Abstract
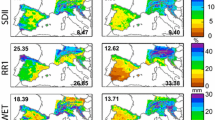
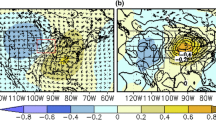
The suitability of dynamical downscaling in producing high-resolution climate scenarios for impact assessments is limited by the quality of the driving data and regional climate model (RCM) error. Multiple RCMs driven by a single global climate model simulation of current climate show a reduction in bias compared to the driving data, and the remaining bias motivates exploration of bias correction and higher RCM resolution. The merits of bias correcting the mean climate of the driving data (boundary bias correction) versus bias correcting the mean of the RCM output data are explored and compared to model resolution sensitivity. This analysis focuses on the simulation of summer temperature and precipitation extremes using a single RCM, the Nested Regional Climate Model (NRCM). The NRCM has a general cool bias for hot and cold extremes, a wet bias for wet extremes and a dry bias for dry extremes. Both bias corrections generally reduced the bias and overall error with some indication that boundary bias correction provided greater benefits than bias correcting the mean of the RCM output data, particularly for precipitation. High resolution tended not to lead to further improvements, though further work is needed using multiple resolution evaluation datasets and convection permitting resolution simulations to comprehensively assess the value of high resolution.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baigorria GA, Jones JW, Shin DW, Mishra A, O'Brien JJ (2007) Assessing uncertainties in crop model simulations using daily bias-corrected regional circulation model outputs. Clim Res 34(3):211–222. doi:10.3354/cr00703
Briegleb BP, Bitz CM, Hunke EC, Lipscomb WH, Holland MM, Schramm JL, Moritz RE (2004) Scientific description of the sea ice component in the Community Climate System Model, version three. NCAR technical note NCAR = TN463-STR, pp 70
Bruyère CL, Done JM, Holland GJ, Fredrick S (2013a) Bias corrections of global models for regional climate simulations of high-impact weather. Clim Dyn. doi:10.1007/s00382-013-2011-6
Bruyère CL, Done JM, Fredrick S, Suzuki-Parker A (2013b) NCAR Nested Regional Climate Model (NRCM). Research data archive at the national center for atmospheric research, computational and information systems laboratory. doi:10.5065/D6Z899DW
Caya D, Laprise R (1999) A semi-implicit semi-lagrangian regional climate model: the Canadian RCM. Mon Weather Rev 127:341–362
Christensen JH, Boberg F, Christensen OB, Lucas-Picher P (2008) On the need for bias correction of regional climate change projections of temperature and precipitation. Geophys Res Lett 35:L20709. doi:10.1029/2008GL035694
Colette A, Vautard R, Vrac M (2012) Regional climate downscaling with prior statistical correction of the global climate forcing. Geophys Res Lett. doi:10.1029/2012GL052258
Collins WD, Bitz CM, Blackmon ML, Bonan GB, Bretherton CS, Carton JA, Chang P, Doney SC, Hack JJ, Henderson TB, Kiehl JT, Large WG, McKenna DS, Santer BD, Smith RD (2006a) The Community Climate System Model: CCSM3. J Clim 19:2122–2143
Collins WD, Rasch PJ, Boville BA, Hack JJ, McCaa JR, Williamson DL, Briegleb BP, Bitz CM, Lin SJ, Zhang M (2006b) The formulation and atmospheric simulation of the Community Atmosphere Model: CAM3. J Clim 19:2144–2161
Dai Y, Zeng X, Dickinson RE, Baker I, Bonan G, Bosilovich M, Denning S, Dirmeyer P, Houser P, Niu G, Oleson K, Schlosser A, Yang ZL (2003) The Common Land Model (CLM). Bull Am Meteorol Soc 84:1013–1023
De Sales F, Xue Y (2011) Assessing the dynamic-downscaling ability over South America using the intensity-scale verification technique. Int J Climatol 31(8):1205–1221. doi:10.1002/joc.2139
Denis B, Laprise R, Caya D, Côté J (2001) Downscaling ability of one-way nested regional climate models: the big-brother experiments. Clim Dyn 18:627–646
Deser C, Phillips AS, Alexander MA, Smoliak BV (2014) Projecting North American Climate over the next 50 years: uncertainty due to internal variability. J Clim 27:2271–2296
Dickinson RE, Errico RM, Giorgi F, Bates GT (1989) A regional climate model for the western United States. Clim Change 15:383–422
Dickinson RE, Oleson KW, Bonan G, Hoffman F, Thornton P, Vertenstein M, Yang Z-L, Zeng X (2006) The Community Land Model and its climate statistics as a component of the Community Climate System Model. J Clim 19:2302–2324
