Abstract
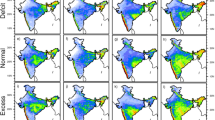
The Indian summer monsoon season of 2014 was erratic and ended up with a seasonal rainfall deficit of 12 % and a record drought in June. In this study we analyze the moisture transport characteristics for the monsoon season of 2014 using both NCEP FNL reanalysis (FNL) and CFSv2 (CFS) model data. In FNL, in June 2014 there was a large area of divergence of moisture flux. In other months also there was lesser flux. This probably is the cause of 2014 drought. The CFS model overestimated the drought and it reproduces poorly the observed rainfall over central India (65E–95E; 5N–35N). The correlation coefficient (CC) between the IMD observed rainfall and CFS model rainfall is only 0.1 while the CC between rainfall and moisture flux convergence in CFS model is only 0.20 and with FNL data −0.78. This clearly shows that the CFS model has serious difficulty in reproducing the moisture flux convergence and rainfall. We found that the rainfall variations are strongly related to the moisture convergence or divergence. The hypothesis of Krishnamurti et al. (J Atmos Sci 67:3423–3441, 2010) namely the intrusion of west African desert air and the associated low convective available potential energy inhibiting convection and rainfall shows some promise to explain dry spells in Indian summer monsoon. However, the rainfall or lack of it is mainly explained by convergence or divergence of moisture flux.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander G, Kesavamurthy RN, De US, Chellapa R, Das SK, Pillai PV (1978) Fluctuations of monsoon activity. Indian J Meteorol Hydrol Geophys 29:76–87
Alory G, Meyers G (2009) Warming of the upper equatorial Indian Ocean and changes in the heat budget (1960–2000). J Clim 22:93–113
Alory G, Wijffels S, Meyers M (2007) Observed temperature trends in the Indian Ocean over 1960–1999 and associated mechanisms. Geophys Res Lett 34(2):L02606
Barnett TP, Dümenil L, Schlese U, Roeckner E, Latif M (1989) The effect of Eurasian snow cover on regional and global climate variations. J Atmos Sci 46(5):661–686
Bhanu Kumar OSRU (1988) Interaction between Eurasian winter snow cover and location of the ridge at the 500 hPa level along 75 E. J Meteorol Soc Jpn 66(3):509–514
Cadet DL, Greco S (1987a) Water vapor transport over the indian ocean during the 1979 summer monsoon. Part I: water vapor fluxes. Mon Weather Rev 115:653–663
Cadet DL, Greco S (1987b) Water vapor transport over the Indian Ocean during the 1979 summer monsoon. Part II: water vapor budgets. Mon Weather Rev 115:2358–2366
Cadet DL, Reverdin G (1981a) The monsoon over the Indian Ocean during summer 1975, Part. l, Mean fields. Mon Weather Rev 103:148–158
Cadet DL, Reverdin G (1981b) Water vapour transport over the Indian Ocean during summer 1975. Tellus 33:476–487
Choudhury A, Krishnan R (2011) Dynamical response of the south Asian monsoon trough to latent heating from stratiform and convective precipitation. J Atmos Sci 68:1347–1363
De US, Lele RR, Natu JC (1998) Breaks in southwest monsoon. India Meteorological Department. Report no. 1998/3
Dickson RR (1984) Eurasian snow cover versus Indian monsoon rainfall—an extension of the Hahn-Shukla results. J Clim Appl Meteorol 23:171–173
Du Y, Xie S-P (2008) Role of atmospheric adjustments in the tropical Indian Ocean warming during the 20th century in climate models. Geophys Res Lett 35:L08712. doi:10.1029/2008GL033631
Ek MB, Mitchell KE, Lin Y, Rogers E, Grunmann P, Koren V, Gayno G, Tarpley JD (2003) Implementation of Noah land surface model advances in the National Centers for Environmental Prediction operational mesoscale Eta model. J Geophys Res 108(D22):8851. doi:10.1029/2002JD003296
Fasullo J (2004) A stratified diagnosis of Indian monsoon-Eurasian snow cover relationship. J Clim 17:1110–1122
