Abstract
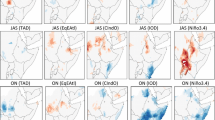
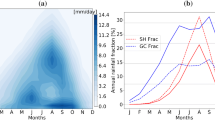
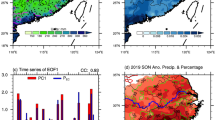
In this study, the oceanic regions that are associated with anomalous Ethiopian summer rains were identified and the teleconnection mechanisms that give rise to these associations have been investigated. Because of the complexities of rainfall climate in the horn of Africa, Ethiopia has been subdivided into six homogeneous rainfall zones and the influence of SST anomalies was analysed separately for each zone. The investigation made use of composite analysis and modelling experiments. Two sets of composites of atmospheric fields were generated, one based on excess/deficit rainfall anomalies and the other based on warm/cold SST anomalies in specific oceanic regions. The aim of the composite analysis was to determine the link between SST and rainfall in terms of large scale features. The modelling experiments were intended to explore the causality of these linkage. The results show that the equatorial Pacific, the midlatitude northwest Pacific and the Gulf of Guinea all exert an influence on the summer rainfall in various part of the country. The results demonstrate that different mechanisms linked to sea surface temperature control variations in rainfall in different parts of Ethiopia. This has important consequences for seasonal forecasting models which are based on statistical correlations between SST and seasonal rainfall totals. It is clear that such statistical models should take account of the local variations in teleconnections.

























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asnani G (2005) Tropical meteorology, vol 1. Praveen Printing Press, India (revised edn)
Black E, Sutton R (2007) The influence of oceanic conditions on the hot European summer of 2003. Clim Dyn 28:53–66
Block P, Rajagopalan B (2007) Interannual variability and ensemble forecast of Upper Blue Nile Basin Kiremt season precipitation. J Hydrometeorol 8:327–343
Camberlin P (1995) June-September rainfall in northeastern Africa and atmospheric signals over the tropics: a zonal perspective. I J Climatol 15:773–783
Chiang J, Bitz C (2005) The influence of high latitude ice cover on the marine intertropical convergence zone. Clim Dyn 25:477–496
Diro G (2008) Seasonal forecasting of ethiopian rainfall. Dissertation, Department of Meteorology, Reading University, Reading
Diro G, Black E, Grimes D (2008) Seasonal forecasting of Ethiopian spring rains. Meteorol Appl 15:73–83
Diro G, Grimes D, Black E, O’Neill A, Pardo-Iguzquiza (2009) Evaluation of reanalysis rainfall estimates over Ethiopia. Int J Climatol 29:67–78
Diro GT, Grimes DIF, Black E (2010) Teleconnections between Ethiopian summer rainfall and sea surface temperature: part II. Seasonal forecasting. Clim Dyn (submitted)
Dyer T (1975) The assignment of rainfall stations into homogeneous groups: an application of principal component analysis. Q J R Meteorol Soc 101:1005–1013
Ehrendorfer M (1987) A regionalization of Austria’s precipitation climate using principal component analysis. J Clim 7:71–89
Gadgil S, Yadumani, Josh N (1993) Coherent rainfall zones of the Indian region. Int J Clim 13:547–566
Gill A (1980) Some simple solutions for heat-induced tropical circulation. Q J R Meteorol Soc106:447–462
Gissila T, Black E, Grimes D, Slingo J (2004) Seasonal forecasting of the Ethiopian summer rains. Int J Clim 24:1345–1358
Goswami B, Xavier P (2005) ENSO control on the Asian monsoon through the length of the rainy season. Geophys Res Lett 32:1–4. doi:10.1029/2005GL023216
Grist J, Nicholson S (2001) A study of the dynamic factors influencing the rainfall variability in the West African Sahel. J Clim 14:1337–1359
Journel A, Huijbregts C (1978) Mining geostatistics. Academic Press, London
Kassahun B (1987) Weather systems over ethiopia. In: Proceedings of First Technical conference on meteorological research in Eastern and Southern Africa. Kenya Meteorological Department, Nairobi, Kenya, pp 53–57
Korecha D, Barnston A (2007) predictability of June-September rainfall in Ethiopia. Mon Weather Rev 135:628–650
Nicholson S, Grist J (2003) The Seasonal Evolution of the Atmospheric Circulation over West Africa and Equatorial Africa. J Clim 16(7):1013–1030
Pope V, Gallani M, Rowntree P, Stratton R (2000) The impact of new physical parameterizations in the Hadley Centre Climate Model: HadAM3. Clim Dyn 16:123–146
Rayner N, Parker D, Horton E, Folland C, Alexander L, Rowell D, Kent E, Kaplan A (2003) Global analysis of Sea surface temperature, sea ice and night marine air temperature since the late nineteenth century. J Geophys Res 108(d14)
Rowell D (2001) Teleconnection between the tropical Pacific and the Sahel. Q J R Meteorol Soc 127:1683–1706
Rowell D (2003) The impact of Mediterranean SSTs on the Sahelian rainfall season. J Clim 16:849–862
Segele ZT, Lamb P (2005) Characterization and variability of Kiremt rainy season over Ethiopia. Meteorol Atmos Phys 89:153–180
Segele ZT, Lamb P, Leslie L (2009a) Large-scale atmospheric circulation and global sea surface temperature associations with Horn of Africa June-September rainfall. Int J Clim 29:1075–1100
Segele ZT, Lamb P, LM L (2009b) Seasonal-to-Interannual variability of Ethiopia/Horn of Africa monsoon. part I: associations of wavelet-filtered large-scale atmospheric circulation and global sea surface temperature. J Clim 22:3396–3421
Shaman J, Tziperman E (2007) Summer time ENSO-North African -Asian jet teleconnection and implications for the Indian monsoons. Geophys Res Lett 34:1–7. doi:10.1029/2006GL029143
Tiedtke M (1989) A comprehensive mass flux scheme for cumulus parameterization in large scale models. Mon Weather Rev 117:1779–1800
Tiedtke M (1993) Representations of clouds in large scale models. Mon Weather Rev 121:3040–3061
Uppala S, Kallberg P, Simmons A, Andrae U, da Costa Bechtold V, Fiorino M, Gibson J, Haseler J, Hernandez A, Kelly G, Li X, Onogi K, Saarinen S, Sokka N, Allan R, Andersson E, Arpe K, Balmaseda M, Beljaars A, van de Berg L, Bidlot J, Bormann N, Caires S, Chevallier F, Dethof A, Dragosavac M, Fisher M, Fuentes M, Hagemann S, Holm E, Hoskins B, Isaksen L, Janssen P, Jenne R, McNally A, Mahfouf JF, Morcrette JJ, Rayner N, Saunders R, Simon P, Sterl A, Trenberth K, Untch A, Vasiljevic D, Viterbo P, Woollen J (2005) The era-40 re-analysis. Q J R Meteorol Soc 131:2961–3012
Vizy E, Cook K (2001) Mechanisms by which Gulf of Guinea and eastern north Atlantic sea surface temperature anomalies can influence African rainfall. J Clim 14:795–821
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the Ethiopian National Meteorological Agency for providing the raingauge data and the UK Met office for providing the HadISST SST data and HadAM3 model.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diro, G.T., Grimes, D.I.F. & Black, E. Teleconnections between Ethiopian summer rainfall and sea surface temperature: part I—observation and modelling. Clim Dyn 37, 103–119 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-010-0837-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-010-0837-8