Done JM, Holland GJ, Bruyère CL, Leung LR, Suzuki-Parker A (2013) Modeling high-impact weather and climate: lessons from a tropical cyclone perspective. Clim Change. doi:10.1007/s10584-013-0954-6
Dosio A, Paruolo P (2011) Bias correction of the ENSEMBLES high-resolution climate change projections for use by impact models: evaluation on the present climate. J Geophys Res 116. doi:10.1029/2011JD015934
Ehret U, Zehe E, Wulfmeyer V, Warrach-Sagi K, Liebert J (2012) Should we apply bias correction to global and regional climate model data? Hydrol Earth Syst Sci Discuss 9:5355–5387. doi:10.5194/hessd-9-5355-2012
Fowler HJ, Ekstrom M, Blenkinsop S, Smith AP (2007) Estimating change in extreme European precipitation using a multi-model ensemble. J Geophys Res 112:D18104. doi:10.1029/2007JD008619
Fu C, Wang S, Xiong Z, Gutowski WJ, Lee DK, McGregor JL, Sato Y, Kato H, Kim JW, Suh MS (2005) Regional climate model intercomparison project for Asia. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 86:257–266
Ghosh S, Mujumdar PP (2009) Climate change impact assessment: uncertainty modeling with imprecise probability. J Geophys Res 114:D18113. doi:10.1029/2008JD011648
Giorgi F (1990) Simulation of regional climate using a limited area modelmnested in general circulation model. J Clim 3:941–963. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(1990)003<0941:SORCUA>2.0.CO;2
Giorgi F, Brodeur CS, Bates GT (1994) Regional climate change scenarios over the United States produced with a nested regional climate model. J Clim 7:357–399
Grell GA, Dudhia J, Stauffer DR (1995) A description of the fifth-generation Penn State/NCAR Mesoscale Model (MM5I), NCAR/TN-398 + STR
Heikkila U, Sandvik A, Sorteberg A (2010) Dynamical downscaling of ERA-40 in complex terrain using the WRF regional climate model. Clim Dyn 37:1551–1564. doi:10.1007/s00382-010-0928-6
Hennessy K, Suppiah R, Page CM (1999) Australian rainfall changes, 1910–1995. Aust Meteorol Mag 48:1–13
Higgins RW, Kousky VE, Silva VBS, Becker E, Xie P (2010) Intercomparison of daily precipitation statistics over the United States in observation and in NCEP reanalysis products. J Clim 23:4637–4650
Holland GJ, Done JM, Bruyère C, Cooper C, Suzuki A (2010) Model investigations of the effects of climate variability and change on future Gulf of Mexico tropical cyclone activity. In: Proceedings offshore technology conference, Houston, TX, ASCE, OTC 20690. http://www.netl.doe.gov/kmd/RPSEA_Project_Outreach/07121-DW1801_OTC-20690-MS.pdf
Ikeda K, Rasmussen R, Liu C, Gochis D, Yates D, Chen F, Tewari M, Barlage M, Dudhia J, Miller K, Arsenault K, Grubišić V, Thompson G, Guttaman E (2010) Simulation of seasonal snowfall over Colorado. Atmos Res 97:462–477
Ines AVM, Hansen JW (2006) Bias correction of daily GCM rainfall for crop simulation studies. Agric For Meteorol 138:44–53. doi:10.1016/j.agrformet.2006.03.009
Kalnay E et al (1996) The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 77:437–477
Karl TR, Koss WJ (1984) Regional and national monthly, seasonal, and annual temperature weighted by area, 1895–1983. Historical climatology series 4–3. National Climatic Data Center, Asheville, pp 38
Leung LR, Qian Y (2005) Downscaling extended weather forecasts for hydrologic prediction. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 86(3):332–333
Leung LR, Hamlet AF, Lettenmaier LP, Kumar A (1999) Simulations of the ENSO hydroclimate signals in the Pacific Northwest Columbia River basin. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 80(11):2313–2329. doi:10.1175/1520-0477(1999)080<2313:SOTEHS>2.0.CO;2
Leung LR, Qian Y, Bian XD, Washington WM, Han JG, Roads JO (2004) Mid-century ensemble regional climate change scenarios for the western United States. Clim Change 62(1–3):75–113. doi:10.1023/B:CLIM.0000013692.50640.55
Levy AAL, Ingram WJ, Jenkinson M, Huntingford C, Lambert FH, Allen M (2012) Can correcting feature location in simulated mean climate improve agreement on projected changes?. Res Lett, Geophysics. doi:10.1029/2012GL053964
Li H, Sheffield J, Wood EF (2010) Bias correction of monthly precipitation and temperature fields from Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change AR4 models using equidistant quantile matching. J Geophys Res 115:D10101. doi:10.1029/2009JD012882