Findlater J (1969) A major low-level air current near the Indian Ocean during the northern summer. Q J R Meteorol Soc 95:362–380
Gadgil S, Joseph PV (2003) On breaks of the Indian monsoon. J Earth Syst Sci 112(4):529–558
Ghosh SK, Pant MC, Devan BN (1978) Influence of the Arabian Sea on the Indian summer monsoon. Tellus 30:117–125
Hahn DG, Shukla J (1976) An apparent relationship between Eurasian snow cover and Indian monsoon rainfall. J Atmos Sci 33(12):2461–2462
Hastenrath S, Greischar L (1993) The monsoonal heat budget of the hydrosphere-atmosphere system in the Indian Ocean sector. J Geophys Res 98(C4):6869–6881. doi:10.1029/92JC02956
Hoell A, Funk C (2014) Indo-Pacific sea surface temperature influences on failed consecutive rainy seasons over eastern Africa. Clim Dyn 43:1645–1660
Kim Y-J, Arakawa A (1995) Improvement of orographic gravity—wave parameterization using a mesoscale gravity-wave model. J Atmos Sci 52:1875–1902
Krishna Kumar K, Rajagopalan B, Hoerling M, Bates G, Cane M (2006) Unraveling the mystery of Indian monsoon failure during El-Nino. Science 314:115–119
Krishnamurti TN (1971) Tropical east west circulations during northern summer. J Atmos Sci 28:1342–1347
Krishnamurti TN, Subrahmanyam D (1982) The 30–50 day mode at 850 Mb during MONEX. J Atmos Sci 39:2088–2095
Krishnamurti TN, Ardanuy P, Ramanathan Y, Pasch R (1980) On the onset vortex of the summer monsoon. J Atmos Sci 109:344–363
Krishnamurti TN, Thomas A, Simon A, Kumar V (2010) Desert air incursions, an overlooked aspect, for the dry spells of the Indian summer monsoon. J Atmos Sci 67:3423–3441
Krishnan R, Sugi M (2000) Dynamics of breaks in the Indian summer monsoon. J Atmos Sci 57:1354–1372
Levine RC, Turner AG (2012) Dependence of Indian monsoon rainfall on moisture fluxes across the Arabian Sea and the impact of coupled model sea surface temperature biases. Clim Dyn 38:2167–2190
Lott F, Miller MJ (1997) A new subgrid scale orographic drag parameterization: its formulation and testing. Q J R Meteorol Soc 123:101–127. doi:10.1002/qj.49712353704
MAUSAM (2015) Weather in India. In: Medha K, Sunitha Devi S Kundale AP (ed) Monsoon season (June–September, 2014), vol 66, pp 657–674
Mitra AK et al (2009) Daily Indian precipitation analysis formed from a merge of rain-gauge data with the TRMM TMPA satellite-derived rainfall estimates. J Meteorol Soc Jpn 87A:265–279. doi:10.2151/jmsj.87A.265
Moorthi S, Pan HL, Caplan P (2001) Changes to the 2001 NCEP operational MRF/AVN global analysis/forecast system. Technical procedures bulletins series no. 484, National Weather Service, Office of Meteorology, Silver Spring, MD. http://www.nws.noaa.gov/om/tpb/484.pdf
Murakami T, Nakazawa T et al (1984) On the 40–50 day oscillation during the 1979 northern hemisphere summer. Part. II: heat and moisture budget. J Meteorol Soc Jpn 62:469–484
Naidu CV, Durgalakshmi K, Muni Krishna K, Rao SRL, Satyanarayana GC, Lakshminarayana P, Malleswara Rao L (2009) Is summer monsoon rainfall decreasing over India in the global warming era? J Geophys Res 114:D24108. doi:10.1029/2008JD011288
Narapusetty B, Murtugudde R, Wang H, Kumar A (2015) Ocean–atmosphere processes driving Indian summer monsoon biases in CFSv2 hindcasts. Clim Dyn. doi:10.1007/s00382-015-2910-9
NCEP FNL (2000) National Centers for Environmental Prediction/National Weather Service/NOAA/U.S. Department of Commerce. 2000, updated daily. NCEP FNL Operational Model Global Tropospheric Analyses, continuing from July 1999. Research Data Archive at the National Center for Atmospheric Research, Computational and Information Systems Laboratory. doi:10.5065/D6M043C6
Pisharoty PR (1965) Evaporation from the Arabian Sea and the Indian southwest monsoon. In: Proceedings of the symposium on meteorological results of international Indian ocean expedition, Bombay, pp 22–26
Prasanna V (2014) Impact of monsoon rainfall on the total food grain yield over India. J Earth Syst Sci 123(5):1129–1145
