB is thankful to CUSAT for providing the necessary facilities. The CCCR, IITM is fully funded by the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES), Govt. of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Varikoden, H., Revadekar, J.V., Kuttippurath, J. et al. Contrasting trends in southwest monsoon rainfall over the Western Ghats region of India. Clim Dyn 52, 4557–4566 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-018-4397-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-018-4397-7