Liang XZ, Kunkel KE, Meehl GA, Jones RG, Wang JXL (2008) Regional climate models downscaling analysis of general circulation models present climate biases propagation into future change projections. Geophys Res Lett 35:L08709. doi:10.1029/2007GL032849
Lo JC, Yang ZL, Pielke RK Sr (2008) Assessment of three dynamical climate downscaling methods using the Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) model. J Geophys Res 113:D09112. doi:10.1029/2007JD009216
Maraun D, Wetterhall F, Ireson AM, Chandler RE, Kendon EJ, Widmann M, Brienen S, Rust HW, Sauter T, Themessl M, Venema VKC, Chun KP, Goodess CM, Jones RG, Onof C, Vrac M, Thiele-Eich I (2010) Precipitation downscaling under climate change: recent developments to bridge the gap between dynamical models and the end user. Rev Geophys 48:Rg3003. doi:10.1029/2009rg000314
Mearns LO et al (2007, updated 2012) The North American regional climate change assessment program dataset, national center for atmospheric research earth system grid data portal. Boulder, CO. Data downloaded 2013-11-25. doi:10.5065/D6RN35ST
Mearns LO, Gutowski WJ, Jones R, Leung LY, McGinnis S, Nunes AMB, Qian Y (2009) A regional climate change assessment program for North America. EOS Trans Am Geophys Union 90:311–312
Meehl GA, Covey C, Taylor KE, Delworth T, Stouffer RJ, Latif M, McAvaney B, Mitchell JFB (2007) The WCRP CMIP3 multimodel dataset: a new era in climate change research. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 88:1383–1394. doi:10.1175/BAMS-88-9-1383
Michalakes J, Dudhia J, Gill D, Henderson T, Klemp J, Skamarock W, Wang W (2004) The weather research and forecast model: software architecture and performance. In: Proceedings of the 11th ECMWF workshop on the use of high performance computing in meteorology, 25–29 October 2004, Reading
Oleson KW, Dai Y, Bonan GB, Bosilovich M, Dickinson R,Dirmeyer P, Hoffman F, Houser P, Levis S, Niu GY, Thornton P, Vertenstein M, Yang ZL, Zeng X (2004) Technical description of Community Land Model (CLM). Technical report NCAR = TN-461.STR, National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, 80307–3000, pp 174
PaiMazumder D, Done JM (2014) Uncertainties to long-term droughts characteristics over Canadian Prairies as simulated by the Canadian RCM. Clim Res. doi:10.3354/cr01196
PaiMazumder D, Sushama L, Laprise R, Khaliq N, Sauchyn D (2013) Canadian RCM projected changes to short- and long-term drought characteristics over the Canadian Prairies. Int J Climatol. doi:10.1002/joc.3521
Piani C, Haerter JO, Coppola E (2010a) Statistical bias correction for daily precipitation in regional climate models over Europe. Theor Appl Climatol 99:187–192. doi:10.1007/s00704-009-0134-9
Piani C, Weedon GP, Best M, Gomes SM, Viterbo P, Hagemann S, Haerter JO (2010b) Statistical bias correction of global simulated daily precipitation and temperature for the application of hydrological models. J Hydrol 395:199–215. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2010.10.024
Prein AF, Holland GJ, Rasmussen RM, Done JM, Ikeda K, Clark MP, Liu, Changhai H (2013) Importance of regional climate model grid spacing for the simulation of heavy precipitation in the Colorado headwaters. J Clim 26:4848–4857
Qian Y, Ghan SJ, Leung LR (2009) Downscaling hydroclimatic changes over the Western US Based on CAM subgrid scheme and WRF regional climate simulations. Int J Climatol 30(5):675–693. doi:10.1002/joc.1928
Raktham C, Bruyère CL, Kreasuwun J, Done JM, Thongbai C, Promnopas W (2014) Regional climate simulation sensitivities over southeast Asia. Clim Dyn. doi:10.1007/s00382-014-2156-y
Randall DA, Wood RA, Bony S, Colman R, Fichefet T, Fyfe J, Kattsov V, Pitman A, Shukla J, Srinivasan J, Stouffer RJ, Sumi A, Taylor KE (2007) Climate models and their evaluation. In: Climate change 2007: the physical science basis, contribution of working group I to the fourth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Rasmussen R et al (2011a) High-resolution coupled climate runoff simulations of seasonal snowfall over Colorado: a process study of current and warmer climate. J Clim 24:3015–3048. doi:10.1175/2010JCLI3985.1
Rasmussen R et al (2011b) Acceleration of the water cycle over the Colorado headwaters region from eight year cloud resolving simulations of the WRF climate model. In: 2011 fall meeting, San Francisco. American Geophysics Union, Abstract A31K-07