Ramamurthy K (1969) Monsoon of India: some aspects of the ‘break’ in the Indian southwest monsoon during July and August. Forecasting manual 1–57 no. IV 18.3, India Meteorological Department, Poona, India
Raman CRV, Rao YP (1981) Blocking highs over Asia and monsoon droughts over India. Nature 289:221–223
Ramaswamy C (1962) Breaks in the Indian summer monsoon as a phenomenon of interaction between the easterly and the sub-tropical westerly jet streams. Tellus 14(3):337–349
Rao YP (1976) Southwest monsoon: meteorological monograph (synoptic meteorology). India Meteorological Department, Pune, N.1/1976, 367
Rao RR, Jitendra V, Girish Kumar MS, Ravischandran M, Ramakrishna SSVS (2015) Interannual variability of the Arabian Sea warm pool: observations and governing mechanisms. Clim Dyn 44:2119–2136
Saha KR, Bavadekar SN (1973) Water vapour budget and precipitation over the Arabian Sea during the northern summer. Q J R Meteorol Soc 99:273–278. doi:10.1002/qj.49709942006
Saha KR, Bavadekar SN (1977) Moisture flux across the west coast of India and rainfall during the southwest monsoon. Q J R Meteorol Soc 103:373–374. doi:10.1002/qj.49710343613
Saha S et al (2014) The NCEP climate forecast system version 2. J Clim 27:2185–2208. doi:10.1175/JCLI-D-12-00823.1
Saji NH, Goswami BN, Vinayachandran PN, Yamagata TA (1999) A dipole mode in the tropical Indian Ocean. Nature 401:360–363
Satyamurty P, Wanzeler CP, da Costa A, Manzi O, Candido LA (2013) A quick look at the 2012 record flood in the Amazon Basin. Geophys Res Lett 40:1396–1401. doi:10.1002/grl.50245
Sikka DR, Gadgil S (1980) On the maximum cloud zone and the ITCZ over Indian longitude during the southwest monsoon. Mon Weather Rev 108:1840–1853
Sikka DR, Narasimha R (1995) Genesis of the monsoon trough boundary layer: boundary layer experiment (MONTBLEX). Proc Indian Acad Sci 104:157–187
Singh D, Tsiang M, Rajaratnam B, Diffenbaugh NS (2014) Observed changes in extreme wet and dry spells during the South Asian summer monsoon season. Nat Clim Change 4:456–461. doi:10.1038/nclimate2208
Swapna P, Krishnan R, Wallace JM (2014) Indian Ocean and monsoon coupled interactions in a warming environment. Clim Dyn 42:2439–2454
Tokinga H, Xie S-P, Deser C, Kosaka Y, Okumura YM (2012) Slowdown of the walker circulation driven by tropical Indo-Pacific warming. Nature 491:439–443. doi:10.1038/nature11576
Vellore RK, Krishnan R, Pendharkar J, Choudhury AD, Sabin TP (2014) On the anomalous precipitation enhancement over the Himalayan foothills during monsoon breaks. Clim Dyn. doi:10.1007/s00382-013-2024-1
Wang B, Rui H (1990) Synoptic climatology of transient tropical intraseasonal convection anomalies: 1975–1985. Meteorol Atmos Phys 44:43–61
Winton M (2000) A reformulated three-layer sea ice model. J Atmos Ocean Technol 17:525–531
Zhou T-J, Yu R-C (2005) Atmospheric water vapor transport associated with typical anomalous summer rainfall patterns in China. J Geophys Res 110:D08104. doi:10.1029/2004JD005431
Acknowledgments
The entire work has been done with the support of the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM), Pune, fully funded by the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES), New Delhi, Govt. of India (Ref. No. MM/SERP/Andhra-Univ/2013/IND-4/002/1307). Figures 1 and 2 are used from the IMD published reports. Plots in this work are made using the GrADS and Origin software which are freely available online. Thanks are due to the two reviewers for their insightful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramakrishna, S.S.V.S., Brahmananda Rao, V., Srinivasa Rao, B.R. et al. A study of 2014 record drought in India with CFSv2 model: role of water vapor transport. Clim Dyn 49, 297–312 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-016-3343-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-016-3343-9