Roy P, Gachon P, Laprise R (2012) Assessment of summer extremes and climate variability over the north-east of North America as simulated by Canadian regional climate model. Int J Climatol 32(11):1615–1627. doi:10.1002/joc.2382
Saha S, Moorthi S, Pan H-L, Wang J, Nadiga S, Tripp P et al (2010) The NCEP climate forecast system reanalysis. Bull Amer Meteorol Soc 91:1015–1057
Sato T, Kimura F, Kitoh A (2007) Projection of global warming onto regional precipitation over Mongolia using a regional climate model. J Hydrol 333:144–154
Serreze MC, Clark MP, Armstrong RL, McGinnis DA, Pulwarty RS (1999) Characteristics of the western United States snowpack from snowpack telemetry (SNOTEL) data. Water Resour Res 35:2145–2160
Singh D, Tsiang M, Rajaratnam B, Diffenbaugh NS (2013) Precipitation extremes over the continental United States in a transient, high-resolution, ensemble climate model experiment. JGR Atmos 118(13):7063–7086. doi:10.1002/jgrd.50543
Skamarock W, Klemp J, Dudhia J, Gill D, Barker D, Wang W, Powers J (2008) A description of the advanced research WRF version 3. NCAR technical note 475, pp 113
Smith RD, Dukowicz JK, Malone RC (1992) Parallel ocean general circulation modeling. Physica D 60:38–61
Teutschbein C, Seibert J (2010) Regional climate models for hydrological impact studies at the catchment scale: a review of recent model strategies. Geogr Compass 4(7):834–860. doi:10.1111/j.1749-8198.2010.00357.x
Themeßl J, Gobiet MA, Leuprecht A (2011) Empirical-statistical downscaling and error correction of daily precipitation from regional climate models. Int J Clim 31(10):1530–1544
van der Linden P, Mitchell JFB, (eds) (2009) ENSEMBLES: climate change and its impacts: summary of research and results from the ENSEMBLES project. Met Office Hadley Centre Report, pp 160. http://ensembleseumetoffice.com/docs/Ensembles_final_report_Nov09.pdf
Wang A, Zeng X (2012) Evaluation of multireanalysis product with in in situ observations over the Tibetan Plateau. J Geophys Res 117:D05102. doi:10.1029/2011JD016553
Wang Y, Leung LR, McGregor JL, Lee DK, Wang WC, Ding Y, Kimura F (2004) Regional climate modeling: progress, challenges, and prospects. J Meteorol Soc Jpn Ser II 82:1599–1628
Wang W, Xie P, Yoo SH, Xue Y, Kumar A, Wu X (2011) An assessment of the surface climate in the NCEP climate forecast system reanalysis. Clim Dyn 37:1601–1620. doi:10.1007/s00382-010-0935-7
Wehner MF (2013) Very extreme seasonal precipitation in the NARCCAP ensemble: model performance and projections. Clim Dyn 40:59–80. doi:10.1007/s00382-012-1393-1
Weller GB, Cooley D, Sain SR, Bukovsky MS, Mearns LO (2013) Two case studies on NARCCAP precipitation extremes. JGG Atmos 118(18):10475–10489
White RH, Toumi R (2013) The limitations of bias correcting regional climate model inputs. Geophys Res Lett 40:2907–2912. doi:10.1002/grl.50612
Wilks DS (2006) Statistical methods in the atmospheric sciences, 2nd edn. International geophysics series, vol 91, Academic Press, New York
Wood AW, Leung LR, Sridhar V, Lettenmaier DP (2004) Hydrologic implications of dynamical and statistical approaches to downscaling climate model outputs. Clim Change 62:189–216. doi:10.1023/B:CLIM.0000013685.99609.9e
Xu Z, Yang ZL (2012) An improved dynamical downscaling method with GCM bias corrections and its validation with 30 years of climate simulations. J Clim 25:6271–6286
Yang B, Qian Y, Lin G, Leung LYR, Zhang Y (2012) Some issues in uncertainty quantification and parameter tuning: a case study of convective parameterization scheme in the WRF regional climate model. Atmos Chem Phys 12(5):2409–2427. doi:10.5194/acp-12-2409-2012
Acknowledgments
This work is partially supported by NSF EASM grants 1048841 and 1048829. NCAR is sponsored by the National Science Foundation. We wish to thank Cindy Bruyère for useful discussions and the North American Regional Climate Change Assessment Program (NARCCAP) for providing data used in this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
PaiMazumder, D., Done, J.M. The roles of bias-correction and resolution in regional climate simulations of summer extremes. Clim Dyn 45, 1565–1581 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-014-2413-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-014-2413-0